[1] KISHORE A, PETREK M. Roles of Macrophage Polarization and Macrophage-Derived miRNAs in Pulmonary Fibrosis. Front Immunol. 2021;12:678457.
[2] CHENG Y, YU Y, ZHUANG Q, et al. Bone erosion in inflammatory arthritis is attenuated by Trichinella spiralis through inhibiting M1 monocyte/macrophage polarization. iScience. 2022;25(3):103979.
[3] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440.
[4] ZHANG L, XIE H, LI S. LncRNA LOXL1-AS1 controls osteogenic and adipocytic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in postmenopausal osteoporosis through regulating the miR-196a-5p/Hmga2 axis. J Bone Miner Metab. 2020;38(6):794-805.
[5] YOSHIDA G, KAWABATA T, TAKAMATSU H, et al. Degradation of the NOTCH intracellular domain by elevated autophagy in osteoblasts promotes osteoblast differentiation and alleviates osteoporosis. Autophagy. 2022; 18(10):2323-2332.
[6] HU Y, HAO X, LIU C, et al. Acvr1 deletion in osteoblasts impaired mandibular bone mass through compromised osteoblast differentiation and enhanced sRANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2021;236(6):4580-4591.
[7] LIU J, ZHAO Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Exosomes derived from macrophages upon Zn ion stimulation promote osteoblast and endothelial cell functions. J Mater Chem B. 2021;9(18):3800-3807.
[8] OLMSTED-DAVIS E, MEJIA J, SALISBURY E, et al. A Population of M2 Macrophages Associated With Bone Formation. Front Immunol. 2021;12: 686769.
[9] BAI X, CHEN D, DAI Y, et al. Bone formation recovery with gold nanoparticle-induced M2 macrophage polarization in mice. Nanomedicine. 2021;38: 102457.
[10] BIGHETTI A, CESTARI TM, SANTOS PS, et al. In vitro and in vivo assessment of CaP materials for bone regenerative therapy. The role of multinucleated giant cells/osteoclasts in bone regeneration. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2020;108(1):282-297.
[11] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-osteoclast interactions. Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[12] DOU C, DING N, ZHAO C, et al. Estrogen Deficiency-Mediated M2 Macrophage Osteoclastogenesis Contributes to M1/M2 Ratio Alteration in Ovariectomized Osteoporotic Mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2018;33(5):899-908.
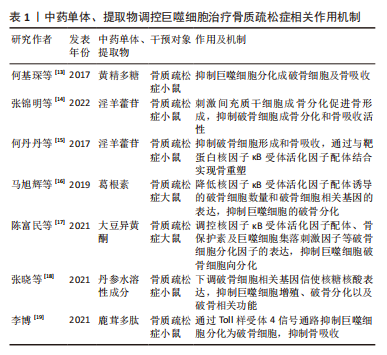
[13] 何基琛, 宗少晖, 曾高峰, 等. 黄精多糖对RANKL诱导骨髓巨噬细胞向破骨细胞分化及体内骨吸收功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2017, 21(20):3117-3122.
[14] 张锦明, 田滢舟, 赵玲, 等. 淫羊藿苷促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化缓解小鼠骨质疏松的机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2022,26(19):2991-2996.
[15] 何丹丹, 夏海建, 蒋俊, 等. 淫羊藿素与RANKL蛋白靶点结合抑制破骨细胞分化抗骨质疏松作用研究[J]. 中草药,2017,48(22):4707-4712.
[16] 马旭辉, 张鹏, 杨屹羚, 等. 葛根素对大鼠下颌骨骨髓源巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2019,17(3):193-197.
[17] 陈富民, 代庆刚, 邬春兰, 等. 大豆异黄酮对颌骨骨髓源巨噬细胞破骨细胞向分化的影响[J]. 中国口腔颌面外科杂志,2021,19(3):197-200.
[18] 张晓, 杨帆, 徐又佳. 丹参水溶性成分对小鼠单核巨噬细胞的增殖、破骨细胞分化的影响及其机制[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2021,38(2):379-380.
[19] 李博. 鹿茸多肽通过TLR4信号通路抑制破骨细胞生成和骨吸收[D]. 长春:吉林大学,2021.
[20] FRANCO-TREPAT E, ALONSO-PEREZ A, GUILLAN-FRESCO M, et al. Amitriptyline blocks innate immune responses mediated by toll-like receptor 4 and IL-1 receptor: Preclinical and clinical evidence in osteoarthritis and gout. Br J Pharmacol. 2022;179(2):270-286.
[21] 张虎林, 王亮, 喻琳, 等. 滑膜巨噬细胞在骨性关节炎发病机制中的作用及其潜在性应用研究进展[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2022,28(4):590-595.
[22] WANG D, CHAI XQ, HU SS, et al. Joint synovial macrophages as a potential target for intra-articular treatment of osteoarthritis-related pain. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2022;30(3):406-415.
[23] ZHANG J, CHENG F, RONG G, et al. Circular RNA hsa_circ_0005567 overexpression promotes M2 type macrophage polarization through miR-492/SOCS2 axis to inhibit osteoarthritis progression. Bioengineered. 2021;12(1):8920-8930.
[24] VON KAEPPLER EP, WANG Q, RAGHU H, et al. Interleukin 4 promotes anti-inflammatory macrophages that clear cartilage debris and inhibits osteoclast development to protect against osteoarthritis. Clin Immunol. 2021;229:108784.
[25] ZHANG B, CHEN H, OUYANG J, et al. SQSTM1-dependent autophagic degradation of PKM2 inhibits the production of mature IL1B/IL-1beta and contributes to LIPUS-mediated anti-inflammatory effect. Autophagy. 2020;16(7):1262-1278.
[26] SHAPOURI-MOGHADDAM A, MOHAMMADIAN S, VAZINI H, et al. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. J Cell Physiol. 2018;233(9):6425-6440.
[27] MA Y, YANG H, ZONG X, et al. Artificial M2 macrophages for disease-modifying osteoarthritis therapeutics. Biomaterials. 2021;274:120865.
[28] LIU Q, PIAN K, TIAN Z, et al. Calcium-binding protein 39 overexpression promotes macrophages from ‘M1’ into ‘M2’ phenotype and improves chondrocyte damage in osteoarthritis by activating the AMP-activated protein kinase/sirtuin 1 axis. Bioengineered. 2022;13(4):9855-9871.
[29] GAURAV R, MIKULS TR, THIELE GM, et al. High-throughput analysis of lung immune cells in a combined murine model of agriculture dust-triggered airway inflammation with rheumatoid arthritis. PloS one. 2021; 16(2):e0240707.
[30] ZHANG H, LIN C, ZENG C, et al. Synovial macrophage M1 polarisation exacerbates experimental osteoarthritis partially through R-spondin-2. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(10):1524-1534.
[31] ARSHADI D, SHAKIBA Y, RAJABIAN A, et al. Cholinergic agonists inhibit proliferation of human fibroblast-like synoviocytes and monocytic cell lines and reduce VEGF and MMPs expression by these cells. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020;42(3):246-254.
[32] OHASHI Y, UCHIDA K, FUKUSHIMA K, et al. NGF Expression and Elevation in Hip Osteoarthritis Patients with Pain and Central Sensitization. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:9212585.
[33] GEORGIEV T, IVANOVA M, VELIKOVA T, et al. Serum levels of matrix metalloproteinase-3 as a prognostic marker for progression of cartilage injury in patients with knee osteoarthritis. Acta Reumatol Port. 2020;45(3): 207-213.
[34] CHEN X, LIU Y, WEN Y, et al. A photothermal-triggered nitric oxide nanogenerator combined with siRNA for precise therapy of osteoarthritis by suppressing macrophage inflammation. Nanoscale. 2019;11(14):6693-6709.
[35] HAMASAKI M, TERKAWI MA, ONODERA T, et al. A Novel Cartilage Fragments Stimulation Model Revealed that Macrophage Inflammatory Response Causes an Upregulation of Catabolic Factors of Chondrocytes In Vitro. Cartilage. 2021;12(3):354-361.
[36] 张纯武. 木犀草素对骨关节炎中巨噬细胞相关性炎症及血管生成因子影响的研究[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2016.
[37] HU Y, GUI Z, ZHOU Y, et al. Quercetin alleviates rat osteoarthritis by inhibiting inflammation and apoptosis of chondrocytes, modulating synovial macrophages polarization to M2 macrophages. Free Radic Biol Med. 2019; 145:146-160.
[38] SA L, WEI X, HUANG Q, et al. Contribution of salidroside to the relieve of symptom and sign in the early acute stage of osteoarthritis in rat model. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020;259:112883.
[39] 田展松. 异补骨脂素调节巨噬细胞极化在骨关节炎中的抗炎作用机制研究[D]. 重庆:中国人民解放军陆军军医大学,2021.
[40] 陈博鉴, 黄永明, 刘文渤, 等. 威灵仙提取物促使M1型THP-1源巨噬细胞向M2型极化的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2021,32(12):2893-2898.
[41] PAN LL, ZHANG QY, LUO XL, et al. (7R,8S)-9-acetyl-dehydrodiconiferyl alcohol inhibits inflammation and migration in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated macrophages. Phytomedicine. 2016;23(5):541-549.
[42] 李晓辰. TRPM7介导膝骨关节炎中滑膜巨噬细胞M1型极化的机制研究及膝痹宁方的干预作用[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2021.
[43] 危一飞, 程桯, 肖潇, 等. 防己黄芪消肿方调控滑膜巨噬细胞极化治疗膝骨关节炎滑膜炎[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2022,28(13):112-122.
[44] 杨楠, 廖太阳, 张力, 等. 三色散干预滑膜巨噬细胞焦亡影响背根神经节TRPA1治疗KOA疼痛的离体研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2022,33(1):33-38.
[45] MCHUGH J. Targeting IL-1beta expression in IVDD. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020;16(4):188.
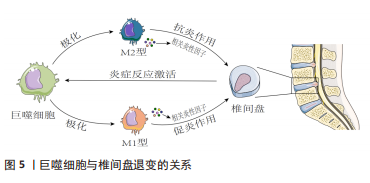
[46] NAKAZAWA KR, WALTER BA, LAUDIER DM, et al. Accumulation and localization of macrophage phenotypes with human intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine J. 2018;18(2):343-356.
[47] NAKAWAKI M, UCHIDA K, MIYAGI M, et al. Sequential CCL2 Expression Profile After Disc Injury in Mice. J Orthop Res. 2020;38(4):895-901.
[48] KAWAKUBO A, UCHIDA K, MIYAGI M, et al. Investigation of resident and recruited macrophages following disc injury in mice. J Orthop Res. 2020; 38(8):1703-1709.
[49] YAMAGISHI A, NAKAJIMA H, KOKUBO Y, et al. Polarization of infiltrating macrophages in the outer annulus fibrosus layer associated with the process of intervertebral disc degeneration and neural ingrowth in the human cervical spine. Spine J. 2022;22(5):877-886.
[50] LI L, WEI K, DING Y, et al. M2a Macrophage-Secreted CHI3L1 Promotes Extracellular Matrix Metabolic Imbalances via Activation of IL-13Ralpha2/MAPK Pathway in Rat Intervertebral Disc Degeneration. Front Immunol. 2021;12:666361.
[51] ZHANG Q, WENG Y, JIANG Y, et al. Overexpression of miR-140-5p inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced human intervertebral disc inflammation and degeneration by downregulating toll-like receptor 4. Oncol Rep. 2018; 40(2):793-802.
[52] HU S, SHAO Z, ZHANG C, et al. Chemerin facilitates intervertebral disc degeneration via TLR4 and CMKLR1 and activation of NF-kB signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY). 2020;12(12):11732-11753.
[53] LIANG H, YANG X, LIU C, et al. Effect of NF-kB signaling pathway on the expression of MIF, TNF-α, IL-6 in the regulation of intervertebral disc degeneration. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Int. 2018;18(4):551-556.
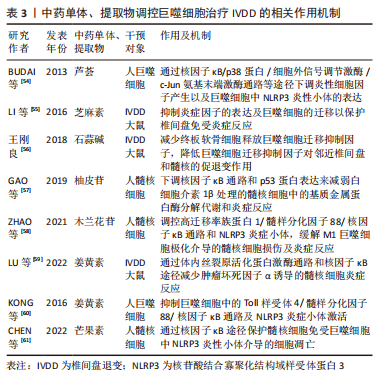
[54] BUDAI MM, VARGA A, MILESZ S, et al. Aloe vera downregulates LPS-induced inflammatory cytokine production and expression of NLRP3 inflammasome in human macrophages. Mol Immunol. 2013;56(4):471-479.
[55] LI K, LI Y, XU B, et al. Sesamin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and extracellular matrix catabolism in rat intervertebral disc. Connect Tissue Res. 2016;57(5):347-359.
[56] 王刚良. 石蒜碱通过抑制NF-κb通路缓解软骨终板退变和腰椎间盘退变[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2018.
[57] GAO G, CHANG F, ZHANG T, et al. Naringin Protects Against Interleukin 1beta (IL-1beta)-Induced Human Nucleus Pulposus Cells Degeneration via Downregulation Nuclear Factor kappa B (NF-kappaB) Pathway and p53 Expression. Med Sci Monit. 2019;25:9963-9972.
[58] ZHAO F, GUO Z, HOU F, et al. Magnoflorine Alleviates “M1” Polarized Macrophage-Induced Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Through Repressing the HMGB1/Myd88/NF-kappaB Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome. Front Pharmacol. 2021;12:701087.
[59] LU B, CHEN X, CHEN H, et al. Demethoxycurcumin mitigates inflammatory responses in lumbar disc herniation via MAPK and NF-kappaB pathways in vivo and in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;108:108914.
[60] KONG F, YE B, CAO J, et al. Curcumin Represses NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB and P2X7R Signaling in PMA-Induced Macrophages. Front Pharmacol. 2016;7:369.
[61] CHEN J, BIAN M, PAN L, et al. alpha-Mangostin protects lipopolysaccharide-stimulated nucleus pulposus cells against NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated apoptosis via the NF-kappaB pathway. J Appl Toxicol. 2022;42(9):1467-1476.
|