中国组织工程研究 ›› 2023, Vol. 27 ›› Issue (26): 4231-4238.doi: 10.12307/2023.564
• 组织构建综述 tissue construction review • 上一篇 下一篇
瘦素对骨关节炎效应细胞的调控作用
周 晶1,伍潇潇1,刘 婉2,3,4,魏 蒙2,3,4,吴 淼2,3,4,郑 岚1
- 1湖北中医药大学,湖北省武汉市 430065;2湖北省中医院,湖北省武汉市 430060;3湖北中医药大学附属医院,湖北省武汉市 430060;4湖北省中医药研究院,湖北省武汉市 430074
-
收稿日期:2022-08-31接受日期:2022-10-14出版日期:2023-09-18发布日期:2023-01-28 -
通讯作者:郑岚,湖北中医药大学,湖北省武汉市 430065 -
作者简介:周晶,男,1980年生,湖北省武汉市人,湖北中医药大学针灸推拿学博士,副主任医师,主要从事推拿在康复医学领域中的应用研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金(82104825),项目负责人:郑岚
Modulatory effect of leptin on the effector cells of osteoarthritis
Zhou Jing1, Wu Xiaoxiao1, Liu Wan2, 3, 4, Wei Meng2, 3, 4, Wu Miao2, 3, 4, Zheng Lan1
- 1Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China; 2Hubei Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine,Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China; 3Affiliated Hospital of Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430060, Hubei Province, China; 4Hubei Province Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430074, Hubei Province, China
-
Received:2022-08-31Accepted:2022-10-14Online:2023-09-18Published:2023-01-28 -
Contact:Zheng Lan, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China -
About author:Zhou Jing, MD, Professor, Associate chief physician, Hubei University of Chinese Medicine, Wuhan 430065, Hubei Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 82104825 (to ZL)
摘要:
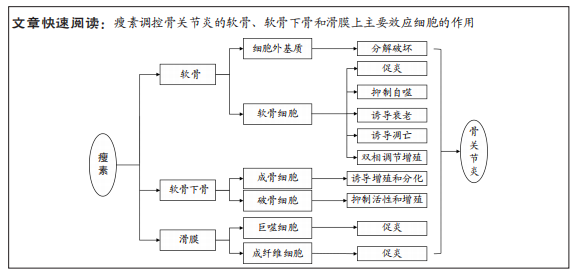
文题释义:
瘦素:是一种由白色脂肪组织分泌的蛋白质荷尔蒙,编码基因ob,位于人类的第七号染色体上,由167个氨基酸构成,大小为16 kD。瘦素具有广泛的生物学效应,早期研究发现其主要作用于下丘脑的代谢调节中枢,发挥抑制食欲、增加能量消耗、抑制脂肪合成的作用,现研究发现其还具有参与调控炎症反应、免疫稳态、软骨和骨代谢、血管生成、造血(血细胞的形成)、细胞增殖等多个进程。效应细胞:是指对刺激产生相应反应并发生改变的一类细胞。效应细胞包括成纤维细胞、肥大细胞、浆细胞、效应T细胞、软骨细胞、小胶质细胞等。此文所研究的成纤维细胞,为滑膜组织的支撑细胞,在瘦素的影响下可发生促炎反应;而软骨细胞为人体软骨内唯一的细胞,瘦素可对其促炎、自噬、凋亡、增殖等方面起到调控作用。
背景:瘦素是由脂肪组织合成的一种多效性脂肪因子和肽激素,最初被认为主要发挥食欲调节和能量平衡的作用。深入研究后发现,瘦素还具有参与调控慢性炎症和肌肉骨骼系统疾病的作用。
目的:就瘦素和瘦素受体的概念、目前瘦素对骨关节炎中软骨、软骨下骨和滑膜上主要效应细胞的调控作用等方面进行综述。
方法:结合英文检索词(leptin、Obese Protein、Obese Gene Product、Gene Product, Obese、Ob Gene Product、Gene Product, Ob、Ob Protein、Osteoarthritis、OA、Osteoarthritides、Osteoarthrosis、Osteoarthroses、Arthritis, Degenerative、Arthritides, Degenerative、Degenerative Arthritides、Degenerative Arthritis、Arthrosis、Arthroses、Osteoarthrosis Deformans)和中文检索词(瘦素、LP、Ob蛋白质、肥胖蛋白质、骨关节炎、OA、退行性骨关节炎、骨关节病、变形骨关节炎),检索PubMed、Web of Science、CNKI(中国知网)、cqVIP(维普资讯网)、万方全文数据库,搜索关于瘦素对骨关节炎主要组织中效应细胞的影响相关领域的文章,进行总结和综述。
结果与结论:①瘦素对骨关节中主要组织效应细胞起到调控作用,影响骨关节炎的发生发展。②瘦素对软骨中的细胞外基质主要起到分解作用,对软骨细胞发挥促炎、抑制自噬、诱导衰老、诱导凋亡、双相调节增殖的作用。③瘦素诱导成骨细胞增殖与分化、抑制破骨细胞活性与增殖,影响软骨下骨骨重塑,导致骨赘的形成。④瘦素对滑膜巨噬细胞与成纤维细胞的调控主要在于介导骨关节炎炎症反应。⑤瘦素未来有望成为骨关节炎预后生物标记物及治疗的潜在靶点。
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8336-7278(周晶)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
周 晶, 伍潇潇, 刘 婉, 魏 蒙, 吴 淼, 郑 岚. 瘦素对骨关节炎效应细胞的调控作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(26): 4231-4238.
Zhou Jing, Wu Xiaoxiao, Liu Wan, Wei Meng, Wu Miao, Zheng Lan. Modulatory effect of leptin on the effector cells of osteoarthritis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2023, 27(26): 4231-4238.

瘦素发挥生物活性的作用主要依赖于瘦素受体(Ob receptor,ObR)的介导[32]。ObR由位于4号染色体上的糖尿病(db)基因编码,属于Ⅰ型细胞因子受体超家族成员[33],通过选择性信使RNA(mRNA)剪接[34],产生至少6种不同的亚型:可溶性受体Ob-Re、短型受体(Ob-Ra, Ob-Rc,Ob-Rd and Ob-Rf)和长型受体Ob-Rb[35]。短型受体几乎表达于身体所有外周组织中[36];长型受体Ob-Rb主要表达于下丘脑以及软骨、成骨细胞、免疫细胞、血管内皮细胞、T淋巴细胞等[37];可溶性瘦素受体Ob-Re是被切割瘦素受体的胞外部分,在血浆中与瘦素1∶1结合成复合体,血浆中的结合型瘦素没有生物学活性。长型受体Ob-Rb在胞内的蛋白停泊点对于信号转导至关重要,而短型受体缺乏这些位点[38],因此长型受体Ob-Rb是唯一能转导瘦素信号的完整细胞内结构域亚型[39]。瘦素通过与长型受体Ob-Rb结合能促进不同信号通路的激活以此来发挥其生物学功能,其主要激活细胞内信号机制酪氨酸激酶/信号转导和转录激活因子(Janus tyrosine kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription,JAK/STAT)胞内信号通路,其中诱导的JAK2-STAT3信号通路与骨关节炎的发生发展密切相关[40],此外还可激活ERK1/2的MAPK通路、通过IRS1磷酸化的PI3K通路、NF-κB、蛋白激酶C(PKC)和细胞外信号调节激酶等[37]。
瘦素可参与骨关节炎的发生,其是连接肥胖与骨关节炎之间重要的因素。肥胖作为骨关节炎的危险因素,不仅影响到承重关节,也在非承重关节(手指和手腕)发生[41]。GRIFFIN等[42]发现瘦素或Ob-Rb缺乏的极度肥胖雌性小鼠与骨关节炎发生率升高无关。此外研究表明关节液中瘦素水平和血清瘦素水平均与体质量指数呈正相关[43-46]。综上,并非所有肥胖都能诱导骨关节炎的发生,除机械刺激外,脂肪因子分泌的瘦素与骨关节炎相关,在肥胖与骨关节炎间发挥桥梁的作用。最新研究显示瘦素具有参与免疫稳态、炎症反应的调节、骨代谢等作用,对骨关节炎的发病机制至关重要。在机体免疫稳态的调节中,瘦素已被证实能对固有免疫和获得性免疫进行调节。在获得性免疫中,瘦素可刺激幼稚T细胞的增殖,促进记忆T细胞向辅助T细胞1(Th1)分化,产生促炎细胞因子,如干扰素(IFNγ)和白细胞介素2,并抑制Th2细胞因子白细胞介素4和白细胞介素10的产生,此外还能刺激B细胞和巨噬细胞产生促炎细胞因子等。在固有免疫中瘦素能增强自然杀伤(NK)细胞活性促其增殖,还能诱导粒细胞、巨噬细胞和树突状细胞等的激活[39,47-48]。在炎症反应的调节中,瘦素本身作为促炎因子也可诱导其他促炎因子的产生,如白细胞介素1、白细胞介素6和肿瘤坏死因子α等,从而加重骨关节炎的炎症状态[49]。在骨代谢中,瘦素可通过中央和外周调节骨的生成等[17]。2003年,DUMOND等[43]得出了支持瘦素在骨关节炎中发挥关键作用的最早证据,此后更多的研究证据发现瘦素能参与骨关节炎的发生发展。
2.2 瘦素对骨关节炎软骨、软骨下骨、滑膜效应细胞的调控
2.2.1 瘦素对骨关节炎软骨的影响 关节软骨的退变是骨关节炎的主要特征,其合成和分解代谢失衡是退变的根本因素[50]。关节软骨主要由软骨细胞和细胞外基质构成,近年来研究表明瘦素可通过细胞外基质和软骨细胞影响关节软骨,促进骨关节炎的进程,见图4。
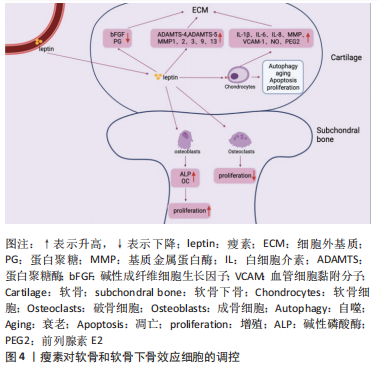
(1)细胞外基质:瘦素对细胞外基质主要发挥分解作用。细胞外基质即软骨基质,是大分子构成的错综复杂的网络,为软骨中唯一的软骨细胞提供生存及活动的场所[51]。细胞外基质的主要成分为Ⅱ型胶原蛋白和蛋白聚糖。在骨关节炎中,瘦素可通过直接或间接介导降解细胞外基质,分解代谢软骨组织。在蛋白聚糖结构域中有两个主要切割位点,一个是MMP切割位点,MMP是一种细胞外基质降解酶,几乎能降解细胞外基质中的各种蛋白成分,破坏软骨内环境稳态,在骨关节炎的发病机制中起着重要作用[49];而另一个切割位点是蛋白聚糖酶(A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs,ADAMTS)的ADAMTS-4和ADAMTS-5,ADAMTS-4和ADAMTS-5是软骨基质蛋白聚蛋白多糖aggrecan的降解酶,和MMP一样可对细胞外基质起到分解作用,破坏软骨稳态[52-53]。且相关研究表明,骨关节炎的病因与软骨稳态的破坏有关[54]。
瘦素促进分解代谢因子MMP和ADAMTS表达发挥直接降解蛋白聚糖和胶原作用,破坏软骨。一项研究发现,将瘦素注射到大鼠的膝关节时,关节软骨中的蛋白聚糖被耗尽,此外瘦素可显著上调相关MMP的基因及其蛋白水平,如MMP-1、MMP-2、MMP-3、MMP-9、MMP-13[44,55-57]。有研究发现细胞在瘦素处理的第7天,软骨胶原降解因子MMP-9、MMP-13含量增加;用来自骨关节炎患者沉默RNA(siRNA)瘦素处理的软骨细胞显示MMP-13表达降低一半,在瘦素重新激活软骨细胞后,MMP-13表达上调[58]。瘦素还可协同其他细胞因子上调分解代谢因子水平,如瘦素协同白细胞介素1β上调骨关节炎软骨中的MMP-1、MMP-3、MMP-13水平[59]。BAO等[60]在其研究中观察到关节内瘦素可增加ADAMTS-4和ADAMTS-5基因,且降低大鼠碱性成纤维细胞生长因子和蛋白聚糖的表达。
瘦素也被证明能分泌产生其他破坏性介质抑制蛋白聚糖和胶原的合成,发挥间接降解作用。如瘦素可通过诱导一氧化氮合酶的分泌影响NO的合成,NO是关节软骨上众所周知的促炎递质,可触发软骨细胞表型丢失、凋亡,还可诱导MMP的表达和激活等[61]。在ZHANG等[62]实验中发现蛋白聚糖随着瘦素浓度的增加而减少,10 ng/mL或100 ng/mL的瘦素能显著降低蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原mRNA的表达和蛋白质水平。
除起到破坏软骨作用外,有学者发现了瘦素对软骨还具有保护作用。用不同浓度瘦素加入血清对软骨细胞进行培养,检测对胶原和蛋白聚糖的影响,发现在10-100 pg/mL时瘦素能显著增强胶原合成,在0.1-1.0 ng/mL时,对蛋白聚糖的合成有较大影响[63]。此外,在大鼠膝关节中施用外源性瘦素诱导软骨细胞STAT1和STAT5的磷酸化,可增加蛋白聚糖的增殖和分泌[37]。SU等[64]通过动物及细胞实验发现通过人类软骨细胞中瘦素诱导的骨形态发生蛋白2自分泌作用可影响瘦素上调MMP-1、MMP-13和ADAMTS-4、ADAMTS-5的mRNA表达;而瘦素诱导的骨形态发生蛋白2自分泌作用还可促进Ⅱ型胶原的合成。因此瘦素对细胞外基质的影响具有既破坏又保护的双重作用,低浓度瘦素可以促进蛋白聚糖和Ⅱ型胶原的生成,而高浓度瘦素可以刺激关节软骨细胞[65-66]。
(2)软骨细胞:软骨细胞是人体软骨内唯一的细胞,其能合成细胞外基质组分,对细胞外基质起到重塑和维持稳态的作用。当软骨细胞出现破坏时,软骨基质降解增加,合成代谢过程减少,最终造成软骨生存微环境的失衡[67]。研究证实,人类软骨细胞可表达瘦素受体Ob-Rb,且在骨关节炎状态下软骨细胞中瘦素水平显著升高,表明瘦素能直接靶向软骨细胞,影响软骨稳态和骨关节炎进展[37,63]。根据最新研究,瘦素主要对软骨细胞促炎、自噬、凋亡、增殖等方面起到调控作用。
促炎:瘦素可促进关节软骨细胞产生促炎因子及破坏性递质,如白细胞介素1β、白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8、MMP、血管细胞黏附分子1、一氧化氮和前列腺素E2改变软骨稳态环境[68]。白细胞介素1β作为一种参与软骨损伤的典型促炎细胞因子,可参与关节的免疫炎症过程、抑制Ⅱ型胶原的合成,白细胞介素1β可诱导软骨细胞释放更多的ADAMTS-4和ADAMTS-5[69]。且白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6都能增强MMP、NO的生成。SIMOPOULOU等[44]发现软骨细胞在经瘦素处理后的第7天,可以检测出白细胞介素1β的表达。另一项研究发现瘦素可通过NF-κB通路上调软骨细胞促炎因子白细胞介素1β和白细胞介素6的表达[39,49];瘦素还可通过激活软骨细胞中JAK2和PI3K通路增加白细胞介素8和血管细胞黏附分子1的表达[70-71];VUOLTEENAHO等[72]收集临床确诊为骨关节炎患者的软骨组织,发现当瘦素与白细胞介素1β协同作用于软骨组织时,可诱导人软骨细胞中诱导型一氧化氮合酶(iNOS)、前列腺素E2和环氧合酶2的生成。因此,瘦素可诱导软骨细胞形成炎性环境,损伤软骨组织。
自噬:目前可证实瘦素能抑制软骨细胞的自噬。自噬能保护软骨细胞免受应激,维持软骨及软骨细胞的稳态,保护软骨细胞免于坏死,而自噬功能的减轻可加速软骨的损伤,导致软骨退变[73]。自噬标志物LC3-Ⅱ和p62为细胞自噬的活性指标,p62蛋白表达水平的高低与自噬活性成反比。ZHAO等[55]在其研究中发现用高剂量的瘦素处理软骨细胞后LC3-Ⅱ水平下降、p62增加,软骨细胞自噬被抑制。运行等[74]在其细胞实验中分别以10 ng/mL和100 ng/mL的瘦素干预软骨细胞后,检测自噬相关因子Parkin、LC3A、LC3B的表达并探测软骨细胞线粒体电位,发现自噬相关蛋白减少、线粒体膜电位降低,推测瘦素可损伤线粒体功能,抑制软骨细胞线粒体自噬。HUANG等[75]通过原代细胞培养实验发现软骨细胞经过瘦素干预后,瘦素可以剂量依赖性的方式刺激赖氨酰氧化酶样蛋白3(lysyl oxidase-like protein 3,LOXL3)的表达,而LOXL3又可通过mTOR信号通路抑制软骨细胞自噬。因此,瘦素可抑制软骨细胞自噬,促进骨关节炎的进展,但相关研究较少,其涉及的具体机制等还需进一步探究。
衰老:瘦素可使骨关节炎状态下的软骨细胞活性降低,诱导软骨细胞衰老。细胞衰老是指细胞无法增殖,其对软骨的稳态具有双重作用。在正常的软骨环境中,软骨细胞增殖能力较弱,而在关节损伤后,软骨细胞迅速增殖修复软骨,加速细胞衰老,促进骨关节炎的发生、发展。ZHAO等[55]收集骨关节炎患者胫骨平台内侧和外侧的软骨样本进行实验处理,发现高剂量瘦素可通过激活骨关节炎软骨细胞中的mTOR途径诱导软骨细胞发生衰老,另发现软骨中含有高表达的Ob-Rb,它可通过激活骨关节炎中的瘦素通路加速软骨细胞的衰老[3]。
凋亡:在软骨细胞中,其增殖和凋亡始终处于平衡状态,以维持软骨细胞的数量、功能及结构。而在骨关节炎中瘦素的参与下,这种平衡状态被打破,越来越多的证据表明瘦素可诱导软骨细胞凋亡。研究表明,在骨关节炎状态下,有18%-21%的软骨细胞出现凋亡,而在健康软骨中,软骨细胞凋亡为2%-5%,表明软骨细胞凋亡是骨关节炎病理状态中最重要的因素之一,瘦素作为促炎脂肪因子可通过激活NF-κB显著降低软骨细胞功能、诱导软骨细胞凋亡、表型丢失[39,76]。WANG等[77]发现瘦素处理后的软骨细胞可显著抑制双特异性蛋白磷酸酶19(dual specificity protein phosphatase 19,DUSP19)的表达,激活JNK通路,促进软骨细胞的凋亡。HUANG等[75]通过在软骨细胞中siRNA LOXL3后发现软骨细胞凋亡标志物显著减少,抗凋亡蛋白显著增加;而瘦素又可刺激LOXL3表达,证明了瘦素可诱导软骨细胞凋亡。WEI[78]在其原代软骨细胞培养实验中也得出了一致的结论。此外,相关研究发现瘦素与解偶联蛋白4呈负相关的关系,抑制解偶联蛋白4时,凋亡增加。HUANG等[79]的原代软骨细胞培养实验数据表明瘦素可通过下调解偶联蛋白4表达诱导活性氧依赖的细胞凋亡。
增殖:瘦素对软骨细胞增殖的影响至今仍不清晰,其对增殖过程的影响似乎是互相矛盾的。FIGENSCHAU等[63]用不同剂量瘦素处理软骨细胞4 d后,发现瘦素以双相方式影响软骨的增殖,在10-100 ng/mL范围内具有显著的刺激增殖作用。但另一项研究表示在相同的培养液中,瘦素可促进正常软骨细胞增殖,而抑制骨关节炎软骨细胞的增殖[80]。汪洋[81]将不同浓度的瘦素分别刺激软骨细胞不同的时间,CCK-8检测软骨细胞增殖情况,得出瘦素以剂量依赖性的方式抑制软骨细胞增殖的结论。因此,瘦素对软骨细胞发挥既增强又抑制的作用,但具体过程可能与局部微环境和自身情况有关[62]。
2.2.2 瘦素对骨关节炎软骨下骨的影响 相关研究表明瘦素与骨关节炎软骨下骨的骨重塑、骨赘形成紧密相关[82-83]。瘦素在软骨下骨中主要发挥双重调节作用,既可在外周组织中直接与成骨细胞和破骨细胞上的Ob-Rb结合起到增强成骨细胞的分化与增殖、降低破骨细胞活性发挥促进骨代谢的作用[83-85],也可在中枢系统中与下丘脑的Ob-Rb结合,间接影响成骨细胞和破骨细胞发挥骨代谢抑制作用。见图4。
(1)成骨细胞:瘦素可促进成骨细胞的增殖与分化。MUTABARUKA等[86]用骨关节炎患者和健康人软骨下骨进行细胞实验证明了成骨细胞表达瘦素与Ob-Rb,且在骨关节炎中表达水平更高。此外该团队还测定了碱性磷酸酶活性、骨钙素释放和转化生长因子β1、胰岛素样生长因子1水平,发现与正常成骨细胞相比,瘦素能显著刺激骨关节炎成骨细胞碱性磷酸酶活性,但对其他指标刺激不明显,而沉默RNA瘦素时,能抑制上述骨形成标志物与促骨生长相关因子参数指标。早前一项人原代成骨细胞实验发现当成骨细胞长期暴露于瘦素下可促进Ⅰ型胶原、转化生长因子β1表达和骨钙素的释放[87]。KALRA等[88]通过向小鼠单侧侧脑室注射瘦素的方法发现瘦素能通过下丘脑刺激成骨细胞增加骨钙素的释放。敲除小鼠瘦素基因会影响OPG/RANKL/RANK 信号通路,通过探究其机制可知,敲除瘦素后会抑制小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞向脂肪细胞的转化,诱导成骨基因的表达并促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化[89]。因此,瘦素可激发成骨细胞的增殖与分化,诱导骨形成标志物的产生,导致过度骨化。
在中枢神经系统中,瘦素与下丘脑Ob-Rb结合后通过β2肾上腺素能受体向成骨细胞传递信号,激活两个分子级联,c-myc和KA/ATF4/RANKL通路,而c-myc能抑制成骨细胞的增殖,KA/ATF4/RANKL通路可增强破骨细胞的骨吸收,因此,瘦素也能发挥骨代谢抑制作用 [90–92]。
(2)破骨细胞:瘦素可抑制破骨细胞的活性与增殖。目前已证明OPG/RANK/RANKL信号通路参与调控破骨细胞的形成。骨细胞可产生并分泌RANKL,RANKL与破骨细胞膜上的RANK结合,促进破骨细胞的形成;而破骨细胞抑制因子OPG可与RANKL竞争性结合RANK,从而降低RANK结合活性,抑制破骨细胞的形成。有小鼠实验表明瘦素能促进OPG mRNA、抑制RANKL mRNA表达,因此瘦素可通过对OPG、RANKL的影响抑制骨吸收[93-94]。BURGUERA等[95]通过动物模型实验发现瘦素可减少骨丢失率,进一步研究后提示瘦素可通过介导RANKL/OPG途径,抑制破骨细胞骨吸收功能,从而防治骨质疏松。
瘦素也可通过中枢介导的交感神经通路间接激活破骨细胞,促进骨吸收[96]。中枢5-羟色胺为一种与骨形成和骨吸收密切相关的神经递质,其可增强成骨细胞功能而抑制破骨[97]。YADAV等[98]动物实验研究发现瘦素缺乏的ob/ob小鼠,其大脑5-羟色胺表达增加,提示瘦素可能抑制5-羟色胺,从而促进骨吸收。故目前研究显示瘦素对破骨细胞也具有双重调节作用。
2.2.3 瘦素对骨关节炎滑膜组织的影响 近年来研究发现关节滑膜炎症也是骨关节炎发病的重要病理机制,其参与骨关节炎疾病的全程,通过炎症加剧软骨的破坏[99-100]。滑膜组织主要由巨噬细胞和成纤维细胞构成,瘦素可通过调控巨噬细胞与成纤维细胞功能介导骨关节炎炎症反应,加剧疼痛症状,促进骨关节炎的发生与进展。见图5。
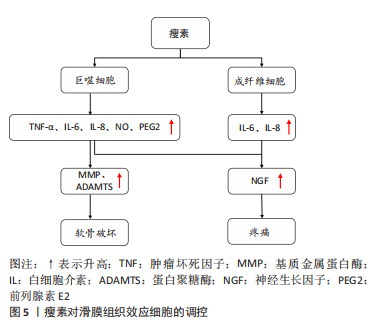
(1)巨噬细胞:作为固有免疫系统中重要细胞组分,巨噬细胞是促炎细胞因子(白细胞介素1、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6)合成和分泌的主要来源,见图5。LOFFREDA等[101]早先发现外源性瘦素可上调巨噬细胞的吞噬功能和促炎细胞因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6和白细胞介素8)的产生,加重滑膜的炎症反应。RASO等[102]细胞实验表明瘦素能以浓度依赖性方式显著增加巨噬细胞中的NO和前列腺素E2的生成。此外,相关研究表明瘦素可激活巨噬细胞中的JAK2-STAT3和PI3K-AKT-mTOR通路促进肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β分泌[103]。目前瘦素通过调控巨噬细胞功能影响骨关节炎的研究相对较少,但已证实瘦素可增强巨噬细胞吞噬作用,诱导促炎细胞因子生成[49]。而生成的这些炎性递质又可作用于疼痛关键分子——神经生长因子发挥作用[104]。神经生长因子为一种神经营养因子,可激活伤害性神经元,调控骨关节炎相关疼痛[105]。TAKANO 等[106]已证实在经过肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1β干预后,巨噬细胞中的神经生长因子表达明显增强。以上研究说明瘦素可调控巨噬细胞功能参与骨关节炎进程。
(2)成纤维细胞:成纤维细胞为滑膜组织的支撑细胞,与骨关节炎患者的滑膜炎症、关节疼痛、软骨分解破坏密切相关,瘦素对其的调控主要体现在促进炎性细胞因子(白细胞介素6、白细胞介素8)的生成上,见图5。PEARSON等[107]的人原代成纤维细胞实验表明来源于软骨细胞中的白细胞介素6可诱导滑膜成纤维细胞分泌白细胞介素6,而瘦素可增强软骨细胞和成纤维细胞这种相互介导的白细胞介素6炎症反应。XIONG等[34]测定了颞下颌关节骨关节炎患者和健康对照者滑膜液中瘦素及受体的水平,发现其滑膜成纤维细胞表达瘦素受体,瘦素通过激活JAK2/STAT3,P38/MAPK或PI3K/Akt信号通路与其受体结合刺激颞下颌关节成纤维细胞中的白细胞介素6 mRNA和蛋白表达。YANG等[108]采集8例骨关节炎患者的滑膜组织,分离人滑膜成纤维细胞后进行培养测定,证实瘦素与受体结合能激活IRS-1/PI3K/Akt信号通路,增强AP-1转录活性并以浓度和时间依赖性方式刺激成纤维细胞诱导白细胞介素6的反式激活。此外瘦素可通过同样通路诱导成纤维细胞中白细胞介素8的激活,以及通过经典通路JAK2和STAT3增加白细胞介素8的表达[109]。而分泌的这些炎症细胞因子又可刺激滑膜成纤维细胞分泌大量的神经生长因子,介导骨关节炎疼痛[104];诱导滑膜成纤维细胞产生蛋白水解酶(MMP、ADAMTS),进一步分解破坏软骨[104,110],以此来加重骨关节炎进展。

| [1] 中华医学会骨科学分会关节外科学组, 中国医师协会骨科医师分会骨关节炎学组, 国家老年疾病临床医学研究中心(湘雅医院), 等. 中国骨关节炎诊疗指南(2021年版)[J]. 中华骨科杂志,2021,41(18):1291-1314. [2] FAVERO M, EL-HADI H, BELLUZZI E, et al. Infrapatellar fat pad features in osteoarthritis: a histopathological and molecular study. Rheumatology. 2017;56(10):1784-1793. [3] XIE J, WANG Y, LU L, et al. Cellular senescence in knee osteoarthritis: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Ageing Res Rev. 2021;70:101413. [4] RICHARD D, LIU Z, CAO J, et al. Evolutionary Selection and Constraint on Human Knee Chondrocyte Regulation Impacts Osteoarthritis Risk. Cell. 2020;181(2):362-381.e28. [5] YAN M, ZHANG J, YANG H, et al. The role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Medicine. 2018;97(14):e0257. [6] MACDONALD I J, LIU S C, HUANG C C, et al. Associations between Adipokines in Arthritic Disease and Implications for Obesity. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(6):1505. [7] 龚凤英,吕枭锐. 瘦素的再认识[J].中华糖尿病杂志,2022,14(3):278-281. [8] MÜNZBERG H, SINGH P, HEYMSFIELD SB, et al. Recent advances in understanding the role of leptin in energy homeostasis. F1000Res. 2020;9: F1000 Faculty Rev-451. [9] SCOTECE M, MOBASHERI A. Leptin in osteoarthritis: Focus on articular cartilage and chondrocytes. Life Sci. 2015;140:75-78. [10] KU JH, LEE CK, JOO BS, et al. Correlation of synovial fluid leptin concentrations with the severity of osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28(12):1431-1435. [11] KING LK, HENNEICKE H, SEIBEL MJ, et al. Association of adipokines and joint biomarkers with cartilage-modifying effects of weight loss in obese subjects. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2015;23(3):397-404. [12] GANDHI R, TAKAHASHI M, SMITH H, et al. The synovial fluid. adiponectin-leptin ratio predicts pain with knee osteoarthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2010; 29(11):1223-1228. [13] ZHANG Y, PROENCA R, MAFFEI M, et al. Positional cloning of the mouse. obese gene and its human homologue. Nature. 1994;372(6505):425-432. [14] TARTAGLIA LA, DEMBSKI M, WENG X, et al. Identification and expression cloning of a leptin receptor, OB-R. Cell.1995;83(7):1263-1271. [15] LORD G M, MATARESE G, HOWARD JK, et al. Leptin modulates the T-cell immune response and reverses starvation-induced immunosuppression. Nature. 1998;394(6696):897-901. [16] SANTOS-ALVAREZ J, GOBERNA R, SÁNCHEZ-MARGALET V. Human leptin stimulates proliferation and activation of human circulating monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1999;194(1):6-11. [17] DUCY P, AMLING M, TAKEDA S, et al. Leptin inhibits bone formation through a hypothalamic relay: a central control of bone mass. Cell. 2000;100(2): 197-207. [18] GUALILLO O, EIRAS S, LAGO F, et al. Elevated serum leptin concentrations induced by experimental acute inflammation. Life Sci. 2000;67(20):2433-2441. [19] TIAN Z, SUN R, WEI H, et al. Impaired natural killer (NK) cell activity in leptin receptor deficient mice: leptin as a critical regulator in NK cell development and activation. Biochem Biophs Res Commun. 2002;298(3):297-302. [20] OTERO M, GOMEZ REINO JJ, GUALILLO O. Synergistic induction of nitric oxide synthase type II: in vitro effect of leptin and interferon-gamma in human chondrocytes and ATDC5 chondrogenic cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48(2):404-409. [21] CONDE J, GOMEZ R, BIANCO G, et al. Expanding the adipokine network in cartilage: identification and regulation of novel factors in human and murine chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(3):551-559. [22] CONDE J, SCOTECE M, LÓPEZ V, et al. Differential expression of adipokines in infrapatellar fat pad (IPFP) and synovium of osteoarthritis patients and healthy individuals. Ann Rheum Dis. 2014;73(3):631-633. [23] DODD GT, DECHERF S, LOH K, et al. Leptin and insulin act on POMC neurons to promote the browning of white fat. Cell. 2015;160(1-2):88-104. [24] XU J, BARTOLOME CL, LOW CS, et al. Genetic identification of leptin neural circuits in energy and glucose homeostases. Nature. 2018;556(7702):505-509. [25] WANG P, LOH KH, WU M, et al. A leptin-BDNF pathway regulating sympathetic innervation of adipose tissue. Nature. 2020;583(7818):839-844. [26] KRATOFIL RM, SHIM HB, SHIM R, et al. A monocyte-leptin-angiogenesis pathway critical for repair post-infection. Nature. 2022;609(7925):166-173. [27] LIN TC, HUANG KW, LIU CW, et al. Leptin signaling axis specifically associates with clinical prognosis and is multifunctional in regulating cancer progression. Oncotarget. 2018;9(24):17210-17219. [28] OTERO M, LAGO R, LAGO F, et al. Leptin, from fat to inflammation: old questions and new insights. FEBS Lett. 2005;579(2):295-301. [29] MASUZAKI H, OGAWA Y, HOSODA K, et al. Glucocorticoid Regulation of Leptin Synthesis and Secretion in Humans: Elevated Plasma Leptin Levels in Cushing’s Syndrome1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1997;82(8):2542-2547. [30] FAGGIONI R, FANTUZZI G, FULLER J, et al. IL-1β mediates leptin induction during inflammation. Am J Physiol-Reg I. 1998;274(1):R204-R208. [31] SARRAF P, FREDERICH RC, TURNER EM, et al. Multiple cytokines and acute inflammation raise mouse leptin levels: potential role in inflammatory anorexia. J Exp Med. 1997;185(1):171-175. [32] TU C, HE J, WU B, et al. An extensive review regarding the adipokines in the pathogenesis and progression of osteoarthritis. Cytokine. 2019;113:1-12. [33] MONTEIRO L, PEREIRA JADS, PALHINHA L, et al. Leptin in the regulation of the immunometabolism of adipose tissue-macrophages. J Leukoc Biol. 2019;106(3):703-716. [34] XIONG H, LI W, LI J, et al. Elevated leptin levels in temporomandibular joint osteoarthritis promote proinflammatory cytokine IL-6 expression in synovial fibroblasts. J Oral Pathol Med. 2019;48(3):251-259. [35] LAGO F, DIEGUEZ C, GÓMEZ-REINO J, et al. The emerging role of adipokines as mediators of inflammation and immune responses. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007;18(3-4):313-325. [36] PÉREZ-PÉREZ A, SÁNCHEZ-JIMÉNEZ F, VILARIÑO-GARCÍA T, et al. Role of Leptin in Inflammation and Vice Versa. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(16):5887. [37] CORDERO-BARREAL A, GONZÁLEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, RUIZ-FERNÁNDEZ C, et al. An Update on the Role of Leptin in the Immuno-Metabolism of Cartilage. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(5):2411. [38] 王春炅,张园,管又飞,等.瘦素在糖脂代谢中的调控作用[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报,2009,25(10):896-902. [39] AZAMAR-LLAMAS D, HERNANDEZ-MOLINA G, RAMOS-AVALOS B, et al. Adipokine Contribution to the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2017;2017:5468023. [40] JIANG M, HE J, SUN Y, et al. Leptin Induced TLR4 Expression via the JAK2-STAT3 Pathway in Obesity-Related Osteoarthritis. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:7385160. [41] YUSUF E, NELISSEN RG, IOAN-FACSINAY A, et al. Association. between weight or body mass index and hand osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Ann Rheum Dis. 2010;69(4):761-765. [42] GRIFFIN TM, HUEBNER JL, KRAUS VB, et al. Extreme obesity due to impaired leptin signaling in mice does not cause knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(10):2935-2944. [43] DUMOND H, PRESLE N, TERLAIN B, et al. Evidence for a key role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3118-3129. [44] SIMOPOULOU T, MALIZOS KN, ILIOPOULOS D, et al. Differential expression of leptin and leptin’s receptor isoform (Ob-Rb) mRNA between advanced and minimally affected osteoarthritic cartilage; effect on cartilage metabolism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(8):872-883. [45] VUOLTEENAHO K, KOSKINEN A, MOILANEN T, et al. Leptin levels are increased and its negative regulators, SOCS-3 and sOb-R are decreased in obese patients with osteoarthritis: a link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71(11):1912-1913. [46] GANDHI R, TAKAHASHI M, SYED K, et al. Relationship between body habitus and joint leptin levels in a knee osteoarthritis population. J Orthop Res. 2010;28(3):329-333. [47] ABELLA V, SCOTECE M, CONDE J, et al. Leptin in the interplay of inflammation, metabolism and immune system disorders. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2017;13(2): 100-109. [48] VERSINI M, JEANDEL PY, ROSENTHAL E, et al. Obesity in autoimmune diseases: not a passive bystander. Autoimmun Rev. 2014;13(9):981-1000. [49] WANG T, HE C. Pro-inflammatory cytokines: The link between obesity and osteoarthritis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2018;44:38-50. [50] SIEBUHR AS, PETERSEN KK, ARENDT-NIELSEN L, et al. Identification and characterisation of osteoarthritis patients with inflammation derived tissue turnover. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014;22(1):44-50. [51] THEOCHARIS AD, SKANDALIS SS, GIALELI C, et al. Extracellular matrix structure. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2016;97:4-27. [52] VERMA P, DALAL K. ADAMTS-4 and ADAMTS-5: key enzymes in osteoarthritis. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(12):3507-3514. [53] CHEN Y, WU Y, SHI H, et al. Melatonin ameliorates intervertebral disc degeneration via the potential mechanisms of mitophagy induction and apoptosis inhibition. J Cell Mol Med. 2019;23(3):2136-2148. [54] MA F, LI G, YU Y, et al. MiR-33b-3p promotes chondrocyte proliferation and inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis and cartilage ECM degradation by targeting DNMT3A in osteoarthritis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2019;519(2): 430-437. [55] ZHAO X, HUANG P, LI G, et al. Activation of the leptin pathway by high expression of the long form of the leptin receptor (Ob-Rb) accelerates chondrocyte senescence in osteoarthritis. Bone Joint Res. 2019;8(9):425-436. [56] SCOTECE M, CONDE J, LÓPEZ V, et al. Adiponectin and leptin: new targets in inflammation. Br J Pharmacol. 2014;114(1): 97-102. [57] FRANCISCO V, PINO J, ANGEL GONZALEZ-GAY M, et al. Adipokines and inflammation: is it a question of weight?. Br J Pharmacol. 2018;175(10): 1569-1579. [58] ILIOPOULOS D, MALIZOS KN, TSEZOU A. Epigenetic regulation of leptin affects MMP-13 expression in osteoarthritic chondrocytes: possible molecular target for osteoarthritis therapeutic intervention. Ann Rheum Dis. 2007;66(12):1616-1621. [59] KOSKINEN A, VUOLTEENAHO K, NIEMINEN R, et al. Leptin enhances MMP-1, MMP-3 and MMP-13 production in human osteoarthritic cartilage and correlates with MMP-1 and MMP-3 in synovial fluid from OA patients.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2011;29(1):57-64. [60] BAO JP, CHEN WP, FENG J, et al. Leptin plays a catabolic role on articular cartilage. Mol Biol Rep. 2010;37(7):3265-3272. [61] LAGO R, GÓMEZ R, LAGO F, et al. Leptin beyond body weight regulation-current concepts concerning its role in immune function and inflammation. Cell Immunol. 2008;252(1-2):139-145. [62] ZHANG S, ZHANG Y, WANG Y, et al. Effects of Leptin on Differentiation and Proliferation of Chondrocytes. J Hard Tissue Biol. 2019;28(1):51-56. [63] FIGENSCHAU Y, KNUTSEN G, SHAHAZEYDI S, et al. Human articular chondrocytes express functional leptin receptors. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2001;287(1):190-197. [64] SU YP, CHEN CN, HUANG KC, et al. Leptin induces MMP1/13 and ADAMTS 4 expressions through bone morphogenetic protein-2 autocrine effect in human chondrocytes. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(4):3716-3724. [65] GIARDULLO L, CORRADO A, MARUOTTI N, et al. Adipokine role in physiopathology of inflammatory and degenerative musculoskeletal diseases. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2021;35:20587384211015034. [66] LOESER RF. Systemic and local regulation of articular cartilage metabolism: where does leptin fit in the puzzle? Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3009-3012. [67] GOLDRING MB, GOLDRING SR. Osteoarthritis. J Cell Physiol. 2007;213(3): 626-634. [68] VUOLTEENAHO K, KOSKINEN A, MOILANEN E. Leptin - a link between obesity and osteoarthritis. applications for prevention and treatment. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol. 2014;114(1):103-108. [69] CORTIAL D, GOUTTENOIRE J, ROUSSEAU CF, et al. Activation by IL-1 of bovine articular chondrocytes in culture within a 3D collagen-based scaffold. An in vitro model to address the effect of compounds with therapeutic potential in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2006;14(7):631-640. [70] CONDE J, SCOTECE M, LÓPEZ V, et al. Adiponectin and leptin induce VCAM-1 expression in human and murine chondrocytes. PloS One. 2012; 7(12):e52533. [71] GÓMEZ R, SCOTECE M, CONDE J, et al. Adiponectin and leptin increase IL-8 production in human chondrocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 2011;70(11):2052-2054. [72] VUOLTEENAHO K, KOSKINEN A, KUKKONEN M, et al. Leptin enhances synthesis of proinflammatory mediators in human osteoarthritic cartilage--mediator role of NO in leptin-induced PGE2, IL-6, and IL-8 production. Mediators Inflamm. 2009;2009:345838. [73] 王欢欢,王青,唐鹏,等.体外冲击波干预骨关节炎大鼠软骨细胞的增殖和自噬[J].中国组织工程研究,2023,27(2):252-257. [74] 运行,魏钰,魏民.瘦素对骨关节炎中软骨细胞线粒体自噬状态的影响[J].解放军医学院学报,2021,42(5):555-559. [75] HUANG ZM, DU SH, HUANG LG, et al. Leptin promotes apoptosis and inhibits autophagy of chondrocytes through upregulating lysyl oxidase-like 3 during osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(7):1246-1253. [76] HÉRAUD F, HÉRAUD A, HARMAND MF. Apoptosis in normal and osteoarthritic human articular cartilage. Ann Rheum Dis. 2000;59(12):959-965. [77] WANG Y, XU Z, WANG J, et al. DUSP19, a downstream effector of leptin, inhibits chondrocyte apoptosis via dephosphorylating JNK during osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Mol Biosyst. 2016;12(3):721-728. [78] WEI Q. Apoptosis Activation and Autophagy Inhibition of Chondrocytes by Leptin by the Upregulation of LOXL3 in Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis. J Healthc Eng. 2022;2022:4026128. [79] HUANG Z, LI J, DU S, et al. Effects of UCP4 on the Proliferation and Apoptosis of Chondrocytes: Its Possible Involvement and Regulation in Osteoarthritis. PLOS ONE. 2016;11(3):e0150684. [80] SIMOPOULOU T, MALIZOS KN, ILIOPOULOS D, et al. Differential expression of leptin and leptin’s receptor isoform (Ob-Rb) mRNA between advanced and minimally affected osteoarthritic cartilage; effect on cartilage metabolism. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2007;15(8):872-883. [81] 汪洋.DUSP19通过NF-κB/MAPKs通路参与骨关节炎的机制研究[D].上海:第二军医大学,2017. [82] AIT ELDJOUDI D, CORDERO BARREAL A, GONZALEZ-RODRÍGUEZ M, et al. Leptin in Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis: Player or Bystander?. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(5):2859. [83] STEPPAN CM, CRAWFORD DT, CHIDSEY-FRINK KL, et al. Leptin is a potent stimulator of bone growth in ob/ob mice. Regul Pept. 2000;92(1-3):73-78. [84] CORNISH J, CALLON KE, BAVA U, et al. Leptin directly regulates bone cell function in vitro and reduces bone fragility in vivo. J Endocrinol. 2002; 175(2):405-415. [85] ELMQUIST JK, STREWLER GJ. Physiology: do neural signals remodel bone?. Nature. 2005;434(7032):447-448. [86] MUTABARUKA MS, AOULAD AISSA M, DELALANDRE A, et al. Local leptin production in osteoarthritis subchondral osteoblasts may be responsible for their abnormal phenotypic expression. Arthritis Res Ther. 2010;12(1):R20. [87] GORDELADZE JO, DREVON CA, SYVERSEN U, et al. Leptin stimulates human osteoblastic cell proliferation, de novo collagen synthesis, and mineralization: Impact on differentiation markers, apoptosis, and osteoclastic signaling. J Cell Biochem. 2002;85(4):825-836. [88] KALRA SP, DUBE MG, IWANIEC UT. Leptin increases osteoblast-specific osteocalcin release through a hypothalamic relay. Peptides. 2009;30(5): 967-973. [89] 陆鹏程,刘波,金圣杰,等.下丘脑:运动改善骨代谢的关键控制器[J].中国组织工程研究,2022,26(32):5201-5208. [90] TAKEDA S, ELEFTERIOU F, LEVASSEUR R, et al. Leptin regulates bone formation via the sympathetic nervous system. Cell. 2002;111(3):305-317. [91] FU L, PATEL MS, BRADLEY A, et al. The molecular clock mediates leptin-regulated bone formation. Cell. 2005;122(5):803-815. [92] XIE C, CHEN Q. Adipokines: New Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis?. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2019;21(12):71. [93] MAO Z, ZHU Y, HAO W, et al. MicroRNA-155 inhibition up-regulates LEPR to inhibit osteoclast activation and bone resorption via activation of AMPK in alendronate-treated osteoporotic mice. IUBMB life. 2019;71(12):1916-1928. [94] MAGGI S, SIVIERO P, BROCCO E, et al. Vitamin D deficiency, serum leptin and osteoprotegerin levels in older diabetic patients: an input to new research avenues. Acta Diabetol. 2014;51(3):461-469. [95] BURGUERA B, HOFBAUER LC, THOMAS T, et al. Leptin reduces ovariectomy-induced bone loss in rats. Endocrinology. 2001;142(8):3546-3553. [96] ARMAIZ-FLORES SA, KELLY NR, GALESCU OA, et al. Evaluating Weight Status and Sex as Moderators of the Association of Serum Leptin with Bone Mineral Density in Children and Adolescents. Horm Res Paediatr. 2017; 87(4):233-243. [97] 柏茂盛,薛凯文,赵建宁.5-HT对骨代谢作用机制的研究进展[J].医学研究生学报,2018,31(11):6. [98] YADAV VK, OURY F, SUDA N, et al. A serotonin-dependent mechanism explains the leptin regulation of bone mass, appetite, and energy expenditure. Cell. 2009;138(5):976-989. [99] 曹建刚,陈德生.骨关节炎中的滑膜巨噬细胞作用与特点[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(29):4731-4736. [100] DUMOND H, PRESLE N, TERLAIN B, et al. Evidence for a key role of leptin in osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2003;48(11):3118-3129. [101] LOFFREDA S, YANG SQ, LIN HZ, et al. Leptin regulates proinflammatory immune responses. FASEB J. 1998;12(1):57-65. [102] RASO GM, PACILIO M, ESPOSITO E, et al. Leptin potentiates IFN-gamma-induced expression of nitric oxide synthase and cyclo-oxygenase-2 in murine macrophage J774A.1. Br J Pharmacol. 2002;137(6):799-804. [103] DICKSON BM, ROELOFS AJ, ROCHFORD JJ, et al. The burden of metabolic syndrome on osteoarthritic joints. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019;21(1):289. [104] 叶小康,白自然,金敏丽,等.滑膜细胞在骨关节炎中的研究进展[J].生物化学与生物物理进展,2021,48(11):1282-1289. [105] WISE BL, SEIDEL MF, LANE NE. The evolution of nerve growth factor inhibition in clinical medicine. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2021;17(1):34-46. [106] TAKANO S, UCHIDA K, INOUE G, et al. Nerve growth factor regulation and production by macrophages in osteoarthritic synovium. Clin Exp Immunol. 2017;190(2):235-243. [107] PEARSON MJ, HERNDLER-BRANDSTETTER D, TARIQ MA, et al. IL-6 secretion in osteoarthritis patients is mediated by chondrocyte-synovial fibroblast cross-talk and is enhanced by obesity. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):3451. [108] YANG WH, LIU SC, TSAI CH, et al. Leptin induces IL-6 expression through OBRl receptor signaling pathway in human synovial fibroblasts. PloS One. 2013;8(9):e75551. [109] TONG KM, SHIEH DC, CHEN CP, et al. Leptin induces IL-8 expression via leptin receptor, IRS-1, PI3K, Akt cascade and promotion of NF-kappaB/p300 binding in human synovial fibroblasts. Cell Signal. 2008;20(8):1478-1488. [110] ZHENG W, ZHANG H, JIN Y, et al. Butein inhibits IL-1β-induced inflammatory response in human osteoarthritis chondrocytes and slows the progression of osteoarthritis in mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;42:1-10. |
| [1] | 孙可欣, 曾今实, 李佳, 蒋海越, 刘霞. 力学刺激提高生物3D打印软骨构建物基质的形成[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(在线): 1-7. |
| [2] | 李晓敏, 田向东 , 谭冶彤 , 朱光宇 , 王荣田 , 王 剑 , 薛志鹏, 马 晟, 胡元一, 黄 叶, 丁天送. 骨质疏松性内侧室膝骨关节炎胫骨高位截骨后下肢力线及膝关节功能的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(9): 1325-1329. |
| [3] | 黄林科, 韦林华, 蒋 捷, 刘 倩, 陈蔚蔚. 雌激素与跑台运动干预卵巢切除模型小鼠骨量和关节软骨的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(8): 1166-1171. |
| [4] | 李 诚, 郑国爽, 蒯贤东, 于炜婷. 海藻酸盐支架修复关节软骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(7): 1080-1088. |
| [5] | 袁长深, 官岩兵, 李 哲, 容伟明, 廖书宁, 陈乐伟, 梅其杰, 段 戡. 骨关节炎坏死性凋亡关键基因的筛选与验证[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(5): 695-700. |
| [6] | 谷明西, 王 博, 田丰德, 安 宁, 郝瑞胡, 王常成, 郭 林. 同期和分期双侧全膝关节置换的早期疗效和安全性比较[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(4): 565-571. |
| [7] | 郭颖奇, 宫先旭, 张 岩, 肖 寒, 王 野, 谷文光. 半月板外突与髌股关节软骨损伤及骨髓病变:MRI半定量评分的评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(4): 600-605. |
| [8] | 张 辉, 王佳洋, 王 茜, 甘洪全, 王志强. 动态培养环境下透明质酸与国产多孔钽复合对软骨细胞功能的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(3): 339-345. |
| [9] | 马 威, 庞 坚, 张洁帆, 许 坤, 王用玉, 张 旻, 陈 博, 石 瑛, 詹红生. 膝骨关节炎患者跌倒恐惧影响因素分析及列线图模型构建[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4690-4695. |
| [10] | 陈 财, 曾 平, 刘金富. 介导软骨细胞相关机制调控骨性关节炎的长链非编码RNA[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4729-4735. |
| [11] | 韦宗波, 苏允裕, 章晓云, 黄 为, 许 航, 刘荣发. 长链非编码RNA调控膝骨关节炎中软骨下骨稳态的作用与机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4736-4744. |
| [12] | 周广智, 邰东旭. 踝关节骨关节炎动物模型构建的研究与进展[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4745-4750. |
| [13] | 陈昌美, 曾宪春, 王荣品, 吴家红. X射线评价正常膝关节解剖学参数的性别及年龄差异[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4647-4651. |
| [14] | 黎少聪, 何 琪, 潘兆丰, 杨均政, 陈柏豪, 王海彬, 周 驰. Micro-CT评价铁超载影响膝骨关节炎模型小鼠软骨类组织的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(29): 4658-4663. |
| [15] | 卢 钰, 向俊宜, 尹本敬, 保超宇, 毕 衡, 李骥征, 陈 帅, 何光雄, 李具宝. 斜扳手法治疗腰椎小关节滑膜嵌顿的有限元分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2023, 27(27): 4271-4276. |
瘦素是由一种由脂肪和软骨等组织产生的多效性肽激素[5],早期研究发现其主要作用于中枢系统,发挥能量代谢的效应[6]。现研究发现瘦素还具有激素和细胞因子的双重作用,可作用于下丘脑中背内侧核、视前区、室旁核、腹侧内侧核、弓状核及下丘脑外区域,参与调控炎症反应、免疫稳态、软骨和骨代谢、骨形成、血管生成、伤口愈合、肠道营养吸收等多个进程[7-8]。虽然骨关节炎的发病机制尚不清楚,但目前研究已证实瘦素与骨关节炎相关,其在骨关节炎的进展中发挥着重要作用[9],例如滑膜液瘦素水平与骨关节炎患者的放射影像学病理严重程度[10]、基质金属蛋白酶(metalloproteinase 1,MMP)1和MMP-3水平[11]、膝关节和髋关节疼痛评分呈正相关[12]。该文主要从骨关节炎受累关节组织角度,综述了瘦素对骨关节炎不同组织效应细胞的调控作用,旨在通过探析瘦素对骨关节炎软骨、软骨下骨、滑膜效应细胞的调控作用及机制,为以瘦素为靶点的骨关节炎相关研究提供思路与借鉴。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
1.1.1 检索人及检索时间 由第一作者在2022年5月进行检索。
1.1.2 检索文献时限 各数据库建库至2022年5月。
1.1.3 检索数据库 PubMed、Web of Science、CNKI(中国知网)、cqVIP(维普资讯网)、万方全文数据库。
1.1.4 检索词 中文检索词为“瘦素、LP、Ob蛋白质、肥胖蛋白质、骨关节炎、OA、退行性骨关节炎、骨关节病、变形骨关节炎”。英文检索词为“leptin、Obese Protein、Obese Gene Product、
Gene Product,Obese、Ob Gene Product、Gene Product,Ob、Ob Protein、Osteoarthritis、OA、Osteoarthritides、Osteoarthrosis、Osteoarthroses、Arthritis,Degenerative、Arthritides,Degenerative、Degenerative Arthritides、Degenerative Arthritis、Arthrosis、Arthroses、Osteoarthrosis Deformans”。
1.1.5 检索文献类型 综述类、评述类、临床实验、动物实验类。
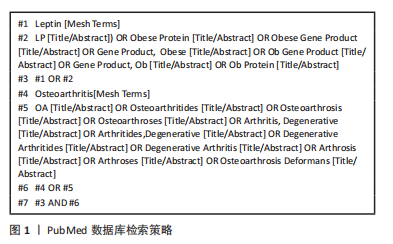
1.1.6 检索策略 以 PubMed 数据库为例,检索策略见图1。此外,还通过手动检索上述检索策略未纳入、但其内容与文章主题契合的文献和书籍。
1.2 纳入标准 涉及瘦素对骨关节炎疾病影响的相关文献。
1.3 排除标准 ①重复性高、与主题相关性低的文献;②逻辑严谨性低且可信度差的文献。
1.4 资料整合 共检索到1 424篇文献,排除与研究目的不相关、重复性以及观点陈旧性文献,最终纳入110篇符合标准的文献进行综述,见图2。
其次研究较多的是瘦素对软骨下骨的调控作用。破骨细胞和成骨细胞是骨组织代谢的基本功能细胞,二者通过吸收旧骨及形成新骨保持骨量的动态平衡。瘦素可通过调控成骨细胞和破骨细胞打破骨代谢平衡,影响软骨下骨骨重塑,导致骨赘的形成。目前瘦素对成骨细胞影响研究较多,而对破骨细胞的效应探析还在研究中。
在该文综述的三大块组织中,瘦素对骨关节炎滑膜组织细胞的调控研究相对较少,其一直未受重视,而对类风湿关节炎滑膜免疫细胞和基质细胞研究相对较多,其中可能与两者主要病理情况有关,近年来研究发现滑膜病变在骨关节炎发生发展中也发挥着关键作用,虽滑膜炎症不能直接诱发骨关节炎的发生,但其参与了骨关节炎的所有阶段。目前瘦素对骨关节炎滑膜组织的成纤维细胞的调控研究主要在发现某种信号通路激活及促进相关炎症因子的释放方面,对巨噬细胞的调控为介导免疫反应及炎症调节,而骨关节炎涉及的关节滑膜部位众多,未来研究应涉及多个关节滑膜,观察瘦素是否对所有骨关节炎滑膜影响相同并找寻其规律。此外滑膜组织包含细胞众多,其中也包括脂肪细胞,本身可产生瘦素,其产生的瘦素对骨关节炎的影响程度也可进一步探究。
3.2 作者综述区别于他人他篇的特点 瘦素是由脂肪组织合成的一种多效性脂肪因子和肽激素,最初被认为主要发挥食欲调节和能量平衡的作用。最新研究表明,瘦素可参与调控骨关节炎的发生发展过程,近年来获得了越来越多学者的关注,发表了大量的论文。国内暂无相关系统总结。
3.3 综述的局限性 文章的局限在于只综述了瘦素对软骨、软骨下骨及滑膜主要效应细胞的影响,而骨关节炎中其他受累组织例如髌下脂肪垫、周围韧带、肌肉等和滑膜组织其他细胞如肥大细胞、脂肪细胞及关节液中的相关免疫细胞还未涉及到。骨关节炎是一个复杂的疾病,瘦素对其作用的具体机制还需进一步明确,临床数据的不足也是其领域的一大缺陷,因此大量的基础通路研究、细胞组织研究及临床真实世界研究仍是探索以瘦素为骨关节炎治疗靶点的未来一大突破口。
3.4 综述的重要意义及课题专家组对未来的建议 该文系统梳理国内外相关研究及目前进展,旨在为后期研究提供相关参考。瘦素兼具调控主要病变组织细胞功能及影响机体代谢的多重作用,在大量炎症性及代谢性疾病的发病中占有重要地位。骨关节炎作为一种常见的炎症性疾病,动物实验及细胞层面的相关研究数据表明瘦素与骨关节炎发病机制相关。因此,瘦素未来有望成为骨关节炎预后生物标记物及治疗的潜在靶点。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程

文题释义:
瘦素:是一种由白色脂肪组织分泌的蛋白质荷尔蒙,编码基因ob,位于人类的第七号染色体上,由167个氨基酸构成,大小为16 kD。瘦素具有广泛的生物学效应,早期研究发现其主要作用于下丘脑的代谢调节中枢,发挥抑制食欲、增加能量消耗、抑制脂肪合成的作用,现研究发现其还具有参与调控炎症反应、免疫稳态、软骨和骨代谢、血管生成、造血(血细胞的形成)、细胞增殖等多个进程。效应细胞:是指对刺激产生相应反应并发生改变的一类细胞。效应细胞包括成纤维细胞、肥大细胞、浆细胞、效应T细胞、软骨细胞、小胶质细胞等。此文所研究的成纤维细胞,为滑膜组织的支撑细胞,在瘦素的影响下可发生促炎反应;而软骨细胞为人体软骨内唯一的细胞,瘦素可对其促炎、自噬、凋亡、增殖等方面起到调控作用。
瘦素是由一种由脂肪和软骨等组织产生的多效性肽激素,早期研究发现其主要作用于中枢系统,发挥能量代谢的效应。现研究发现瘦素还具有激素和细胞因子的双重作用,可作用于下丘脑中背内侧核,视前区、室旁核、腹侧内侧核、弓状核及下丘脑外区域,参与调控炎症反应、免疫稳态、软骨和骨代谢、骨形成、血管生成、伤口愈合、肠道营养吸收等多个进程。虽然骨关节炎的发病机制尚不清楚,但目前研究已证实瘦素与骨关节炎相关,其在骨关节炎的进展中发挥着重要作用。本文主要从骨关节炎受累关节组织角度,综述了瘦素对骨关节炎不同组织效应细胞的调控作用,旨在通过探析瘦素对骨关节炎软骨、软骨下骨、滑膜效应细胞的调控作用及机制,为以瘦素为靶点的骨关节炎相关研究提供思路与借鉴。
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||