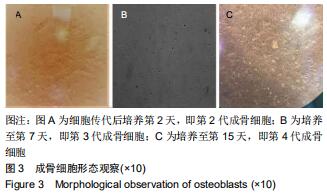
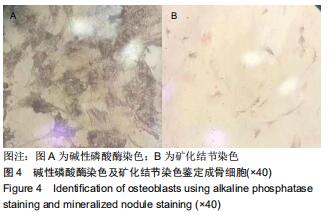
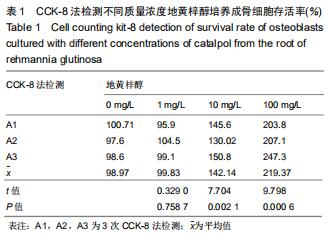
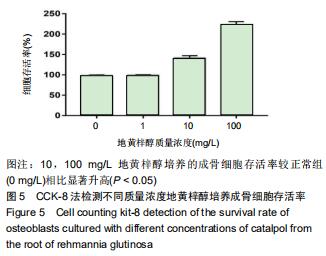
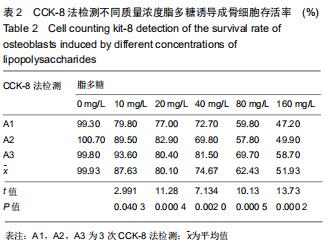
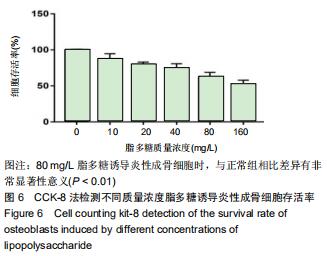
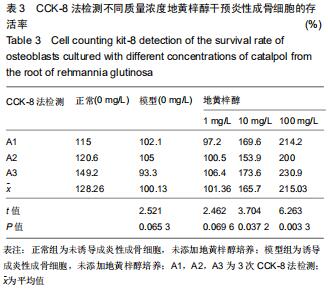
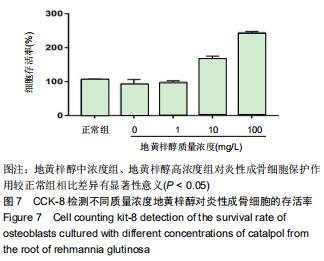
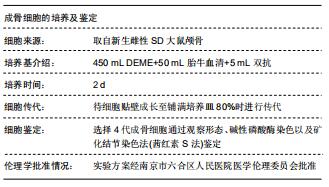
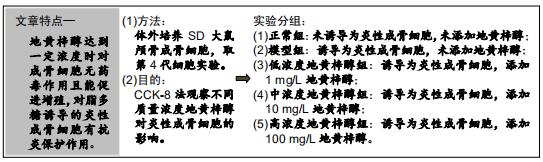
|
[1] MARUOTTI N, CORRADO A, CANTATORE FP.Osteoblast role in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232(11): 2957-2963.
[2] GLYN-JONES S, PALMER AJ, AGRICOLA R, et al. Osteoarthritis. Lancet. 2015;386:376-387.
[3] HOCHBERG MC, ALTMAN RD, APRIL KT, et al. American College of Rheumatology 2012 recommendations for the use of nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic therapies in osteoarthritis of the hand, hip, and knee. Arthritis Care Res. 2012;64:465-474.
[4] SHEN H, LIN H, SUN AX, et al. Acceleration of chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells by sustained growth factor release in 3D graphene oxide incorporated hydrogels.Acta Biomater.Acta Biomater. 2020; 105:44-55.
[5] JUNKER S, FROMMER KW, KRUMBHOLZ G,et al.Expression of adipokines in osteoarthritis osteophytes and their effect on osteoblasts.Matrix Biol. 2017;10(62):75-91.
[6] SHAO J, DING Z, LI L, et al. Improved accumulation of TGF-βby photopolymerized chitosan/silk protein bio-hydrogel matrix to improve differentiations of mesenchymal stem cells in articular cartilage tissue regeneration.J Photochem Photobiol B. 2020;203:111744.
[7] MOHAN G, PERILLI E, KULIWABA JS, et al. Application of in vivo micro-computed tomography in the temporal characterization of subchondral bone architecture in a rat model of low-dose monosodium iodoacetate-induced osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2011;13(6):R210.
[8] 黄孝闻,王绪平,张扬,等.淫羊藿苷对脂多糖诱导成骨细胞骨架F-actin损伤的保护作用[J].中国现代应用药学,2019,36(13): 1612-1616.
[9] AN J, YANG H, ZHANG Q, et al.Natural products for treatment of osteoporosis: The effects and mechanisms on promoting osteoblast-mediated bone formation.Life Sciences. 2016;15(147): 46-58.
[10] 王昌军,尹宏.肌肉组织和脂肪组织对绝经后女性骨密度及骨强度的影响及作用机制[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2019,25(10): 1502-1508.
[11] ZHU P, WU Y, YANG A, et al. Catalpol suppressed proliferation, growth and invasion of CT26 colon cancer by inhibiting inflammation and tumor angiogenesis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;11(95):68-76.
[12] LEE WC, GUNTUR AR, LONG F, et al. Energy Metabolism of the Osteoblast: Implications for Osteoporosis.Endocr Rev. 2017;38(3):255-266.
[13] 何强,尹宏,代凤雷,等.早期膝骨性关节炎模型大鼠的建立与验证[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(27):4338-4343.
[14] YUAN R, MA S, ZHU X, et al.Core level regulatory network of osteoblast as molecular mechanism for osteoporosis and treatment.Oncotarget. 2016; 7(4): 3692–3701.
[15] 杨柳,尹宏.连接蛋白43介导机械应力刺激下骨重建的研究进展[J].广东医学,2015,36(19):3075-3077.
[16] CHEN X, WANG Z, DUAN N, et al. Osteoblast-Osteoclast Interactions.Connect Tissue Res. 2018;59(2):99-107.
[17] 杨柳,尹宏.淫羊藿对破骨细胞吸收功能及机制研究进展[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2015,17(7):117-120.
[18] RATHINAVELU S, GUIDRY-ELIZONDO C, BANU J. Molecular Modulation of Osteoblasts and Osteoclasts in Type 2 Diabetes.J Diabetes Res. 2018;10(4):6354787.
[19] 何强,尹宏,代凤雷,等.膝骨关节炎大鼠滑膜组织中半乳糖凝集素3(Galectin-3)变化趋势研究[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2020, 22(2):86-90.
[20] CHEN Y, HUANG YC, YAN CH, et al. Abnormal subchondral bone remodeling and its association with articular cartilage degradation in knees of type 2 diabetes patients.Bone Res. 2017;5:17034.
[21] ZHENG W, DING B, LI X, et al. Knee loading repairs osteoporotic osteoarthritis by relieving abnormal remodeling of subchondral bone via Wnt/β-catenin signaling.FASEB J. 2020;34(2):3399-3412.
[22] O'NEIL CK, HANLON JT, MARCUM ZA. Adverse effects of analgesics commonly used by older adults with osteoarthritis: focus on non-opioid and opioid analgesics. Am J Geriatr Pharmacother. 2012;10(6):331-342.
[23] QIAN W, SU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Secretome analysis of rat osteoblasts during icariin treatment induced osteogenesis.Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(5):6515-6525.
[24] JHUN JY, NA HS, SHIN JW, et al. Notoginseng Radix and Rehmanniae Radix Preparata Extract Combination (YH23537) Reduces Pain and Cartilage Degeneration in Rats with Monosodium Iodoacetate-Induced Osteoarthritis.J Med Food. 2018;21(8):745-754.
[25] 石上梅.逐步完善中药质量标准体系和质量控制模式——解读2015年版《中国药典》(一部)[J].中国药学杂志, 2015,50(20): 1752-1753.
|