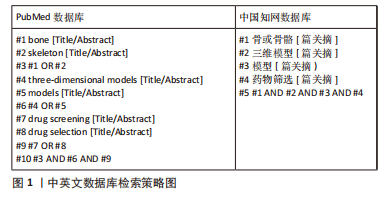
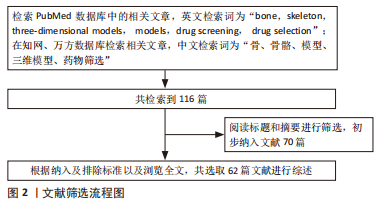
[1] DIMASI JA, GRABOWSKI HG. Economics of new oncology drug development. J Clin Oncol. 2007;25(2):209-216.
[2] AMELIAN A, WASILEWSKA K, MEGIAS D, et al. Application of standard cell cultures and 3D in vitro tissue models as an effective tool in drug design and development. Pharmacol Rep. 2017;69(5):861-870.
[3] TOVAR-LOPEZ FJ, DOMINGUEZ-HERNANDEZ VM, DIEZ-GARCIA MDEL P, et al. Finite-element analysis of the effect of basic hip movements on the mechanical stimulus within a proximal femur. Rev Invest Clin. 2014;66 Suppl 1:S32-S38.
[4] WRZESINSKI K, FEY S J. From 2D to 3D--a new dimension for modelling the effect of natural products on human tissue. Cur Pharm Design. 2015;21(38):5605-5616.
[5] MALTMAN DJ, PRZYBORSKI SA. Developments in three-dimensional cell culture technology aimed at improving the accuracy of in vitro analyses. Biochem Soc Transact. 2010;38(4):1072-1075.
[6] LANGHANS SA. Three-dimensional in vitro cell culture models in drug discovery and drug repositioning. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:6.
[7] 刘劲松.体外构建三维肝肿瘤模型及药物筛选[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(27):4389-4394.
[8] OLIVEIRA FA, MATOS AA, SANTESSO MR, et al. Low intensity lasers differently induce primary human osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J Photochem Photobiol B. 2016;163:14-21.
[9] WEYTS FA, BOSMANS B, NIESING R, et al. Mechanical control of human osteoblast apoptosis and proliferation in relation to differentiation. Calcif Tissue Int. 2003;72(4):505-512.
[10] KNIGHT E, PRZYBORSKI S. Advances in 3D cell culture technologies enabling tissue-like structures to be created in vitro. J Anat. 2015; 227(6):746-756.
[11] RAVICHANDRAN R, SUNDARAMURTHI D, GANDHI S, et al. Bioinspired hybrid mesoporous silica–gelatin sandwich construct for bone tissue engineering. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2014;187:53-62.
[12] XU X, WANG W, KRATZ K, et al. Controlling major cellular processes of human mesenchymal stem cells using microwell structures. Adv Healthc Mater. 2014;3(12):1991-2003.
[13] IHALAINEN T O, AIRES L, HERZOG F A, et al. Differential basal-to-apical accessibility of lamin A/C epitopes in the nuclear lamina regulated by changes in cytoskeletal tension. Nat Mater. 2015; 14(12):1252-1261.
[14] BOUET G, MARCHAT D, CRUEL M, et al. In vitro three-dimensional bone tissue models: from cells to controlled and dynamic environment. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2015;21(1):133-156.
[15] BUTTERY L, BIELBY R, HOWARD D, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of embryonic stem cells in 2D and 3D culture. Methods Mol Biol. 2011; 695:281-308.
[16] RAVI M, PARAMESH V, KAVIYA SR, et al. 3D cell culture systems: advantages and applications. J Cell Physiol. 2015;230(1):16-26.
[17] LIU X, SUN Q, WANG Q, et al. Epithelial cells in 2D and 3D cultures exhibit large differences in higher-order genomic interactions. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2022;20(1):101-109.
[18] SON YB, BHARTI D, KIM S B, et al. Comparison of pluripotency, differentiation, and mitochondrial metabolism capacity in three-dimensional spheroid formation of dental pulp-derived mesenchymal stem cells. BioMed Res Int. 2021;2021:5540877.
[19] HAN X, TANG S, WANG L, et al. Multicellular spheroids formation on hydrogel enhances osteogenic/odontogenic differentiation of dental pulp stem cells under magnetic nanoparticles induction. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:5101-5115.
[20] WHITEHEAD J, GRIFFIN K H, GIONET-GONZALES M, et al. Hydrogel mechanics are a key driver of bone formation by mesenchymal stromal cell spheroids. Biomaterials. 2021;269:120607.
[21] KIM BC, KWACK KH, CHUN J, et al. Comparative transcriptome analysis of human adipose-derived stem cells undergoing osteogenesis in 2D and 3D culture conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. doi:10.3390/ijms22157939.
[22] TORTELLI F, PUJIC N, LIU Y, et al. Osteoblast and osteoclast differentiation in an in vitro three-dimensional model of bone .Tissue engineering Part A. 2009;15(9):2373-2383.
[23] CUI X, BREITENKAMP K, LOTZ M, et al. Synergistic action of fibroblast growth factor-2 and transforming growth factor-beta1 enhances bioprinted human neocartilage formation. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2012; 109(9):2357-2368.
[24] LIN RZ, CHANG HY. Recent advances in three-dimensional multicellular spheroid culture for biomedical research. Biotechnol J. 2008;3(9-10): 1172-1184.
[25] 何云影,李玲婕,张舒淇,等.聚丙烯酸/琼脂糖三维培养构建细胞球的方法[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(4):553-559.
[26] GURUMURTHY B, BIERDEMAN PC, JANORKAR AV. Spheroid model for functional osteogenic evaluation of human adipose derived stem cells. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2017;105(4):1230-1236.
[27] RUMINSKI S, KALASZCZYNSKA I, DLUGOSZ A, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived stem cells in 3D conditions - comparison of spheroids and polystyrene scaffolds. Eur Cell Mater. 2019;37:382-401.
[28] KIM J, ADACHI T. Cell condensation triggers the differentiation of osteoblast precursor cells to osteocyte-like cells. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:288.
[29] MA Y, LIN M, HUANG G, et al. 3D spatiotemporal mechanical microenvironment: a hydrogel-based platform for guiding stem cell fate. Adv Mater. 2018;30(49):e1705911.
[30] TROJANI C, WEISS P, MICHIELS JF, et al. Three-dimensional culture and differentiation of human osteogenic cells in an injectable hydroxypropylmethylcellulose hydrogel. Biomaterials. 2005;26(27): 5509-5517.
[31] QIAO Y, LIU X, ZHOU X, et al. Gelatin templated polypeptide co-cross-linked hydrogel for bone regeneration. Adv Healthc Mater. 2020;9(1): e1901239.
[32] LI D, ZHOU J, ZHANG M, et al. Long-term delivery of alendronate through an injectable tetra-PEG hydrogel to promote osteoporosis therapy. Biomater Sci. 2020;8(11):3138-3146.
[33] NAFEE N, ZEWAIL M, BORAIE N. Alendronate-loaded, biodegradable smart hydrogel: a promising injectable depot formulation for osteoporosis. J Drug Target. 2018;26(7):563-575.
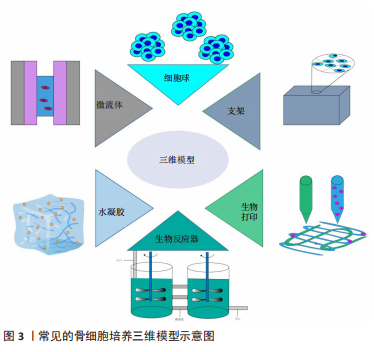
[34] LI XJ, VALADEZ AV, ZUO P, et al. Microfluidic 3D cell culture:potential application for tissue-based bioassays. Bioanalysis. 2012;4(12):1509-1525.
[35] VAN DUINEN V, TRIETSCH SJ, JOORE J, et al. Microfluidic 3D cell culture: from tools to tissue models. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2015; 35:118-126.
[36] KNOWLTON S, YU CH, ERSOY F, et al. 3D-printed microfluidic chips with patterned, cell-laden hydrogel constructs. Biofabrication. 2016; 8(2):025019.
[37] ZUO Y, HE X, YANG Y, et al. Microfluidic-based generation of functional microfibers for biomimetic complex tissue construction. Acta Biomater. 2016;38:153-162.
[38] AN C, LIU W, ZHANG Y, et al. Continuous microfluidic encapsulation of single mesenchymal stem cells using alginate microgels as injectable fillers for bone regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2020;111:181-196.
[39] LIN Z, LI Z, LI E N, et al. Osteochondral tissue chip derived from iPSCs: modeling OA pathologies and testing drugs. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019;7:411.
[40] HOSPODIUK M, DEY M, SOSNOSKI D, et al. The bioink: a comprehensive review on bioprintable materials. Biotechnol Adv. 2017;35(2):217-239.
[41] BYAMBAA B, ANNABI N, YUE K, et al. Bioprinted osteogenic and vasculogenic patterns for engineering 3D bone tissue. Adv Healthc Mater. 2017. doi:10.1002/adhm. 201700015.
[42] BREATHWAITE E, WEAVER J, ODANGA J, et al. 3D bioprinted osteogenic tissue models for in vitro drug screening. Molecules. 2020. doi:10.3390/molecules25153442.
[43] LI Y C, ZHANG YS, AKPEK A, et al. 4D bioprinting:the next-generation technology for biofabrication enabled by stimuli-responsive materials. Biofabrication. 2016;9(1):012001.
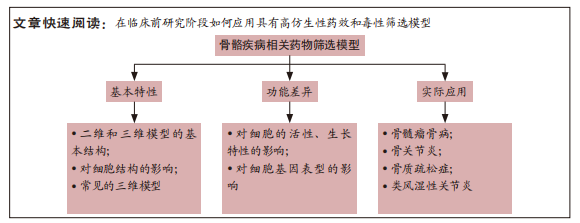
[44] 高彤,丁冠守,苏萍萍,等.药物筛选模型的研究进展[J].海峡药学, 2021,33(7):1-5.
[45] HAMEED A, BRADY JJ, DOWLING P, et al. Bone disease in multiple myeloma: pathophysiology and management.Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2014;7:33-42.
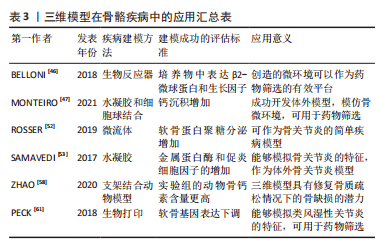
[46] BELLONI D, HELTAI S, PONZONI M, et al. Modeling multiple myeloma-bone marrow interactions and response to drugs in a 3D surrogate microenvironment. Haematologica. 2018;103(4):707-716.
[47] MONTEIRO CF, CUSTODIO CA, MANO JF. Bioengineering a humanized 3D tri-culture osteosarcoma model to assess tumor invasiveness and therapy response. Acta Biomater. 2021;134:204-214.
[48] RIMANN M, LATERNSER S, GVOZDENOVIC A, et al. An in vitro osteosarcoma 3D microtissue model for drug development. J Biotechnol. 2014;189:129-135.
[49] CORTES I, MATSUI R AM, AZEVEDO MS, et al. A scaffold- and serum-free method to mimic human stable cartilage validated by secretome. Tissue Eng Part A. 2021;27(5-6):311-327.
[50] LOTZ MK, CARAMES B. Autophagy and cartilage homeostasis mechanisms in joint health, aging and OA. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011; 7(10):579-587.
[51] DIEKMAN BO, SESSIONS GA, COLLINS J A, et al. Expression of p16(INK) (4a) is a biomarker of chondrocyte aging but does not cause osteoarthritis. Aging Cell. 2018;17(4):e12771.
[52] ROSSER J, BACHMANN B, JORDAN C, et al. Microfluidic nutrient gradient-based three-dimensional chondrocyte culture-on-a-chip as an in vitro equine arthritis model. Mater Today Bio. 2019;4:100023.
[53] SAMAVEDI S, DIAZ-RODRIGUEZ P, ERNDT-MARINO JD, et al. A three-dimensional chondrocyte-macrophage coculture system to probe inflammation in experimental osteoarthritis. Tissue Eng Part A. 2017; 23(3-4):101-114.
[54] REID IR. A broader strategy for osteoporosis interventions. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020;16(6):333-339.
[55] CHEN LR, KO NY, CHEN KH. Medical treatment for osteoporosis: from molecular to clinical opinions. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. doi:10.3390/ijms20092213.
[56] ZHENG Z, YU C, WEI H. Injectable hydrogels as three-dimensional network reservoirs for osteoporosis treatment. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2021;27(5):430-454.
[57] 林建立,蔡敏,林庆明,等. 微流控芯片关键技术及其在骨质疏松症和糖尿病发病机制研究的应用[Z].福建省立医院.2017.
[58] ZHAO R, CHEN S, ZHAO W, et al. A bioceramic scaffold composed of strontium-doped three-dimensional hydroxyapatite whiskers for enhanced bone regeneration in osteoporotic defects. Theranostics. 2020;10(4):1572-1589.
[59] KAMEL R, EL-WAKIL NA, ABDELKHALEK AA, et al. Nanofibrillated cellulose/cyclodextrin based 3D scaffolds loaded with raloxifene hydrochloride for bone regeneration. Int J Biol Macromol. 2020;156: 704-716.
[60] 李利青,张逢,彭馥芝,等.类风湿关节炎实验性动物模型研究进展[J].中国药理学通报,2021,37(11):1492-1497.
[61] PECK Y, LEOM LT, LOW PFP, et al. Establishment of an in vitro three-dimensional model for cartilage damage in rheumatoid arthritis. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(1): e237-e249.
[62] AGOSTINI SBN, MALTA IHS, RODRIGUES RF, et al. Preclinical evaluation of methotrexate-loaded polyelectrolyte complexes and thermosensitive hydrogels as treatment for rheumatoid arthritis. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2021; 163:105856. |