中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (27): 4381-4386.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1389
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
乌头汤对膝骨关节炎模型大鼠滑膜组织TLR4/NF-κB信号通路的影响
陈 俊1,林 洁2,赵忠胜2,黄艳峰2,吴广文3
- (1福建中医药大学中西医结合学院,福建省福州市 350122;2福建中医药大学中西医结合研究院,福建省福州市 350122;3福建省中西医结合老年性疾病重点实验室,福建省福州市 350122)
Effect of Wutou Decoction on TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway in synovial tissue of rat models with knee osteoarthritis
Chen Jun1, Lin Jie2, Zhao Zhongsheng2, Huang Yanfeng2, Wu Guangwen3
- (1College of Integrative Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 2Academy of Integrative Medicine, Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China; 3Fujian Provincial Key Laboratory of Integrative Medicine on Geriatrics, Fuzhou 350122, Fujian Province, China)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
.jpg) 文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。摘要
背景:前期研究表明乌头汤可有效抑制膝骨关节炎炎症反应,但具体机制尚不明确。
目的:观察乌头汤对膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜组织TLR4/NF-κB通路相关调节因子的影响,探讨乌头汤治疗膝骨关节炎的作用机制。
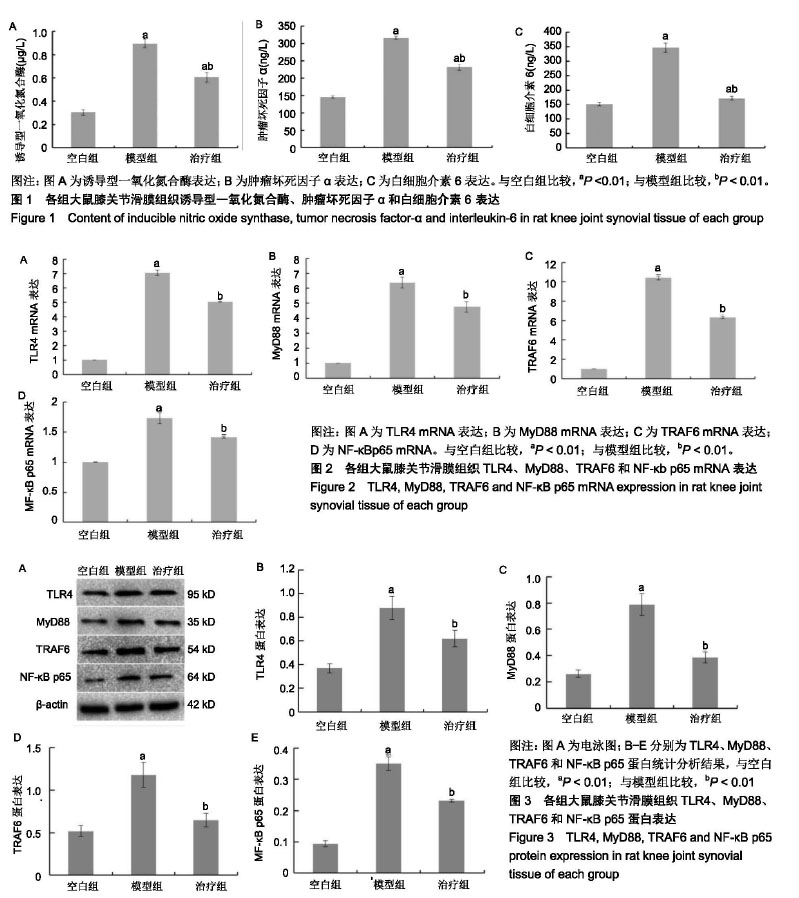
方法:SPF级雄性SD大鼠36只,购自上海斯莱克实验动物有限责任公司。实验方案经福建中医药大学动物实验伦理委员会批准。大鼠适应性喂养1周后,采用随机数字表法分为空白组、模型组和治疗组。模型组和治疗组均采用改良Hulth法复制双膝膝骨关节炎模型,术后1周空白组和模型组给予生理盐水,按照 10 mL/(kg•d)的量进行灌胃;治疗组给予乌头汤,按照4.2 g/(kg•d)的药量进行灌胃。治疗8周后,取大鼠膝关节滑膜组织。ELISA法检测诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6含量变化;Real-time PCR法检测TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6和NF-κB p65 mRNA表达;Western blot法检测TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6和NF-κB p65蛋白表达。
结果与结论:①ELISA结果显示,与模型组相比,乌头汤可有效抑制诱导型一氧化氮合酶、肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素6表达(P < 0.01);②Real-time PCR结果表明,乌头汤能抑制TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6和NF-κB p65 mRNA表达(P < 0.01);③Western blot结果与Real-time PCR结果趋势一致,即乌头汤能抑制TLR4、MyD88、TRAF6和NF-κB p65蛋白表达(P < 0.01);④结果提示,乌头汤可通过调控TLR4/NF-κB信号通路,抑制膝骨关节炎滑膜炎症反应,从而起到治疗膝骨关节炎作用。
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。
文题释义:
TLR4/NF-κB信号通路:MyD88是TLR4信号通路中重要的衔接蛋白,TLR4的结构域与MyD88的同源结构域相结合,活化MyD88,进而引起IRAK自磷酸化,磷酸化的IRAK与肿瘤坏死因子受体相关因子6(TRAF6)相互作用形成复合物,促使NIK活化,进而活化IKK,降解ⅠκB,释放转录因子NF-κB(如NF-κB p65),由胞质转位到核内,刺激各种细胞因子等的表达。NF-κB是一种与炎症因子产生、细胞增殖、细胞外基质交联和细胞凋亡密切相关的转录因子,参与多种炎症的信号转导,在细胞中最常见的作用形式为NF-κB p65及NF-κB p50。
乌头汤:乌头汤出自《金匮要略》,由麻黄、芍药、黄芪、甘草、川乌组成,具有散寒祛湿、除痹止痛之功,可有效缓解寒湿痹阻型膝骨关节炎患者临床症状。