中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (18): 2879-2887.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2641
• 骨与关节循证医学 evidence-based medicine of the bone and joint • 上一篇 下一篇
穴位注射改善膝骨关节炎患者疼痛及关节功能的Meta分析
邓凯烽1,尚鑫阳1,朱圣旺1,李书振2,朱 英2,陈日兰2
- 1广西中医药大学,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530001;2广西中医药大学附属瑞康医院,广西壮族自治区南宁市 530011
Meta-analysis of the effect of acupoint injection on pain
improvement and joint function in patients with knee osteoarthritis
Deng Kaifeng1, Shang Xinyang1, Zhu Shengwang1, Li Shuzhen2, Zhu Ying2, Chen Rilan2
- 1Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Ruikang Hospital Affiliated to Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530011, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China
摘要:

文题释义:
穴位注射法:将药液注入穴位使药物直接应用于穴位,既发挥药物作用又能发挥经络传导的作用,通过药物刺激调节人体经络系统,达到舒筋通络的作用。
膝骨关节炎:又称为膝关节增生性关节炎、退行性膝关节炎,是中老年人常见的一种慢性骨关节病,主要病理特点为关节软骨退变、破坏、软骨下骨硬化、关节边缘软骨下骨增生,进而引起滑膜炎症、半月板损伤、游离体形成及关节外组织炎症等一系列病变,临床症状以膝关节的疼痛、肿胀、变形及活动受限为主。
背景:大量临床研究显示,穴位注射治疗膝骨关节炎具有治疗效果好、不良反应少等优点,但当前穴位注射治疗该病缺乏多中心大样本的临床研究试验。
目的:应用Meta分析法系统评价穴位注射疗法对膝骨关节炎患者疼痛改善及关节功能的影响。
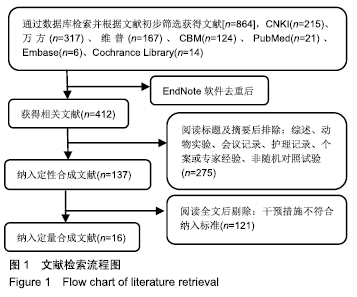
方法:检索中国知网、万方数据库、维普数据库、中国生物医学文献数据库、PubMed、Embase及Cochrane Library等数据库中自建库以来至2019年5月有关穴位注射治疗膝骨关节炎的临床随机对照试验,观察组为穴位注射或穴位注射联合其他疗法,对照组为不同于穴位注射疗法的其他治疗方法,检索语言中、英文不限,筛选后使用Review
Manager 5.3软件提取文献数据进行Meta分析。
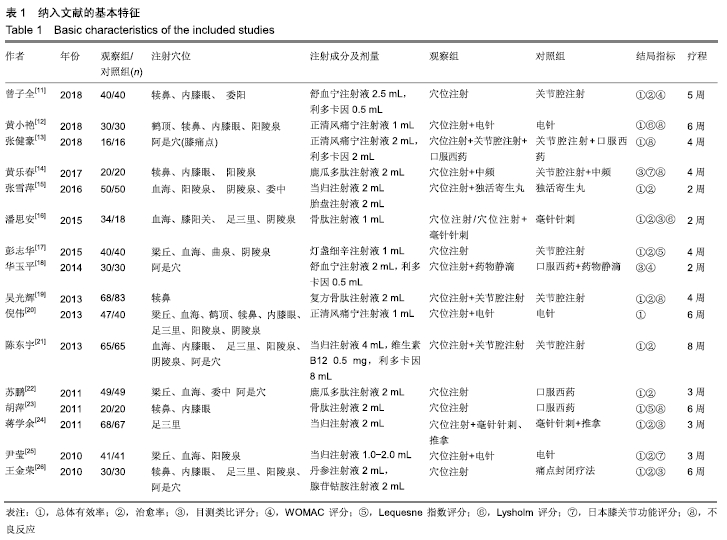
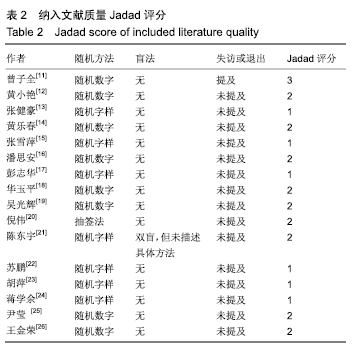
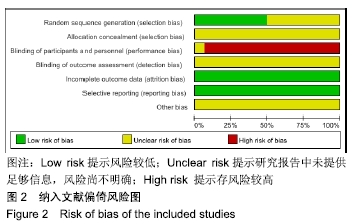
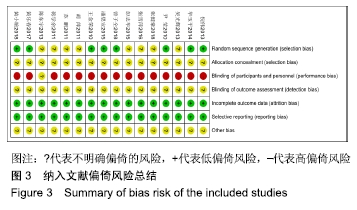
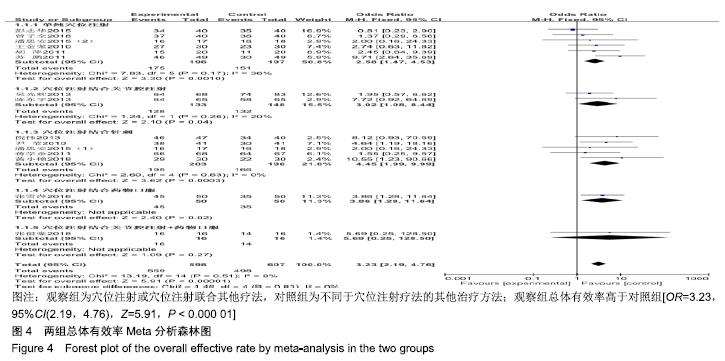
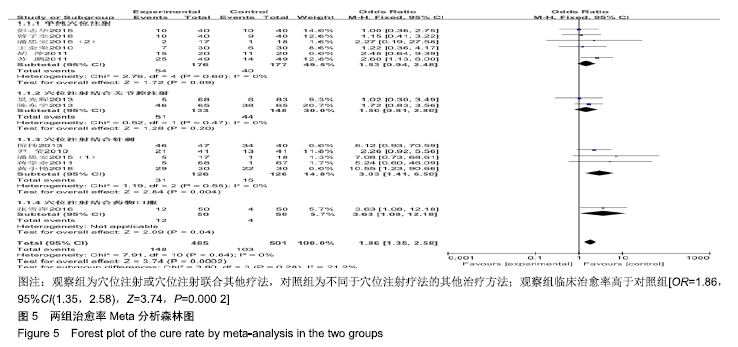
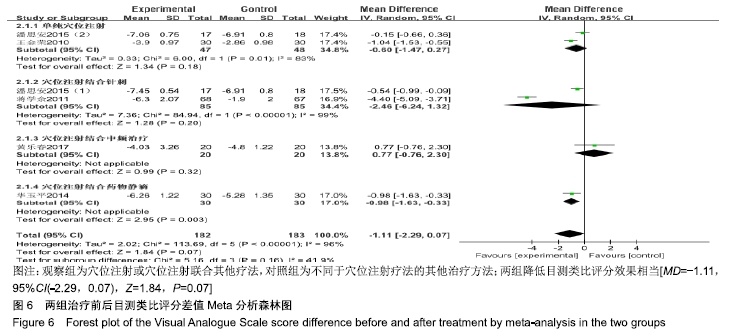
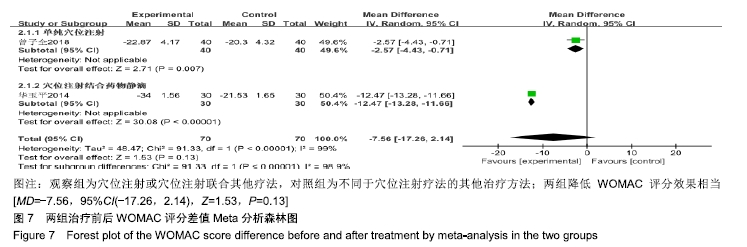
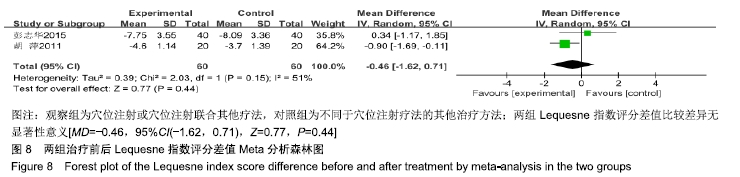
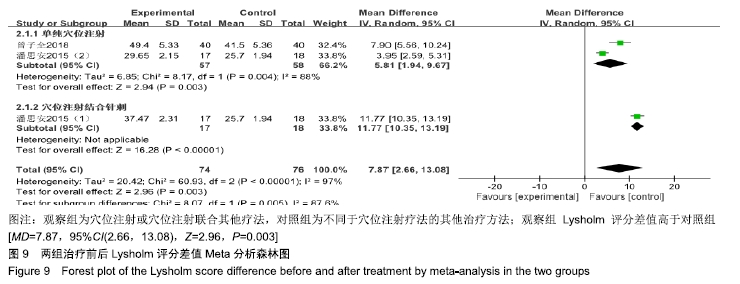
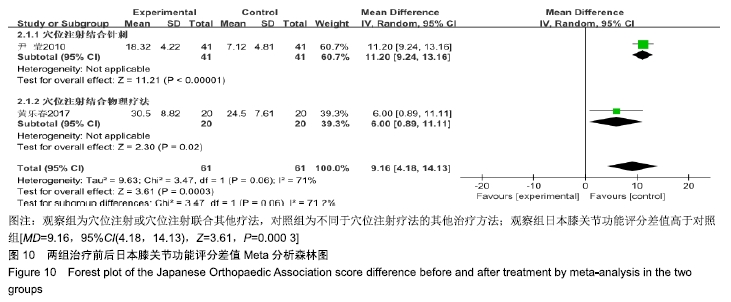
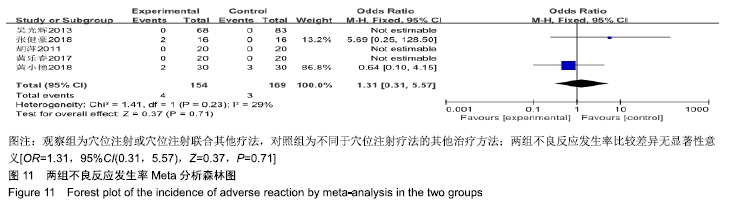
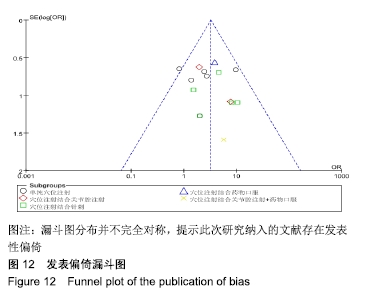
结果与结论:①共纳入16篇随机对照试验,涉及患者1 287例,其中观察组648例,对照组639例;②Meta分析显示,观察组的总体有效率、治愈率、Lysholm评分、日本膝关节功能评分均高于对照组[OR=3.23,95%CI(2.19,4.76),Z=5.91,P < 0.000 01;OR=1.86,95%CI(1.35,2.58),Z=3.74,P=0.000 2;MD=7.87,95%CI(2.66,13.08),Z=2.96,P=0.003;MD=9.16,95%CI(4.18,14.13),Z=3.61,P=0.000 3],两组目测类比评分、WOMAC评分、Lequesne指数及不良反应发生率比较差异均无显著性意义[MD=-1.11,95%CI(-2.29,0.07),Z=1.84,P=0.07;MD=-7.56,95%CI(-17.26,2.14),Z=1.53,P=0.13;MD=-0.46,95%CI(-1.62,0.71),Z=0.77,P=0.44;OR=1.31,95%CI(0.31,5.57),Z=0.37,P=0.71];③结果表明穴位注射治疗膝骨关节炎的疗效确切,但由于纳入研究的文献质量普遍不高及可能存在偏倚等因素,仍需更多更高质量的随机对照试验来验证结论。
ORCID: 0000-0002-7859-7850(邓凯烽)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号: