| [1]Alini M, Li W, Markovic P, et al. The potential and limitations of a cell-seeded collagen/hyaluronan scaffold to engineer an intervertebral disc-like matrix. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).2003; 28(5):446-454.
[2]Urban JP, Roberts S. Degeneration of the intervertebral disc. Arthritis Res Ther. 2003,5(3):120-130.
[3]An HS, Anderson PA, Haughton VM, et al. Introduction: disc degeneration: summary. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2004;29(23): 2677-2678.
[4]Hiyama A, Mochida J, Iwashina T, et al. Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells in a canine disc degeneration model. J Orthop Res. 2008;26(5):589-600.
[5]Watanabe T, Sakai D, Yamamoto Y, et al. Human nucleus pulposus cells significantly enhanced biological properties in a coculture system with direct cell-to-cell contact with autologous mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Res.2010; 28(5):623-630.
[6]Comes ME, Bossano CM, Johnston CM, et al. In vitro localization of bone growth factors in constructs of biodegradable scaffolds seeded with marrow stromal cells and cultured in a flow perfusion bioreactod. Tissue Eng. 2006; 12(1):177-188.
[7]Smith LJ,Chiaro JA,Nerurkar NL,et al.Nucleus pulposus cells synthesize a functional extracellular matrix and respond to inflammatory cytokine challenge following long-term agarose culture.Eur Cell Mater.2011;22:291-301.
[8]Roberts S,Evans H,Trivedi J,et at.Histology and pathology of the human intervertebral disc. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2006; 88(S2):10-14.
[9]Wang H,Liu H,Zheng ZM,et al.Role of death receptor,mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticutum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis. 2011;16(10): 990-1003.
[10]Zhao CQ,Wang LM,Jiang LS. et al.The cell biology of intervertebral disc aging and degeneration.Ageing Res Rev. 2007; 6(3):247-261.
[11]Yang SH, Wu CC, Shih TT, et al. Three-dimensional culture of human nucleus pulposus cells in fibrin clot: comparisons on cellular proliferation and matrix synthesis with cells in alginate. Artif Organs. 2008;32(1): 70-73.
[12]王锋,吴小涛,王运涛,等.单纯Ⅱ型胶原酶消化法分离、培养人退变椎间盘髓核细胞的形态学观察[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2010, 20(4):300-304.
[13]孙浩林,李淳德.原代培养差速贴壁法分离纯化大鼠腰椎间盘髓核细胞[J]. 中国组织工程研,2011,15(46):8569-8573.
[14]Wang H,Liu H,Zheng ZM,et al.Role of death receptor, mitochondrial and endoplasmic reticutum pathways in different stages of degenerative human lumbar disc. Apoptosis. 2011;16(10):990-1003.
[15]Yang Z, Huang CY, Candiotti KA, et al. Sox-9 facilitates differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells into a chondrocyte-like phenotype in vitro.J Orthop Res. 2011;29(8): 1291-1297.
[16]Hu MH, Hung LW, Yang SH, et al. Lovastatin promotes redifferentiation of human nucleus pulposu s cells during expansion in monolayer culture. Artif Organs.2011;35(4): 411-416.
[17]Kluba T, Niemeyer T, Gaissmaier C, et al. Human anulus fibrosis and nucleus pulposus cells of the intervertebral disc: effect of degeneration and culture system on cell phenotype. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30(24): 2743-2748. |

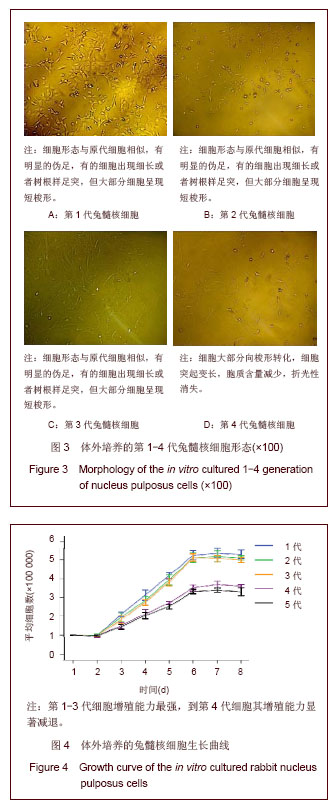
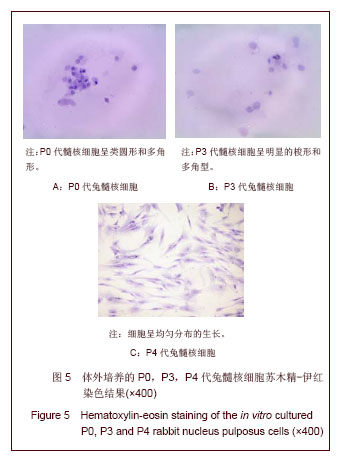
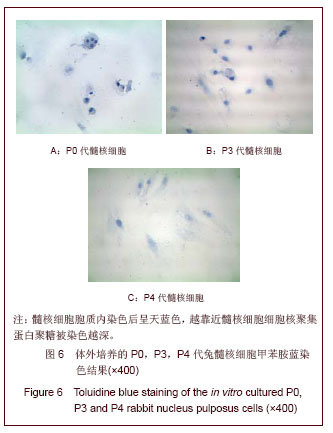

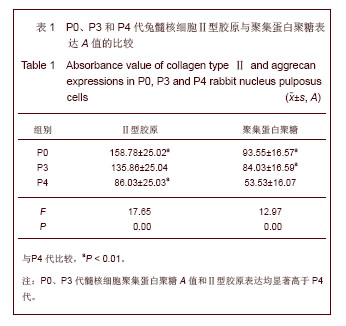
.jpg)