[1] USLU AB. Effect of dipyridamole on random pattern skin flap viability in rats. J Plast Surg Hand Surg. 2020;54(4):240-247.
[2] BOSCÁ MM, ALÓS R, MAROTO N, et al. Recommendations of the Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis spanish working group (GETECCU) for the treatment of perianal fistulas of Crohn’s disease. Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;43(3):155-168.
[3] KALOGERIS T, BAINES CP, KRENZ M, et al. Ischemia/reperfusion. Compr Physiol. 2016;7:113-170.
[4] BIAN F, XIAO Y, ZAHEER M, et al. Inhibition of NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway by Butyrate Improves Corneal Wound Healing in Corneal Alkali Burn. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(3):562.
[5] SHARMA A, TATE M, MATHEW G, et al. Oxidative Stress and NLRP3-Inflammasome Activity as Significant Drivers of Diabetic Cardiovascular Complications: Therapeutic Implications. Front Physiol. 2018;9:114.
[6] SORIA-JUAN B, ESCACENA N, CAPILLA-GONZÁLEZ V, et al. Cost-effective,safe,and personalized cell therapy for critical limb ischemia in type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;482:281-294.
[7] BROWN C, MCKEE C, BAKSHI S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells:Cell therapy and regeneration potential. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019;13(9):1738-1755.
[8] LEE DE, AYOUB N, AGRAWAL DK. Mesenchymal stem cells and cutaneous wound healing: novel methods to increase cell delivery and therapeutic efficacy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2016;7:37.
[9] OZMEN S, AYHAN S, DEMIR Y, et al. Impact of gradual blood flow increase on ischaemia-reperfusion injury in the rat cremaster microcirculation model. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2008;61:939e48.
[10] CAI L, HUANG W, LIN D. Effects of traditional Chinese medicine Shuxuetong injection on random skin flap survival in rats. ScientificWorldJournal. 2014; 2014:816545.
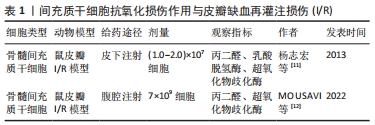
[11] 杨志宏,上官守琴,杨萍,等.骨髓基质干细胞移植促进皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤修复的机制初步探讨[J].医学研究杂志,2013,42(2):78-81.
[12] MOUSAVI M, KHANIFAR A, MOUSAVI N, et al. Coactivity of Mast Cells and Stem Cells on Angiogenesis and Antioxidants’ Potentials at Inflammation, Proliferation, and Tissue Remodeling Phases of Wound. Arch Plast Surg. 2022;49(3):462-470.
[13] WANG Q, LIU T, ZHANG Y, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of human placental-derived mesenchymal stem cells on immune rejection in mouse allogeneic skin transplantation. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2013;27(7):775-780.
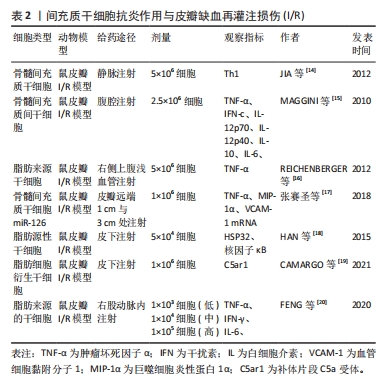
[14] JIA Z, JIAO C, ZHAO S, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of mesenchymal stem cells in a rat corneal allograft rejection model. Exp Eye Res. 2012;102: 44-49.
[15] MAGGINI J, MIRKIN G, BOGNANNI I, et al. Mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells turn activated macrophages into a regulatory-like profile. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9252.
[16] REICHENBERGER MA, HEIMER S, SCHAEFER A, et al. Adipose derived stem cells protect skin flaps against ischemia-reperfusion injury. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2012;8(3):854-862.
[17] 张赛圣,程丽霞.骨髓间充质干细胞miR-126高表达在游离皮瓣移植后皮瓣血管新生中的促进作用及机制研究[J].现代医学,2018,46(2):126-130.
[18] HAN HH, LIM YM, PARK SW, et al. Improved skin flap survival in venous ischemia-reperfusion injury with the use of adipose-derived stem cells. Microsurgery. 2015;35(8):645-652.
[19] CAMARGO CP, KUBRUSLY MS, MORAIS-BESTEIRO J, et al. The influence of adipocyte-derived stem cells (ASCs) on the ischemic epigastric flap survival in diabetic rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2021;36(9):e360907.
[20] FENG CJ, PERNG CK, LIN CH, et al. Intra-arterial injection of human adipose-derived stem cells improves viability of the random component of axial skin flaps in nude mice. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2020;73(3):598-607.
[21] DU W, ZHANG K, ZHANG S, et al. Enhanced proangiogenic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by a nitric oxide releasing polymer. Biomaterials. 2017;133:70-81.
[22] HE JB, MA XY, LI WJ, et al. Exenatide inhibits necrosis by enhancing angiogenesis and ameliorating ischemia/reperfusion injury in a random skin flap rat model. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;90:107192.
[23] MAYO JS, KURATA WE, O’CONNOR KM, et al. Oxidative stress alters angiogenic and antimicrobial content of extracellular vesicles and improves flap survival. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2019;7(12):e2588.
[24] ASHINA K, TSUBOSAKA Y, KOBAYASHI K, et al. VEGF-induced blood flow increase causes vascular hyper-permeability in vivo. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2015;464(2):590-595.
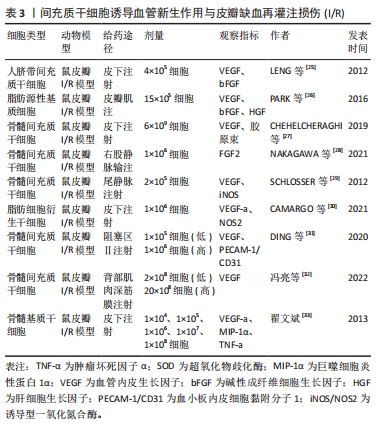
[25] LENG X, ZHANG Q, ZHAI X, et al. Local transplant of human umbilical cord matrix stem cells improves skin flap survival in a mouse model. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2012;227(3):191-197.
[26] PARK IS, CHUNG PS, AHN JC. Angiogenic Synergistic Effect of Adipose-Derived Stromal Cell Spheroids with Low-Level Light Therapy in a Model of Acute Skin Flap Ischemia. Cells Tissues Organs. 2016;202(5-6):307-318.
[27] CHEHELCHERAGHI F, CHIEN S, BAYAT M. Mesenchymal stem cells improve survival in ischemic diabetic random skin flap via increased angiogenesis and VEGF expression. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120(10):17491-17499.
[28] NAKAGAWA T, SASAKI M, KATAOKA-SASAKI Y, et al. Intravenous Infusion of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promotes the Survival of Random Pattern Flaps in Rats. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2021;148(4):799-807.
[29] SCHLOSSER S, DENNLER C, SCHWEIZER R, et al. Paracrine effects of mesenchymal stem cells enhance vascular regeneration in ischemic murine skin. Microvasc Res. 2012;83(3):267-275.
[30] CAMARGO CP, KUBRUSLY MS, MORAIS-BESTEIRO J, et al. The influence of adipocyte-derived stem cells (ASCs) on the ischemic epigastric flap survival in diabetic rats. Acta Cir Bras. 2021;36(9):e360907.
[31] DING JP, CHEN B, QIAN WJ,et al. Effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on perforator skin flap survival area in rats. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2020;58(6):669-674.
[32] 冯亮,樊力.骨髓间充质干细胞通过增加血管生成和血管内皮生长因子表达影响大鼠随意型皮瓣存活实验研究[J].陕西医学杂志,2022, 51(3):298-302.
[33] 翟文斌.不同剂量MSCs移植促进大鼠任意皮瓣成活的实验研究[D].延安:延安大学,2013.
[34] SCHNEIDER RK, PÜLLEN A, KRAMANN R, et al. Long term survival and characterisation of human umbilical cord‑derived mesenchymal stem cells on dermal equivalents. Differentiation. 2010;79:182‑193.
[35] MAZINI L, ROCHETTE L, ADMOU B, et al. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(4):1306.
[36] KUCIA M, RECA R, MIEKUS K, et al. Trafficking of normal stem cells and metastasis of cancer stem cells involve similar mechanisms: pivotal role of the SDF-1-CXCR4 axis. Stem Cells. 2005;23(7):879-894.
[37] SELL S. On the stem cell origin of cancer.Am J Pathol. 2010;176(6):2584-494.
[38] LOMBARDI F, PALUMBO P, AUGELLO FR, et al. Secretome of Adipose Tissue-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) as a Novel Trend in Chronic Non-Healing Wounds: An Overview of Experimental In Vitro and In Vivo Studies and Methodological Variables. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(15):3721.
[39] CHOI EW, SEO MK, WOO EY, et al. Exosomes from human adipose-derived stem cells promote proliferation and migration of skin fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 2018;27(10):1170-1172.
[40] GIANNASI C, NIADA S, DELLA MORTE E, et al. Towards Secretome Standardization: Identifying Key Ingredients of MSC-Derived Therapeutic Cocktail. Stem Cells Int. 2021;2021:3086122.
[41] BORN LJ, HARMON JW, JAY SM. Therapeutic potential of extracellular vesicle-associated long noncoding RNA. Bioeng Transl Med. 2020;5(3):e10172.
[42] UEDA M, NISHINO Y. Cell-based cytokine therapy for skin rejuvenation. J Craniofac Surg. 2010;21(6):1861-1866.
[43] KWON TR, OH CT, CHOI EJ, et al. Conditioned medium from human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes skin moisturization and effacement of wrinkles in UVB-irradiated SKH-1 hairless mice. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2016;32(3):120-128.
[44] COOPER DR, WANG C, PATEL R, et al. Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Conditioned Media and Exosomes Containing MALAT1 Promote Human Dermal Fibroblast Migration and Ischemic Wound Healing. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2018;7(9):299-308.
[45] 刘美林,傅松涛,王培森,等.人脐带间充质干细胞条件培养基脂质体修复大鼠皮肤创面损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(5):734-740.
[46] 张畅.脂肪来源干细胞及其条件培养基在防治血管内皮细胞氧化应激和皮瓣缺血再灌注中的研究[D].北京:北京协和医学院,2022.
[47] LA NOCE M, PAINO F, SPINA A, et al. Dental pulp stem cells: state of the art and suggestions for a true translation of research into therapy. J Dent. 2014;42(7):761-768.
[48] LENER T, GIMONA M, AIGNER L, et al. Applying extracellular vesicles based therapeutics in clinical trials - an ISEV position paper. J Extracell Vesicles. 2015;4:30087.
[49] PALMULLI R, VAN NIEL G. To be or not to be secreted as exosomes, a balance finely tuned by the mechanisms of biogenesis. Essays Biochem. 2018;62(2):177-191.
[50] TKACH M, KOWAL J, THÉRY C. Why the need and how to approach the functional diversity of extracellular vesicles. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2018;373(1737):20160479.
[51] LI P, KASLAN M, LEE SH, et al. Progress in Exosome Isolation Techniques. Theranostics. 2017;7(3):789-804.
[53] NOJIMA H, FREEMAN CM, SCHUSTER RM, et al. Hepatocyte exosomes mediate liver repair and regeneration via sphingosine-1-phosphate. J Hepatol. 2016;64(1):60-68.
[53] ZHANG FX, LIU P, DING W, et al. Injectable Mussel-Inspired highly adhesive hydrogel with exosomes for endogenous cell recruitment and cartilage defect regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021;278:121169.
[54] GUAN P, LIU C, XIE D, et al. Exosome-loaded extracellular matrix-mimic hydrogel with anti-inflammatory property Facilitates/promotes growth plate injury repair. Bioact Mater. 2021;10:145-158.
[55] NIU Q, YANG Y, LI D, et al. Exosomes Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Promote Survival of Skin Flaps in Rats. Life (Basel). 2022;12(10):1567.
[56] XIE L, WANG J, ZHANG Y, et al. The effects of local injection of exosomes derived from BMSCs on random skin flap in rats.Am J Transl Res. 2019; 11(11):7063-7073.
[57] 胡玄,易阳艳,朱元正,等.脂肪干细胞来源外泌体促进大鼠皮瓣移植后血管新生的研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2019,33(12):1560-1565.
[58] XIONG J, LIU Z, WU M, et al. Comparison of Proangiogenic Effects of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells and Foreskin Fibroblast Exosomes on Artificial Dermis Prefabricated Flaps. Stem Cells Int. 2020;2020:5293850.
[59] MERINO-GONZÁLEZ C, ZUÑIGA FA, ESCUDERO C, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Promote Angiogenesis: Potencial Clinical Application. Front Physiol. 2016;7:24.
[60] ZHENG M, HUANG M, MA X, et al. Harnessing Exosomes for the Development of Brain Drug Delivery Systems. Bioconjug Chem. 2019;30(4): 994-1005.
[61] YU B, ZHANG X, LI X. Exosomes derived from mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(3):4142-4157.
[62] LI M, LI S, DU C, et al. Exosomes from different cells: Characteristics, modifications, and therapeutic applications. Eur J Med Chem. 2020;207: 112784.
[63] DE ALMEIDA PE, RANSOHOFF JD, NAHID A, et al. Immunogenicity of pluripotent stem cells and their derivatives. Circ Res. 2013;112(3):549-561.
[64] 李华.经血管内皮生长因子基因修饰的脂肪干细胞移植促进皮瓣预构的实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2010.
[65] 尹朝奇,周建大,罗成群,等.转染TGF-β1的骨髓间充质干细胞移植对预构皮瓣存活影响的实验研究[J].中国普通外科杂志,2016,25(6):875-881.
[66] LENG X, FAN Y, WANG Y, et al. Treatment of Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury of the Skin Flap Using Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUC-MSCs) Transfected with “F-5” Gene. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:2751-2764.
[67] 刘家明,孙健,马小睦,等.携带“F-5”基因片段hUC-MSCs对大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的效果[J].青岛大学学报(医学版),2018,54(5):536-539+543.
[68] 董政,常谨,樊勇乐,等.携带“F-5”基因片段人脐带间充质干细胞治疗大鼠皮瓣缺血再灌注损伤的研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2019, 30(4):197-201.
[69] 刘林奇.低氧预处理的人脂肪来源干细胞促进血管生成的体外实验研究[D].广州:南方医科大学,2013.
[70] 宋慧芳,郭蕊,张亮.低氧预处理通过激活AKT通路提高老年hBM-MSCs对氧化应激损伤的耐受能力[J].中国病理生理杂志,2016,32(5): 912-916.
[71] 宋慧芳,谈佳音,康毅,等.低氧预处理增强老年人骨髓间充质干细胞条件培养基对H9C2细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(1):1-6.
[72] 胡玄. 低氧预处理脂肪干细胞—胞外囊泡促进皮瓣移植后血管新生的实验研究[D].南昌:南昌大学,2020.
[73] BAI Y, HAN YD, YAN XL, et al. Adipose mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes stimulated by hydrogen peroxide enhanced skin flap recovery in ischemia-reperfusion injury. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2018;500(2): 310-317.
[74] 刘流,刘琳,梁力川,等.IL-1β预处理脂肪间充质干细胞促进VEGF蛋白分泌和巨噬细胞M_2型极化的研究[J].四川大学学报(医学版), 2019,50(2):171-176.
|