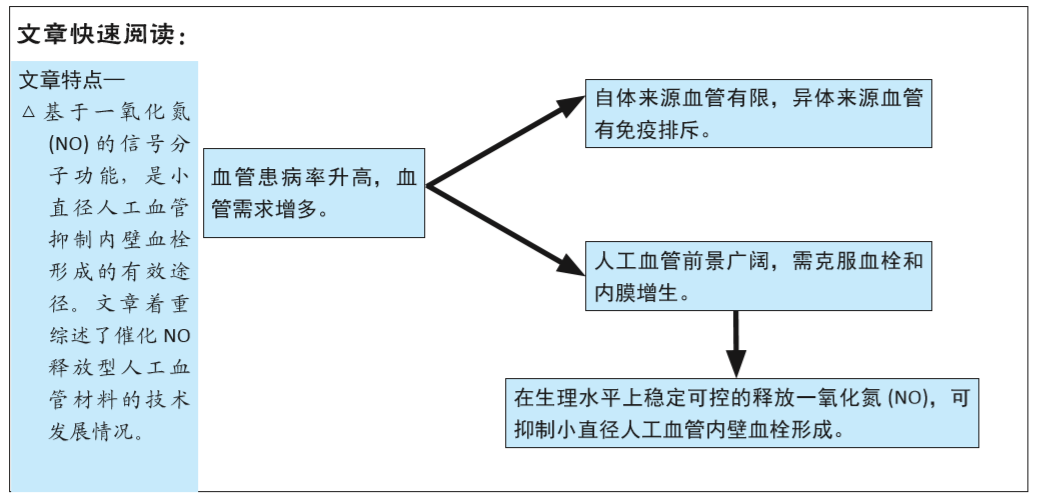
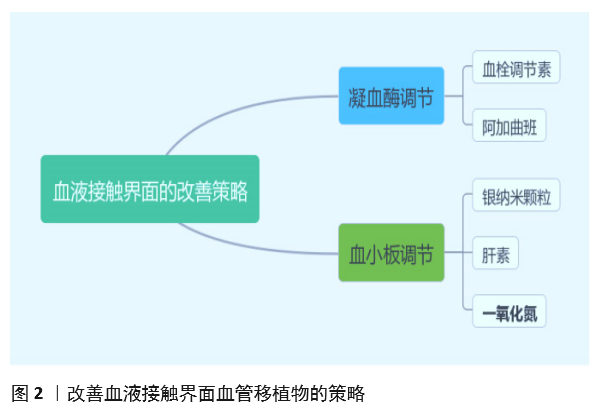
[1] BENJAMIN EJ, MUNTNER P, ALONSO A, et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report From the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2019;139(10):e56-e66.
[2] CATTO V, FARÈ S, FREDDI G, et al. Vascular Tissue Engineering: Recent Advances in Small Diameter Blood Vessel Regeneration. ISRN Otolaryngol. 2014;134(4):1-27.
[3] RAVI S, CHAIKOF EL. Biomaterials for vascular tissue engineering. Regen Med. 2010;5(1):107-120.
[4] RAMEZANIFARD R, KABIRI M, AHVAZ HH. Effects of platelet rich plasma and chondrocyte co-culture on MSC chondrogenesis, hypertrophy and pathological responses. Excli J. 2017;16(1):1031-1045.
[5] BORDENAVE L, MENU P, BAQUEY C. Developments towards tissue-engineered, small-diameter arterial substitutes. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2008;5(3):337-347.
[6] RATHORE A, CLEARY M, NAITO Y, et al. Development of tissue engineered vascular grafts and application of nanomedicine. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2012;4(3):257-272.
[7] PECK M, GEBHART D, DUSSERRE N, et al. The Evolution of Vascular Tissue Engineering and Current State of the Art. Cells Tissues Organs. 2012;195(12):144-158.
[8] L’HEUREUX N, DUSSERRE N, MARINI A, et al. Technology insight: the evolution of tissue-engineered vascular grafts--from research to clinical practice. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 2007;4(7):389-395.
[9] COUET F, RAJAN N, MANTOVANI D. Macromolecular biomaterials for scaffold-based vascular tissue engineering. Macromol Biosci. 2007;7(5): 701-718.
[10] DEAN EW, UDELSMAN B, BREUER CK. Current advances in the translation of vascular tissue engineering to the treatment of pediatric congenital heart disease. Yale J Biol Med. 2012;85(2):229-238.
[11] RICCIO DA, SCHOENFISCH MH. Nitric oxide release: part I. Macromolecular scaffolds. Chem Soc Rev. 2012;41(10):3731-3741.
[12] LEI J, VODOVOTZ Y, TZENG E, et al. Nitric oxide, a protective molecule in the cardiovascular system. Nitric Oxide. 2013;35(2):175-185.
[13] JEN MC, SERRANO MC, VAN LITH R, et al. Polymer-Based Nitric Oxide Therapies: Recent Insights for Biomedical Applications. Adv Funct Mater. 2012;22(2):239-260.
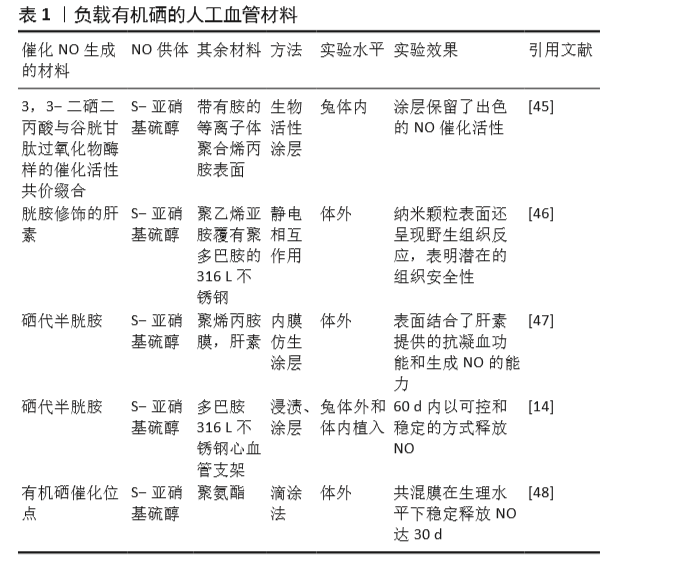
[14] YANG Z, YANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Mussel-inspired catalytic selenocystamine-dopamine coatings for long-term generation of therapeutic gas on cardiovascular stents. Biomaterials. 2018;178(4):1-10.
[15] YANG Y, LI Y, LI X, et al. Development of nitric oxide catalytic coatings by conjugating 3,3-disulfodipropionic acid and 3,3-diselenodipropionic acid for improving hemocompatibility. Biointerphases. 2015;10(4):303-311.
[16] YANG Z, YANG Y, XIONG K, et al. Metal-Phenolic Surfaces for Generating Therapeutic Nitric Oxide Gas. Chem Mater, 2018, 30(15): 5220-5226.
[17] SCHULZ R, KELM M, HEUSCH G. Nitric oxide in myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury. Cardiovasc Res. 2004;61(3):402-413.
[18] BALLIGAND JL, CANNON PJ. Nitric oxide synthases and cardiac muscle. Autocrine and paracrine influences. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 1997;17(10):1846-1858.
[19] FURCHGOTT RF, ZAWADZKI JV. The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature. 1980;288(5789):373-376.
[20] PALMER RM, FERRIGE AG, MONCADA S. Nitric oxide release accounts for the biological activity of endothelium-derived relaxing factor. Nature. 1987;327(6122):524-526.
[21] IGNARRO LJ, BUGA GM, WOOD KS, et al. Endothelium-derived relaxing factor produced and released from artery and vein is nitric oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987;84(24):9265-9269.
[22] 阮怀珍.医学神经生物学基础[M].北京:科学出版社,2006:34-35.
[23] 钟慈声,孙安阳.一氧化氮的生物医学[M].上海:上海医科大学出版社,1997:23-25.
[24] RADOMSKI MW, VALLANCE P, WHITLEY G, et al. Platelet adhesion to human vascular endothelium is modulated by constitutive and cytokine induced nitric oxide. Cardiovasc Res. 1993;27(7):1380-1382.
[25] MICHIELS C. Endothelial cell functions. J Cell Physiol. 2003;196(3): 430-443.
[26] VAUGHN MW, KUO L, LIAO JC. Estimation of nitric oxide production and reactionrates in tissue by use of a mathematical model .Am J Physiol. 1998;274(6):H2163-H2176.
[27] CANEBA CA, YANG L, BADDOUR J, et al. Nitric oxide is a positive regulator of the Warburg effect in ovarian cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2014;5(6):e1302.
[28] THOMAS DD, RIDNOUR LA, ISENBERG JS, et al. The chemical biology of nitric oxide: implications in cellular signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2008;45(1):18-31.
[29] GRISHAM MB, JOURD’HEUIL D, WINK DA. Nitric oxide. I. Physiological chemistry of nitric oxide and its metabolites: implications in inflammation. Am J Physiol. 1999;276(2):G315-321.
[30] PRYOR WA, SQUADRITO GL. The chemistry of peroxynitrite: a product from the reaction of nitric oxide with superoxide. Am J Physiol. 1995; 268(5 Pt 1):L699-722.
[31] KUDO S, NAGASAKI Y. A novel nitric oxide-based anticancer therapeutics by macrophage-targeted poly(l-arginine)-based nanoparticles. J Control Release. 2015;217(2):256-262.
[32] WINK DA, DARBYSHIRE JF, NIMS RW, et al. Reactions of the bioregulatory agent nitric oxide in oxygenated aqueous media: determination of the kinetics for oxidation and nitrosation by intermediates generated in the NO/O2 reaction. Chem Res Toxicol. 1993;6(1):23-27.
[33] NAGHAVI N, DE MEL A, ALAVIJEH OS, et al. Nitric oxide donors for cardiovascular implant applications. Small. 2013;9(1):22-35.
[34] TYURIN VA, TYURINA YY, LIU SX, et al. Quantitation of S-nitrosothiols in cells and biological fluids. Methods Enzymol. 2002;352(5):347-360.
[35] WANG PG, XIAN M, TANG X, et al. Nitric oxide donors: chemical activities and biological applications. Chem Rev. 2002;102(4):1091-1134.
[36] HWANG S, MEYERHOFF ME. Polyurethane with tethered copper(II)-cyclen complex: preparation, characterization and catalytic generation of nitric oxide from S-nitrosothiols. Biomaterials. 2008;29(16):2443-2452.
[37] JOSLIN JM, LANTVIT SM, REYNOLDS MM. Nitric oxide releasing Tygon materials: studies in donor leaching and localized nitric oxide release at a polymer-buffer interface. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2013;5(19): 9285-9294.
[38] ZHANG K, XU H, JIA X, et al. Ultrasound-Triggered Nitric Oxide Release Platform Based on Energy Transformation for Targeted Inhibition of Pancreatic Tumor. ACS Nano. 2016;10(12):10816-10828.
[39] FAN W, LU N, HUANG P, et al. Glucose-Responsive Sequential Generation of Hydrogen Peroxide and Nitric Oxide for Synergistic Cancer Starving-Like/Gas Therapy. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017;56(5): 1229-1233.
[40] Shrivastava S, Bera T, Singh SK, et al. Characterization of antiplatelet properties of silver nanoparticles. ACS Nano. 2009;3(6): 1357-1364.
[41] FRÖHLICH E. Action of Nanoparticles on Platelet Activation and Plasmatic Coagulation. Curr Med Chem. 2016;23(5):408-430.
[42] HOSHI RA, VAN LITH R, JEN MC, et al. The blood and vascular cell compatibility of heparin-modified ePTFE vascular grafts. Biomaterials. 2013;34(1):30-41.
[43] DORIGO W, PULLI R, CASTELLI P, et al. A multicenter comparison between autologous saphenous vein and heparin-bonded expanded polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) graft in the treatment of critical limb ischemia in diabetics. J Vasc Surg. 2011;54(5): 1332-1338.
[44] MUGESH G, SINGH HB. Synthetic organoselenium compounds as antioxidants: glutathione peroxidase activity. Chem Soc Rev. 2000;29(5): 347-357.
[45] YANG Z, YANG Y, XIONG K, et al. Nitric oxide producing coating mimicking endothelium function for multifunctional vascular stents. Biomaterials. 2015;63(9):80-92.
[46] LUO R, ZHANG J, ZHUANG W, et al. Multifunctional coatings that mimic the endothelium: surface bound active heparin nanoparticles with in situ generation of nitric oxide from nitrosothiols. J Mater Chem B. 2018;6(35):5582-5595.
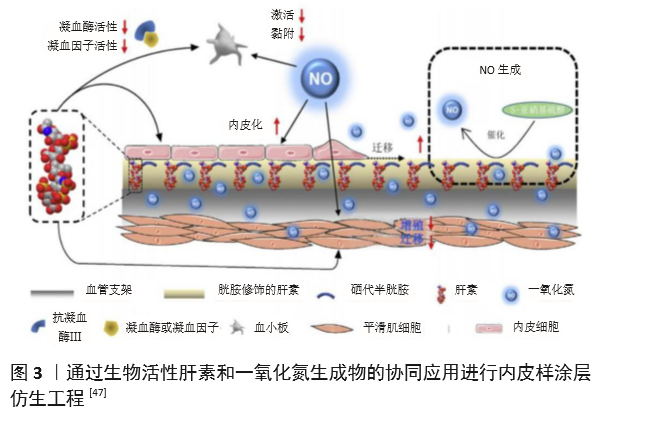
[47] QIU H, QI P, LIU J, et al. Biomimetic engineering endothelium-like coating on cardiovascular stent through heparin and nitric oxide-generating compound synergistic modification strategy. Biomaterials. 2019;207(9):10-22.
[48] QU B, YUAN L, LI J, et al. Selenium-containing polyurethane with elevated catalytic stability for sustained nitric oxide release. J Mater Chem B. 2019;7(1):150-156.
[49] CHEN S, AN J, WENG L, et al. Construction and biofunctional evaluation of electrospun vascular graft loaded with selenocystamine for in situ catalytic generation of nitric oxide. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2014;45(2):491-496.
[50] WANG Y, CHEN S, PAN Y, et al. Rapid in situ endothelialization of a small diameter vascular graft with catalytic nitric oxide generation and promoted endothelial cell adhesion. J Mater Chem B. 2015;3(47): 9212-9222.
[51] AN J, CHEN S, GAO J, et al. Construction and evaluation of nitric oxide generating vascular graft material loaded with organoselenium catalyst via layer-by-layer self-assembly. Sci China Life Sci. 2015;58(8):765-772.
[52] GAO J, WANG Y, CHEN S, et al. Electrospun poly-ε-caprolactone scaffold modified with catalytic nitric oxide generation and heparin for small-diameter vascular graft. RSC Adv. 2017;7(30):18775-18784.
[53] TANG D, CHEN S, HOU D, et al. Regulation of macrophage polarization and promotion of endothelialization by NO generating and PEG-YIGSR modified vascular graft. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2018;84(1): 1-11.
[54] ZHANG X, SHI J, CHEN S, et al. Polycaprolactone/gelatin degradable vascular grafts simulating endothelium functions modified by nitric oxide generation. Regen Med. 2019;14(12):1089-1105.
[55] MAJOR TC, BRANT DO, BURNEY CP, et al. The hemocompatibility of a nitric oxide generating polymer that catalyzes S-nitrosothiol decomposition in an extracorporeal circulation model. Biomaterials. 2011;32(26):5957-5969.
[56] PANT J, GOUDIE MJ, HOPKINS SP, et al. Tunable Nitric Oxide Release from S-Nitroso-N-acetylpenicillamine via Catalytic Copper Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(18): 15254-15264.
[57] LUO R, LIU Y, YAO H, et al. Copper-Incorporated Collagen/Catechol Film for in Situ Generation of Nitric Oxide. ACS BiomaterSci Eng. 2015;1(9): 771-779.
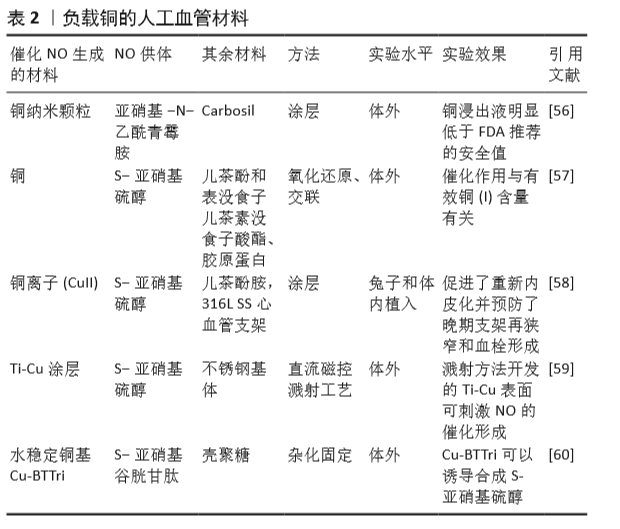
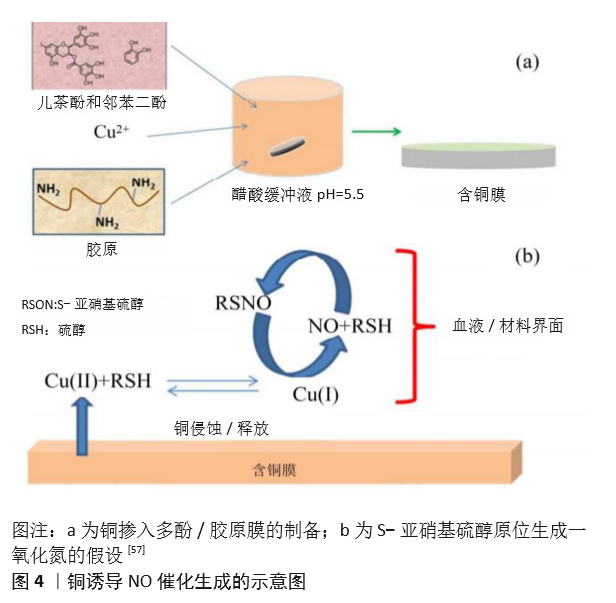
[58] ZHANG F, ZHANG Q, LI X, et al. Mussel-inspired dopamine-Cu(II) coatings for sustained in situ generation of nitric oxide for prevention of stent thrombosis and restenosis. Biomaterials. 2019;194(6):117-129.
[59] WANG Q, AKHAVAN B, JING F, et al. Catalytic Formation of Nitric Oxide Mediated by Ti–Cu Coatings Provides Multifunctional Interfaces for Cardiovascular Applications. Adv Mater Interfaces. 2018;5(6):1701487.
[60] NEUFELD MJ, LUTZKE A, TAPIA JB, et al. Metal-Organic Framework/Chitosan Hybrid Materials Promote Nitric Oxide Release from S-Nitrosoglutathione in Aqueous Solution. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2017;9(6):5139-5148.
[61] HUANG N, YANG Z, WANG J, et al. Method for preparing coating with nitric oxide (NO) catalytic activity. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2002;71(6):2231-2252.
[62] LI X, QIU H, GAO P, et al. Synergetic coordination and catecholamine chemistry for catalytic generation of nitric oxide on vascular stents. Npg Asia Mater. 2018;10(6): 482-496.
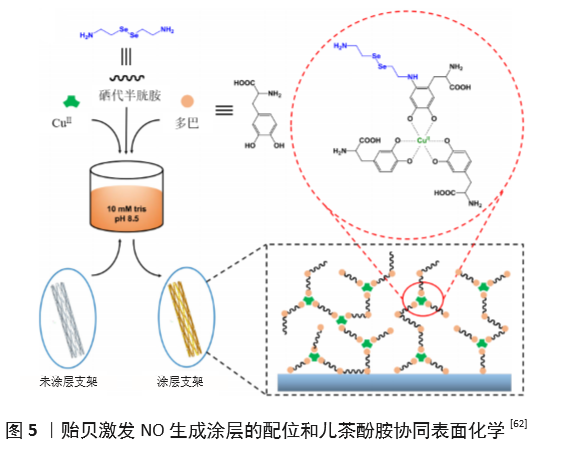
[63] JIN X, WANG Y, YUAN J, et al. Extraction, characterization, and NO release potential of keratin from human hair. Mater Lett. 2016;175(15): 188-190.
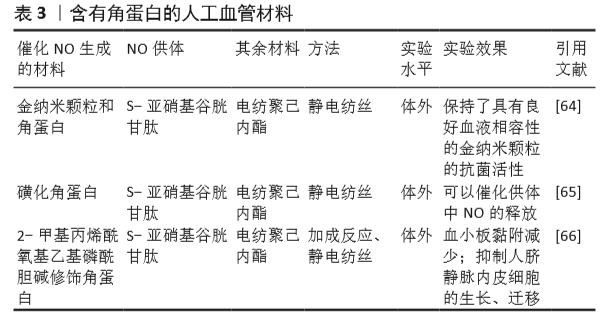
[64] WAN X, LIU P, JIN X, et al. Electrospun PCL/keratin/AuNPs mats with the catalytic generation of nitric oxide for potential of vascular tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2018;106(12):3239-3247.
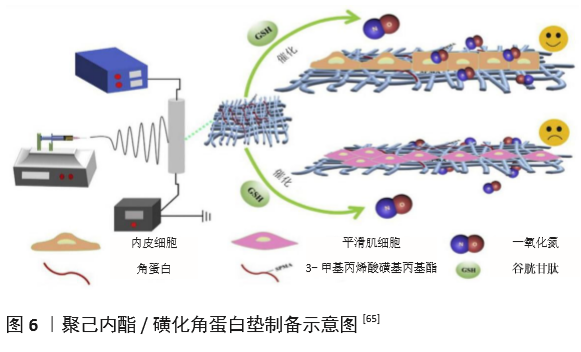
[65] DOU J, WANG Y, JIN X, et al. PCL/sulfonated keratin mats for vascular tissue engineering scaffold with potential of catalytic nitric oxide generation. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2020;107:110246.
[66] LI P, WANG Y, JIN X, et al. Catalytic Generation of Nitric Oxide from Poly(ε-caprolactone)/Phosphobetainized Keratin Mats for a Vascular Tissue Engineering Scaffold. Langmuir. 2020;36(16):4396-4404.
[67] WANG Z, LU Y, QIN K, et al. Enzyme-functionalized vascular grafts catalyze in-situ release of nitric oxide from exogenous NO prodrug. J Control Release. 2015;210(1):179-188.
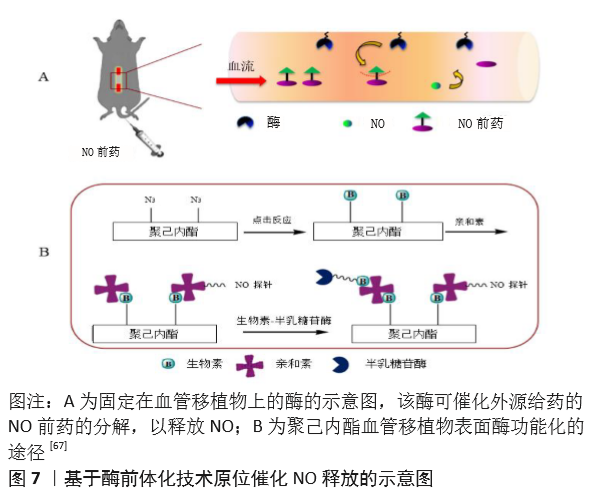
[68] DU Z, DOU R, ZU M, et al. Nitric oxide-generating l-cysteine-grafted graphene film as a blood-contacting biomaterial. Biomater Sci. 2016; 4(6):938-942.
[69] KABIRIAN F, BROUKI MILAN P, ZAMANIAN A, et al. Nitric oxide-releasing vascular grafts: A therapeutic strategy to promote angiogenic activity and endothelium regeneration. Acta biomater. 2019;92(1):82-91.
[70] 刘志明,吴文健,胡碧茹,等.一种纳米金-纤维素纳米复合体的制备方法: 中国, 201711273751 .0[P]. 2018-05-18.
|