中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (10): 1556-1561.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.10.015
• 干细胞移植 stem cell transplantation • 上一篇 下一篇
骨髓间充质干细胞对脓毒症急性肺损伤大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞NF-κB的调控
张继峰1,张紫琦2,雒晓甜3,侯林义1,姜 琴1,吕洁萍4,张文凯5
- 1山西医科大学,山西省太原市 030001;2太原市第五中学,山西省太原市 030001;3四川大学华西医院康复医学中心,四川省成都市 610041;4山西医科大学第一附属医院麻醉科,山西省太原市 030001;5山西医科大学第二附属医院外科ICU,山西省太原市 030001
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulate nuclear factor kappaB expression in alveolar macrophages of acute lung injury rats with sepsis
Zhang Ji-feng1, Zhang Zi-qi2, Luo Xiao-tian3, Hou Lin-yi1, Jiang Qin1, Lv Jie-ping4, Zhang Wen-kai5
- 1Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Taiyuan Fifth High School, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Rehabilitation Medicine Center, West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China; 4Department of Anesthesiology, First Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 5Department of Surgical ICU, Second Affiliated Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
摘要:
背景:骨髓间充质干细胞对急性肺损伤具有治疗作用,但其机制尚不清楚,探究其机制可使广大急性肺损伤患者获益。
目的:探讨骨髓间充质干细胞治疗大鼠脓毒症急性肺损伤的可能机制。
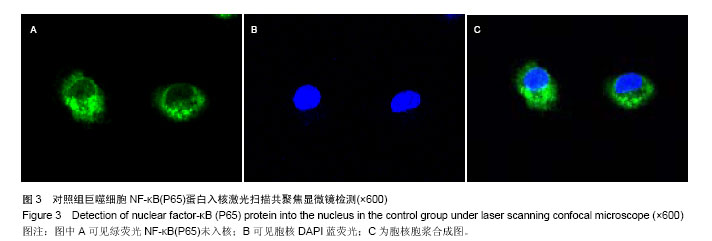
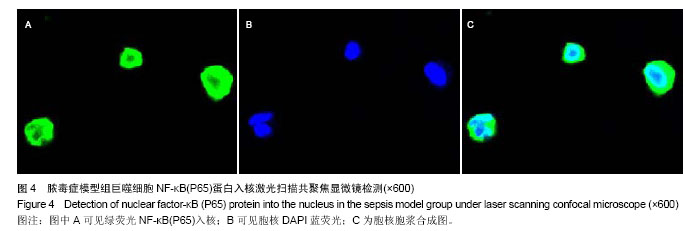
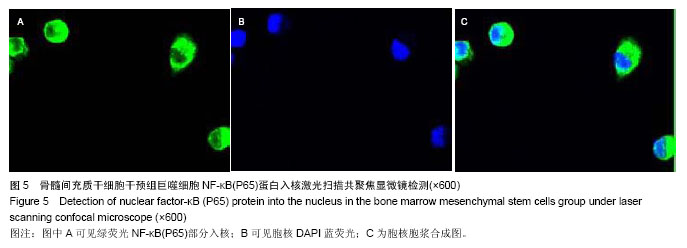
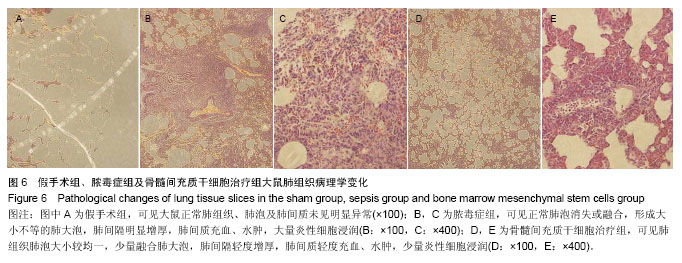
方法: ①36只成年Wistar大鼠随机均分为3组:假手术组、脓毒症组和骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组,后2组采用盲肠结扎穿孔术建立脓毒症急性肺损伤模型,假手术组大鼠仅翻动盲肠,不结扎穿孔。骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组术后经股静脉注射骨髓间充质干细胞悬液1 mL(1×109 L-1),其他2组同法注射生理盐水1 mL,6 h后测定3组大鼠血清中白细胞介素10、巨噬细胞炎性蛋白2水平,取肺组织进行苏木精-伊红染色,光镜下观察肺组织病理结构的改变。②支气管肺泡灌洗法获取大鼠肺泡巨噬细胞,所获肺泡巨噬细胞接种于24孔培养板,分为3组:对照组加入生理盐水,脓毒症模型组加入脓毒症大鼠血浆,骨髓间充质干细胞干预组加入脓毒症大鼠血浆和骨髓间充质干细胞共同干预,于37 ℃、体积分数为5%CO2培养箱孵育1 h。留取肺泡巨噬细胞,采用激光扫描共聚焦显微镜检测肺泡巨噬细胞NF-κB(P65)蛋白入核情况。
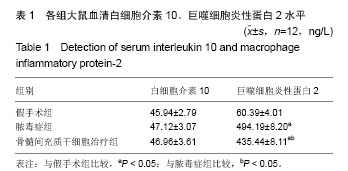
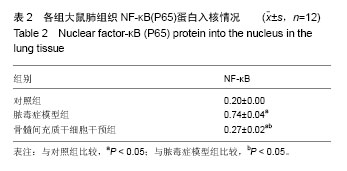
结果与结论: ①动物实验:与假手术组相比,脓毒症组、骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组血清巨噬细胞炎性蛋白2水平升高(P < 0.05),但骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组巨噬细胞炎性蛋白2水平明显低于脓毒症组(P < 0.05);各组血清白细胞介素10水平差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05);脓毒症组和骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组肺内大量炎性细胞浸润、肺间质水肿、肺内出血,但骨髓间充质干细胞治疗组症状较脓毒症组有所减轻。②细胞实验:与对照组相比,脓毒症模型组、骨髓间充质干细胞干预组肺泡巨噬细胞的NF-κB(P65)蛋白入核明显升高(P < 0.05),但骨髓间充质干细胞干预组明显低于脓毒症模型组(P < 0.05)。结果表明骨髓间充质干细胞在脓毒症急性肺损伤时可能调控肺泡巨噬细胞NF-κB(P65)蛋白入核,使其减少促炎细胞因子巨噬细胞炎性蛋白2表达,进而减少中性粒细胞浸润起到肺保护作用,暂不能说明骨髓间充质干细胞对白细胞介素10有影响。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)