中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4620-4625.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2777
• 骨组织构建 bone tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
骨碎补影响破骨细胞分化的程度与含药血清浓度有关
许金松,邓 娜,张 潇
- 濮阳市安阳地区医院骨一科,河南省安阳市 455000
Effect of Rhizoma Drynariae on osteoclast differentiation is related to the concentration of drug-containing serum
Xu Jinsong, Deng Na, Zhang Xiao
- Department of Orthopedics, Anyang District Hospital of Puyang City, Anyang 455000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
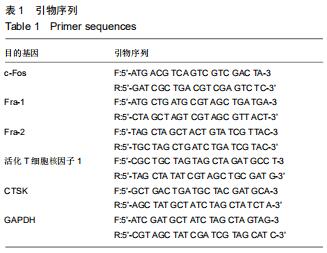
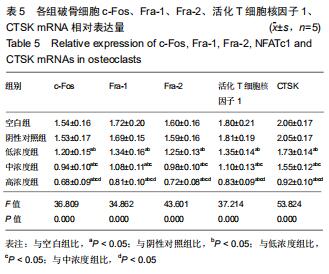
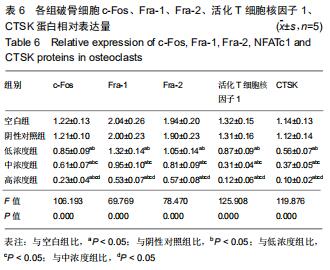
活化T细胞核因子1:属于NFAT家族重要成员之一,是破骨细胞分化形成中的重要转录因子,活化T细胞核因子1激活后可由细胞质转位至细胞核,在此过程中c-Fos/AP1信号通路起关键作用。CTSK、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶是破骨细胞特异性蛋白,活化T细胞核因子1活化的同时,可将CTSK、抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶转录出细胞核,促进破骨细胞分化。
中药含药血清:是指动物灌胃给予中药或单体制剂,经吸收进入血液循环,在一定时间内采取血液,分离所得血清,必定还有一定量的该药物成分,可反映机体真实血药浓度;将此血清进行体外细胞培养体系,可观察体外药理作用。
背景:已有报道骨碎补总黄酮有防治骨质疏松症的效果,但其作用机制多集中于对成骨细胞的作用,而对破骨细胞分化的影响研究较少。
目的:探讨骨碎补通过活化T细胞核因子1信号通路对破骨细胞分化的影响。
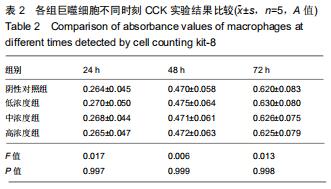
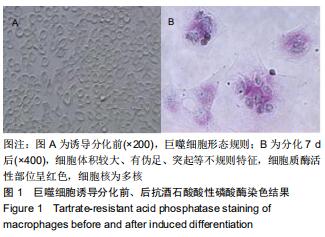
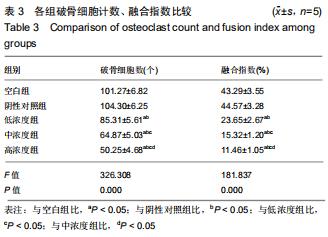
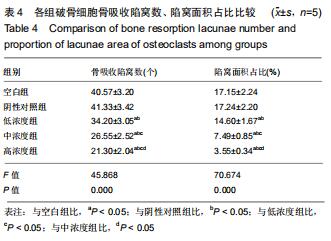
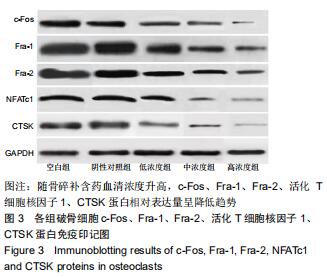
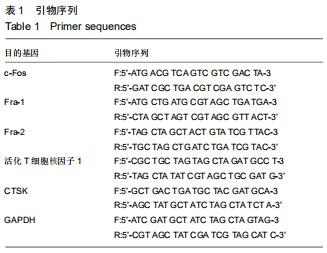
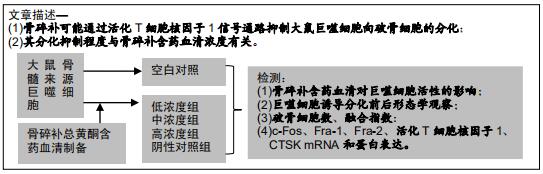
方法:40只SD大鼠随机分为4组,分别以0,11.6,34.8,104.4 g/kg的骨碎补总黄酮灌胃,获得阴性对照血清及低、中、高浓度含药血清。另取5周龄大鼠分离获取骨髓巨噬细胞,采用CCK-8法检测不同含药血清对巨噬细胞活性的影响;取巨噬细胞分为低、中、高浓度组、阴性对照组、空白组,每孔5个复孔,分别加入低、中、高浓度含药血清、阴性对照血清培养液、正常培养液;所有培养液均用20 μg/L巨噬细胞集落刺激因子、100 μg/L核因子κB受体活化因子配体进行破骨细胞诱导分化。诱导分化7 d,抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色检测破骨细胞数、融合指数,实时荧光定量PCR、Western blot检测各组细胞c-Fos、Fra-1、Fra-2、活化T细胞核因子1、组织蛋白酶KmRNA和蛋白表达;诱导分化14 d,骨片吸收陷窝试验检测破骨细胞骨吸收陷窝数、陷窝面积占比。实验方案经濮阳市安阳地区医院动物实验伦理委员会批准,批准号为PYSAYDQ-2019096。
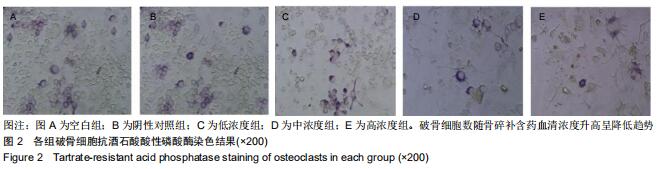
结果与结论:①不同浓度骨碎补含药血清对巨噬细胞活性影响无明显变化;②诱导分化前巨噬细胞形态规则,诱导分化后行抗酒石酸酸性磷酸酶染色证实为破骨细胞;③与空白组、阴性对照组比较,低、中、高浓度组破骨细胞数、融合指数、骨吸收陷窝数、陷窝面积占比、c-Fos、Fra-1、Fra-2、活化T细胞核因子1、组织蛋白酶K mRNA和蛋白相对表达量均明显降低(P < 0.05),且上述指标均随骨碎补含药血清浓度升高呈降低趋势:低浓度组>中浓度组>高浓度组,各浓度组间比较差异均有显著性意义(P < 0.05);④结果说明,骨碎补可能通过活化T细胞核因子1信号通路抑制大鼠巨噬细胞向破骨细胞的分化,且分化抑制程度与骨碎补含药血清浓度有关。
ORCID: 0000-0003-3948-4631(许金松)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号: