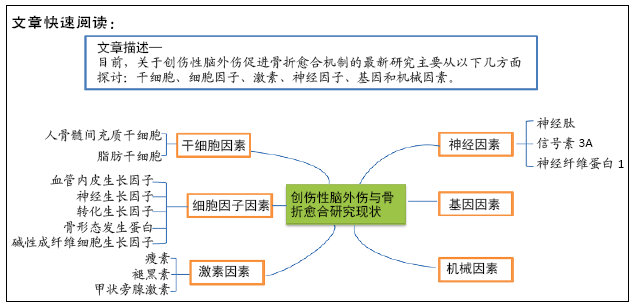
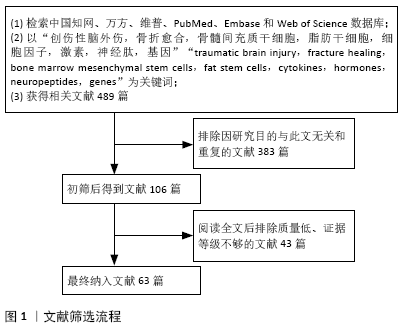
[1] ROBERTS PH. Heterotopic ossification complicating paralysis of intracranial origin. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1968;50-B(1):70-77.
[2] KHAN SN, DURAINE G, VIRK SS, et al. The temporal role of leptin within fracture healing and the effect of local application of recombinant leptin on fracture healing. J Orthop Trauma. 2013;27(11):656-662.
[3] BRADY RD, GRILLS BL, CHURCH JE, et al. Closed head experimental traumatic brain injury increases size and bone volume of callus in mice with concomitant tibial fracture. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34491.
[4] BARGELLESI S, CAVASIN L, SCARPONI F, et al. Occurrence and predictive factors of heterotopic ossification in severe acquired brain injured patients during rehabilitation stay: cross-sectional survey. Clin Rehabil. 2018;32(2):255-262.
[5] TSITSILONIS S, SEEMANN R, MISCH M, et al. The effect of traumatic brain injury on bone healing: an experimental study in a novel in vivo animal model. Injury. 2015;46(4):661-665.
[6] ANTHONISSEN J, STEFFEN CT, ALESSANDRI B, et al. Traumatic brain injury enhances the formation of heterotopic ossification around the hip: an animal model study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2020; 140(8):1029-1035.
[7] ARIK M, EKINCI Y, GÜRBÜZ K, et al. The effects of focal brain damage on fracture healing: An experimental rat study. Eklem Hastalik Cerrahisi. 2019;30(3):267-274.
[8] LIN W, XU L, ZWINGENBERGER S, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells homing to improve bone healing. J Orthop Translat. 2017;9:19-27.
[9] CHOU YF, ZUK PA, CHANG TL, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells and BMP2: part 1. BMP2-treated adipose-derived stem cells do not improve repair of segmental femoral defects. Connect Tissue Res. 2011;52(2):109-118.
[10] MIZUNO D, AGATA H, FURUE H, et al. Limited but heterogeneous osteogenic response of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to bone morphogenetic protein-2 and serum. Growth Factors. 2010;28(1):34-43.
[11] ZUK P, CHOU YF, MUSSANO F, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells and BMP2: part 2. BMP2 may not influence the osteogenic fate of human adipose-derived stem cells. Connect Tissue Res. 2011;52(2):119-132.
[12] MADHU V, LI CJ, DIGHE AS, et al. BMP-non-responsive Sca1+ CD73+ CD44+ mouse bone marrow derived osteoprogenitor cells respond to combination of VEGF and BMP-6 to display enhanced osteoblastic differentiation and ectopic bone formation. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e103060.
[13] WEI FY, LEUNG KS, LI G, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound enhanced mesenchymal stem cell recruitment through stromal derived factor-1 signaling in fracture healing. PLoS One. 2014;9(9):e106722.
[14] HONG D, CHEN HX, GE R, et al. Genetically engineered mesenchymal stem cells: The ongoing research for bone tissue engineering. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2010;293(3):531-537.
[15] BOES M, KAIN M, KAKAR S, et al. Osteogenic effects of traumatic brain injury on experimental fracture-healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(4):738-743.
[16] CAO H, SUN ZB, ZHANG L, et al. Adenovirus-mediated bone morphogenetic protein-2 promotes osteogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells in vitro. Exp Ther Med. 2017;14(1):377-382.
[17] 王晔恺,孙伟方,刘晓光,等.脑外伤与四肢骨折患者血清BMP-2与异位骨化的临床对照试验[J].中国骨伤,2011,24(5): 399-403.
[18] HUANG H, CHENG WX, HU YP, et al. Relationship between heterotopic ossification and traumatic brain injury: Why severe traumatic brain injury increases the risk of heterotopic ossification. J Orthop Translat. 2017;12:16-25.
[19] 吴尉,胡平安,梁芳,等.较高浓度神经肽Y抑制人脂肪干细胞增殖并促进其分化[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2016,32(2):185-190.
[20] GU XC, ZHANG XB, HU B, et al. Neuropeptide Y accelerates post-fracture bone healing by promoting osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells. Neuropeptides. 2016;60:61-66.
[21] 陈犹白,张启旭, BUTLER CE, et al.血管内皮生长因子基因转染的人脂肪干细胞具有较强的增殖和分化能力[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2017,33(3):352-356,361.
[22] RAJABIOUN M, ALIPOUR F, GHASEMI S, et al. Application of mesenchymal stem cells to enhance non-union bone fracture healing. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2019;107(2):301-311.
[23] ZHANG R, LIANG Y, WEI S. The expressions of NGF and VEGF in the fracture tissues are closely associated with accelerated clavicle fracture healing in patients with traumatic brain injury. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2018;14:2315-2322.
[24] SANG Q, SUN D, CHEN Z, et al. NGF and PI3K/Akt signaling participate in the ventral motor neuronal protection of curcumin in sciatic nerve injury rat models. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;103:1146-1153.
[25] 钱洲曜,王勇平.血管内皮生长因子有望成为加速骨折愈合的全新治疗手段[J].中国组织工程研究,2020,24(17):2759-2769.
[26] 沈峰,潘海涛,麻松,等.脑外伤合并骨折患者骨折愈合过程中血管内皮生长因子在血清和骨痂中的表达[J].首都医科大学学报, 2011,32(5):681-687.
[27] BLUTEAU G, JULIEN M, MAGNE D, et al. VEGF and VEGF receptors are differentially expressed in chondrocytes. Bone. 2007;40(3):568-576.
[28] LIU Y, BERENDSEN AD, JIA S, et al. Intracellular VEGF regulates the balance between osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation. J Clin Invest. 2012;122(9):3101-3113.
[29] BERENDSEN AD, OLSEN BR. How vascular endothelial growth factor-A (VEGF) regulates differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J Histochem Cytochem. 2014;62(2):103-108.
[30] BERENDSEN AD, OLSEN BR. Regulation of adipogenesis and osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells by vascular endothelial growth factor A. J Intern Med. 2015;277(6):674-680.
[31] WANG WD, CHENG BZ, KANG WB, et al. Investigation for TGF-β1 expression in type 2 diabetes and protective effects of TGF-β1 on osteoblasts under high glucose environment. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2018;22(19):6500-6506.
[32] HARA Y, GHAZIZADEH M, SHIMIZU H, et al. Delayed Expression of Circulating TGF-β1 and BMP-2 Levels in Human Nonunion Long Bone Fracture Healing. J Nippon Med Sch. 2017;84(1):12-18.
[33] 吴兴明,邹永根,石睿.伴有颅脑损伤对骨折患者血清中VEGF和TGF-β1水平影响研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2015,19(1):32-34.
[34] 沈峰,曾峥,潘海涛.脑外伤合并骨折患者骨折愈合过程中TGF-β1的作用[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2012,27(7):601-604.
[35] SHEN X, ZHANG Y, GU Y, et al. Sequential and sustained release of SDF-1 and BMP-2 from silk fibroin-nanohydroxyapatite scaffold for the enhancement of bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2016;106:205-216.
[36] DUMIC-CULE I, PERIC M, KUCKO L, et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins in fracture repair. Int Orthop. 2018;42(11):2619-2626.
[37] LIU DB, SUI C, WU TT, et al. Association of Bone Morphogenetic Protein (BMP)/Smad Signaling Pathway with Fracture Healing and Osteogenic Ability in Senile Osteoporotic Fracture in Humans and Rats. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24:4363-4371.
[38] HAN XG, WANG DK, GAO F, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 2 and decorin expression in old fracture fragments and surrounding tissues. Genet Mol Res. 2015;14(3):11063-11072.
[39] ABLOVE RH, ABRAMS SS. The use of BMP-2 and screw exchange in the treatment of scaphoid fracture non-union. Hand Surg. 2015;20(1): 167-171.
[40] 曾景,严远森,谷瑞辰.骨折合并颅脑外伤患者血清bFGF、IGF-Ⅰ、SEMA 3水平与骨痂形成时间相关性研究[J].临床和实验医学杂志,2017,16(4):347-350.
[41] 李维超,马维.不同程度脑外伤对骨折愈合中bFGF表达的影响[J].中国卫生产业,2013,10(17):1-2.
[42] ZHANG H, KOT A, LAY YE, et al. Acceleration of Fracture Healing by Overexpression of Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor in the Mesenchymal Stromal Cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6(10):1880-1893.
[43] FRIEDMAN JM, HALAAS JL. Leptin and the regulation of body weight in mammals. Nature. 1998;395(6704):763-770.
[44] TURNER RT, KALRA SP, WONG CP, et al. Peripheral leptin regulates bone formation. J Bone Miner Res. 2013;28(1):22-34.
[45] BARTELL SM, RAYALAM S, AMBATI S, et al. Central (ICV) leptin injection increases bone formation, bone mineral density, muscle mass, serum IGF-1, and the expression of osteogenic genes in leptin-deficient ob/ob mice. J Bone Miner Res. 2011;26(8):1710-1720.
[46] YAN H, ZHANG HW, FU P, et al. Leptin’s effect on accelerated fracture healing after traumatic brain injury. Neurol Res. 2013;35(5):537-544.
[47] WU Z, SHAO P, DASS CR, et al. Systemic leptin administration alters callus VEGF levels and enhances bone fracture healing in wildtype and ob/ob mice. Injury. 2018;49(10):1739-1745.
[48] GRAEF F, SEEMANN R, GARBE A, et al. Impaired fracture healing with high non-union rates remains irreversible after traumatic brain injury in leptin-deficient mice. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2017;17(2):78-85.
[49] SOLÁ-RUIZ MF, PÉREZ-MARTÍNEZ C, MARTÍN-DEL-LLANO JJ, et al. In vitro preliminary study of osteoblast response to surface roughness of titanium discs and topical application of melatonin. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2015;20(1):e88-93.
[50] 徐锐.创伤性颅脑损伤合并骨折早期PTH、CT及25D相关性研究[D].昆明:昆明医科大学,2017.
[51] ZHOU W, YU L, FAN J, et al. Endogenous Parathyroid Hormone Promotes Fracture Healing by Increasing Expression of BMPR2 through cAMP/PKA/CREB Pathway in Mice. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;42(2):551-563.
[52] SONG Y, BI L, ZHANG Z, et al. Increased levels of calcitonin gene-related peptide in serum accelerate fracture healing following traumatic brain injury. Mol Med Rep. 2012;5(2):432-438.
[53] SONG Y, HAN GX, CHEN L, et al. The role of the hippocampus and the function of calcitonin gene-related peptide in the mechanism of traumatic brain injury accelerating fracture-healing. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017;21(7):1522-1531.
[54] 郑若昆,汪贺轩.神经肽Y、血管活性肠肽在脑外伤合并股骨骨折大鼠模型骨痂中的表达及意义[J].中医学报,2013,28(3):375-377.
[55] TANG P, DUAN C, WANG Z, et al. NPY and CGRP Inhibitor Influence on ERK Pathway and Macrophage Aggregation during Fracture Healing. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;41(4):1457-1467.
[56] 李争争,赵军伟,罗伟,等.神经毡蛋白-1在创伤性颅脑损伤伴胫骨骨折愈合过程中的表达变化[J].中南大学学报(医学版), 2017, 42(2):154-160.
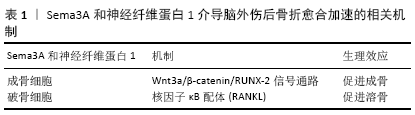
[57] FUKUDA T, TAKEDA S, XU R, et al. Sema3A regulates bone-mass accrual through sensory innervations. Nature. 2013;497(7450):490-493.
[58] HAYASHI M, NAKASHIMA T, TANIGUCHI M, et al. Osteoprotection by semaphorin 3A. Nature. 2012;485(7396):69-74.
[59] 王永辉,胡朝晖.脑外伤促进骨再生形成机制的研究进展[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(8):894-896.
[60] 孙庆仲,刘丕熙.合并颅脑损伤的肢体骨折异常骨化及其原因分析[J].中国厂矿医学,1998(6):411-412.
[61] VAN KAMPEN PJ, MARTINA JD, VOS PE, et al. Potential risk factors for developing heterotopic ossification in patients with severe traumatic brain injury. J Head Trauma Rehabil. 2011;26(5):384-391.
[62] SAKELLARIOU VI, GRIGORIOU E, MAVROGENIS AF, et al. Heterotopic ossification following traumatic brain injury and spinal cord injury: insight into the etiology and pathophysiology. J Musculoskelet Neuronal Interact. 2012;12(4):230-240.
[63] PERKINS R, SKIRVING AP. Callus formation and the rate of healing of femoral fractures in patients with head injuries. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1987;69(4):521-524. |