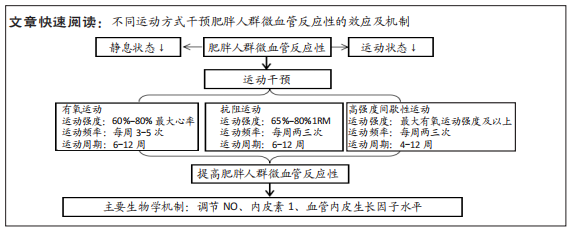
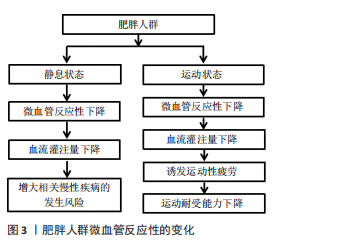
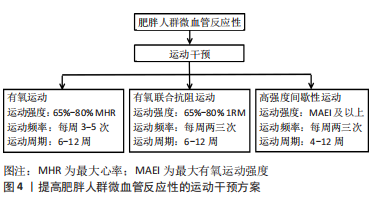
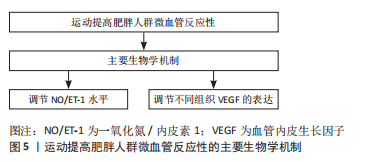
[1] 中国营养学会肥胖防治学组、中国营养学会临床营养学组、中国预防医学会行为健康学组等.中国居民肥胖防治专家共识[J].中国预防医学杂志,2022,23(5):321-339.
[2] 王亮亮,黄瑜,郭伟,等.肥胖和中心性肥胖对高血压的交互作用分析[J].预防医学,2022,34(2):129-134.
[3] 刘烨,王海宁.2021年ADA/EASD《糖尿病缓解专家共识》与《2022年ADA糖尿病指南:2型糖尿病的预防和治疗中肥胖与体重管理》解读——糖尿病缓解的定义与治疗策略[J].临床内科杂志,2022, 39(5):299-302.
[4] 柯居中,刘晓琳,吴抗,等.社区居民肥胖、中心性肥胖与冠心病发病风险的前瞻性队列研究[J].现代预防医学,2020,47(7):1310-1314.
[5] 陈燕子,刘莉,付晓丽,等.肥胖与癌症的关系的知识图谱分析[J].中华疾病控制杂志,2016,20(6):604-608.
[6] 陈浩,龚涛,王晓霞,等.中国多学科微血管疾病诊断与治疗专家共识[J].中国循环杂志,2020,35(12):1149-1165.
[7] GRAUPERA M, CLARET M. Endothelial cells: new players in obesity and related metabolic disorders. Trends Endol Metab. 2018;29(11):781-794.
[8] TANG DH, BAI S, LI XL, et al. Improvement of microvascular endothelial dysfunction induced by exercise and diet is associated with microRNA-126 in obese adolescents. Microvasc Res. 2019;123:86-91.
[9] 肖哲,朱欢,胡江平,等.10周有氧运动和有氧结合抗阻运动对肥胖大学生微循环功能的影响及机制研究[J].中国全科医学,2022, 25(19):2349-2355+2362.
[10] DIAS I, FARINATTI P, DE SOUZA MG, et al. Effects of resistance training on obese adolescents. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(12):2636-2644.
[11] 唐东辉,侯玉洁,杨东升,等. 有氧运动结合抗阻训练对肥胖青少年微血管内皮功能的影响[C]//第四届(2016)全国运动生理与生物化学学术会议——运动·体质·健康论文摘要汇编[G].2016:56-57.
[12] COCKS M, SHAW CS, SHEPHERD SO, et al. Sprint interval and moderate-intensity continuous training have equal benefits on aerobic capacity, insulin sensitivity, muscle capillarisation and endothelial eNOS/NAD(P)hoxidase protein ratio in obese men. J Physiol. 2016;594(8):2307-2321.
[13] 唐元梁,李桂香,姚立平,等.皮肤微血管调节功能无创检测技术进展[J].中国医疗设备,2022,37(6):153-157.
[14] LA FAVOR JD, DUBIS GS, YAN H, et al. Microvascular endothelial dysfunction in sedentary, obese Humans is mediated by NADPH oxidase: influence of exercise training. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2016;36(12):2412-2420.
[15] KWAIFA IK, BAHARI H, YONG YK, et al. Endothelial dysfunction in obesity-induced inflammation: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications.Biomo. 2020;10(2):291-311.
[16] 邓林华,温玉,张运娇,等.血管内皮功能障碍与高血压关系的研究进展[J].中华高血压杂志,2021,29(10):935-940.
[17] PIENAAR PR, MICKLESFIELD LK, LEVITT NS, et al. Insulin resistance is associated with lower acetylcholine-induced microvascular reactivity in nondiabetic women. Metab Syndr Relat Disord. 2014;12(3):178-184.
[18] MURIS DM, HOUBEN AJ, SCHRAM MT, et al. Microvascular dysfunction: an emerging pathway in the pathogenesis of obesity-related insulin resistance. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013;14(1):29-38.
[19] 沈英华,傅汉菁,赵静.糖尿病患者足部皮肤反应性充血在三种血流阻断压力下的变化[J].微循环学杂志,2009,19(2):36-37+40+ 77+80.
[20] 朱欢,高炳宏.微血管反应性在耐力性运动员训练中的应用[J].中国运动医学杂志,2019,38(10):907-914.
[21] ZHANG H, JIANG L, YANG YJ, et al. Aerobic exercise improves endothelial function and serum adropin levels in obese adolescents independent of body weight loss. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):17717-17724.
[22] MARANHãO PA, DE SOUZA MD, KRAEMER-AGUIAR LG, et al. Dynamic nailfold videocapillaroscopy may be used for early detection of microvascular dysfunction in obesity. Microvasc Res. 2016;106:31-35.
[23] LIMBERG JK, HARRELL JW, JOHANSSON RE, et al. Microvascular function in younger adults with obesity and metabolic syndrome: role of oxidative stress. Am J Physiol Heart CircPhysiol. 2013;305(8): H1230-H1237.
[24] MONTERO D, WALTHER G, PEREZ-MARTIN A, et al. Effects of a lifestyle program on vascular reactivity in macro- and microcirculation in severely obese adolescents. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014;99(3):1019-1026.
[25] FRANCO RL, FALLOW BA, HUANG CJ, et al. Forearm blood flow response to acute exercise in obese and non-obese males. Eur J Appl Physiol. 2013;113(8):2015-2023.
[26] VINET A, KARPOFF L, WALTHER G, et al. Vascular reactivity at rest and during exercise in middle-aged obese men: effects of short-term, low-intensity, exercise training. Int J Obes (Lond). 2011;35(6):820-828.
[27] 张昊楠,高炳宏,朱欢.男子赛艇运动员赛前6周训练微循环血流储备能力与相关生化指标的关系[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2017, 33(2):112-116+120.
[28] 董徽徽,高炳宏,朱欢.下肢间歇负压疗法对优秀赛艇运动员股四头肌皮肤微循环血流灌注量的急性效应[J].南京体育学院学报, 2019,2(9):47-52.
[29] 田广,高炳宏,朱欢.下肢间歇负压对优秀男子跆拳道运动员微循环功能的急性干预效应[C]//.第十二届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编——墙报交流(运动训练分会) [G].2022:74-75.
[30] PASQUALINI L, SCHILLACI G, INNOCENTE S, et al. Lifestyle intervention improves microvascular reactivity and increases serum adiponectin in overweight hypertensive patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2010; 20(2):87-92.
[31] 孔凡明,朱苗苗,米靖,等.运动与脂肪氧化动力学特征的应用启示[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(29):4709-4715.
[32] 李盈盈,黄丽,彭莉.肥胖女大学生最大脂肪氧化强度研究[J].中国学校卫生,2021(9):1407-1410+1414.
[33] 周术锋,肖哲,朱欢,等.12周有氧运动对习惯久坐大学生微循环功能的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2021,42(9):1332-1335+1339.
[34] BRUYNDONCKX L, HOYMANS VY, DE GUCHTENAERE A, et al. Diet, exercise, and endothelial function in obese adolescents. Pediatrics. 2015;135(3):e653-e661.
[35] LAMPRECHT M, OBERMAYER G, STEINBAUER K, et al. Supplementation with a juice powder concentrate and exercise decrease oxidation and inflammation, and improve the microcirculation in obese women: randomised controlled trial data. Br JNutr. 2013;110(9):1685-1695.
[36] GILL JM, Al-MAMARI A, FERRELL WR, et al. Effects of prior moderate exercise on postprandial metabolism and vascular function in lean and centrally obese men. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2004;44(12):2375-2382.
[37] 胥祉涵,王世强,李丹,等.2022年美国运动医学会《2型糖尿病患者的运动/身体活动指南》解读及启示[J].中国全科医学,2022, 25(25):3083-3088.
[38] BEIJER Å, DEGENS H, WEBER T, et al. Microcirculation of skeletal muscle adapts differently to a resistive exercise intervention with and without superimposed whole-body vibrations. Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2015;35(6):425-435.
[39] 李娟,唐东辉,陈巍.有氧运动结合抗阻训练对男性肥胖青少年心血管功能的改善及可能机制[J].体育科学,2013,33(8):37-42.
[40] 赵军,梁晋裕.有氧运动结合抗阻训练对肥胖男性大学生身体成分、心血管功能及血清C反应蛋白水平的改善作用[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2019,45(5):1134-1140.
[41] 中国2型糖尿病防治指南(2017年版)[J].中国实用内科杂志,2018, 38(4):292-344.
[42] 孙文新,秦曼,李丽丽,等.高强度间歇训练对超重肥胖女大学生减脂效果的Meta分析[J].中国学校卫生,2021,42(10):1480-1486.
[43] 高靖波. HIIT对大学生自行车运动员专项运动能力影响的实验研究[D].呼和浩特:内蒙古师范大学,2022.
[44] 王成浩,何辉,熊开宇.不同强度有氧运动对中高度近视女大学生眼压的影响[J].中国学校卫生,2019,40(8):1254-1257.
[45] 魏胜敏,高前进,王二利.高强度间歇训练对肥胖青年血清adropin水平和血管内皮功能的影响[J].中国康复医学杂志,2019,34(9): 1058-1064.
[46] TJøNNA AE, STøLEN TO, BYE A, et al. Aerobic interval training reduces cardiovascular risk factors more than a multitreatment approach in overweight adolescents. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009;116(4):317-326.
[47] 王珅,廖静雯,黄俊豪,等.高强度有氧间隔训练对肥胖青少年血管内皮功能的影响及机制[J].山东医药,2018,58(20):45-47.
[48] RAMOS JS, DALLECK LC, TJONNA AE, et al. The impact of high-intensity interval training versus moderate-intensity continuous training on vascular function: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Med. 2015;45(5):679-692.
[49] MORRISSEY C, MONTERO D, RAVERDY C, et al. Effects of exercise intensity on microvascular function in obese adolescents. Int J Sports Med. 2018;39(6):450-455.
[50] TODA N, OKAMURA T. Obesity impairs vasodilatation and blood flow increase mediated by endothelial nitric oxide: an overview. J Clin Pharmacol. 2013;53(12):1228-1239.
[51] 罗丽珊,孙嘉.微循环障碍相关细胞信号通路的研究进展[J].微循环学杂志,2013,23(1):67-70.
[52] 朱欢,高炳宏.有氧运动对人体微血管反应性的作用及机制研究进展[J].生命科学,2020,32(8):855-863.
[53] 王成科,朱欢,董徽徽,等.运动对高血压患者微血管反应性的干预效应及可能机制研究进展[J].中国预防医学杂志,2021,22(9): 726-731.
[54] SILHA JV, KRSEK M, SUCHARDA P, et al. Angiogenic factors are elevated in overweight and obese individuals. Int J Obes (Lond). 2005; 29(11):1308-1314.
[55] AHMADI-KANI GOLZAR F, FATHI R, MAHJOUB S. High-fat diet leads to adiposity and adipose tissue inflammation: the effect of whey protein supplementation and aerobic exercise training. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab. 2019;44(3):255-262.
[56] 刘雨佳,梅婷,陈瞳. AMPK/PGC-1α/VEGF通路在运动训练调节肥胖大鼠骨骼肌毛细血管生成中的作用[C].第十二届全国体育科学大会论文摘要汇编——墙报交流(运动生理生化分会)[G]. 2022:215-216.
[57] 张靓,马谨,陈雪飞,等.跑台运动对肥胖大鼠比目鱼肌毛细血管生成及apelin表达的影响[J].中国运动医学杂志,2017,36(5):383-389.
[58] 李靖.跑台运动通过增加MicroRNA-126改善高脂饮食诱导的肥胖大鼠血运重建[J].井冈山大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(1):95-101.
[59] HE Z, OPLAND DM, WAY KJ, et al. Regulation of vascular endothelial growth factor expression and vascularization in the myocardium by insulin receptor and PI3K/Akt pathways in insulin resistance and ischemia. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2006;26(4):787-793.
[60] AHN N, KIM K. Effects of Aerobic and Resistance Exercise on Myokines in High Fat Diet-Induced Middle-Aged Obese Rats. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(8):2685-2695.
[61] SHIN KO, BAE JY, WOO J, et al. The effect of exercise on expression of myokine and angiogenesis mRNA in skeletal muscle of high fat diet induced obese rat. J Exerc Nutrition Biochem. 2015;19(2):91-98. |