| [1] Zeckey C, Hildebrand F, Frink M, et al. Heterotopic ossifications following implant surgery--epidemiology, therapeutical approaches and current concepts. Semin Immunopathol. 2011;33(3):273-286.[2] Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1973;55(8): 1629-1632.[3] Neal B. Effects of heterotopic bone formation on outcome after hip arthroplasty. ANZ J Surg. 2003;73: 422-426.[4] Shehab D, Elgazzar AH, Collier BD. Heterotopic ossification. J Nucl Med. 2002;43:346-353.[5] Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Inherited human diseases of heterotopic bone formation. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2010; 6: 518-527.[6] 陈松,高悠水,周祖彬,等. 获得性异位骨化发病机制研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志,2014,35(1):21-23.[7] Shore EM, Kaplan FS. Fibroregulation of mesenchymal progenitor cells by BMP-4 after traumatic muscle injury. J Orthop Trauma. 2012;26: 693-698.[8] Davis TA, O'Brien FP, Anam K, et al. Heterotopic ossification in complex orthopaedic combat wounds: quantification and characterization of osteogenic precursor cell activity in traumatized muscle.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2011;93: 1122-1131.[9] Ranganathan K, Loder S, Agarwal S, et al. Heterotopic ossification: basic-science principles and clinical correlates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2015;97: 1101-1111.[10] Ramirez DM, Ramirez MR, Reginato AM, et al. Molecular and cellular mechanisms of heterotopic ossification. Histol. Histopathol. 2014;29:1281-1285.[11] Yu PB, Deng DY, Lai CS, et al. BMP type I receptor inhibition reduces heterotopic [corrected] ossification. Nat Med. 2008; 14(12): 1363-1369.[12] Medici D, Olsen BR. The role of endothelial-mesenchymal transition in heterotopic ossification. J Bone Miner Res. 2012; 27: 1619-1622.[13] Coons D, Godleski M. Range of motion exercises in the setting of burn-associated heterotopic ossification at the elbow: case series and discussion. Burns. 2013;39: e34-38.[14] DeLee J,Ferrari A,Charnley J, et al. Ectopic bone formation following low friction arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976;(121): 53-59.[15] Kjaersgaard-Andersen P,Sletgård J,Gjerløff C, et al. Heterotopic bone formation after noncemented total hip arthroplasty. Location of ectopic bone and the influence of postoperative antiinflammatory treatment. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1990;(252):156-162.[16] Della Valle AG, Ruzo PS, Pavone V, et al. Heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty: a critical analysis of the Brooker classification and proposal of a simplified rating system. J Arthroplasty. 2002; 17: 870-875.[17] Hug KT, Alton TB, Gee AO. Classifications in brief: Brooker classification of heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2015; 473: 2154-2157.[18] Ekelund A,Brosjö O,Nilsson O S, Experimental induction of heterotopic bone. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1991;(263):102-112.[19] Kantak AP, Shah NN. Extensive surgical wound lavage reduces the incidence and severity of heterotopic ossification in primary total hip replacement: a study of 175 hip replacements. Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(4):234-239.[20] 刘勇,霍少川,唐宏宇,等. 强直性脊柱炎患者全髋关节置换后异位骨化的危险因素[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(11): 1641-1646.[21] Thilak J, Panakkal JJ, Kim TY, et al. Risk Factors of Heterotopic Ossification Following Total Hip Arthroplasty in Patients With Ankylosing Spondylitis. J Arthroplasty. 2015; 30: 2304-2307.[22] Davis G,Patel RP,Tan TL, et al. Ethnic differences in heterotopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2016;98-B(6):761-766.[23] Fahrer H, Koch P, Ballmer P, et al. Ectopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty: is diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis a risk factor? Br J Rheumatol. 1988; 27: 187-190.[24] Ferguson DJ, Itonaga I, Maki M, et al. Heterotopic bone formation following hip arthroplasty in Paget's disease. Bone. 2004; 34(6): 1078-1083.[25] Pavlou G, Salhab M, Murugesan L, et al. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in primary total hip arthroplasty. Hip Int. 2012; 22: 50-55.[26] Aljurayyan A, Tanzer D, Tanzer M. Acute revision hip arthroplasty: a previously unrecognized risk factor for heterotopic ossification. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2016;26(2):1-6.[27] Edwards DS,Barbur SA,Bull AM, et al. Posterior mini-incision total hip arthroplasty controls the extent of post-operative formation of heterotopic ossification. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2015;25(6):1051-1055.[28] Zhu Y, Zhang F, Chen W, et al. Incidence and risk factors for heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty: a meta-analysis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2015;135(9): 1307-1314.[29] Kocic M, Lazovic M, Mitkovic M, et al Clinical signi?cance of the heterotopic ossi?cation after total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1):16.[30] Bal BS, Lowe JA, Gietler A, et al. Heterotopic ossification after 2-incision total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2010;25: 538-540.[31] Eggli S,Woo A. Risk factors for heterotopic ossification in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2001;121: 531-535.[32] 吴锋锋,吴立东.全髋关节置换术后异位骨化及其研究进展[J].中华骨科杂志, 2006,26(8):558-561.[33] Kocic M, Lazovic M, Mitkovic M, et al. Clinical significance of the heterotopic ossification after total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics. 2010; 33(1): 16.[34] Grzegorzewski A,Koz?owski P,Synder M,et al. Heterotopic ossification as a complication of total hip replacement. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2000; 65: 255-260.[35] Eggli S, Rodriguez J, Ganz R. Heterotopic ossification in total hip arthroplasty: the significance for clinical outcome. Acta Orthop Belg. 2000;66(2): 174-180.[36] Bressler EL,Marn CS,Gore RM, et al. Evaluation of ectopic bone by CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987; 148: 931-935.[37] 鞠金勇,喻都,王永建,等. 异位骨化影像学早期诊断研究进展[J]. 国际骨科学杂志, 2016, 37(5):282-285.[38] Foley KL, Hebela N, Keenan MA, et al. Histopathology of periarticular non-hereditary heterotopic ossification. Bone. 2018;109: 65-70.[39] Rama KR, Vendittoli PA, Ganapathi M, et al. Heterotopic ossification after surface replacement arthroplasty and total hip arthroplasty: a randomized study. J Arthroplasty. 2009; 24(2): 256-262.[40] Metzner G,Lindner B,Neumann D, et al. Incidence of anterior intertrochanteric ossifications after total hip arthroplasty--a retrospective long-term follow-up study. Z Orthop Unfall. 2010; 148(2): 174-179.[41] Lee YH, Park KK, Song HT, et al. Metal artefact reduction in gemstone spectral imaging dual-energy CT with and without metal artefact reduction software. Eur Radiol. 2012; 22(6): 1331-1340.[42] Zagarella A, Impellizzeri E, Maiolino R, et al. Pelvic heterotopic ossification: when CT comes to the aid of MR imaging. Insights Imaging. 2013; 4(5): 595-603.[43] Fritz J, Lurie B, Miller TT. Imaging of hip arthroplasty. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2013;17: 316-327.[44] Hayter CL, Koff MF, Potter HG. Magnetic resonance imaging of the postoperative hip. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012;35(5): 1013-1025.[45] Khodarahmi I, Fritz J. Advanced MR imaging after total hip arthroplasty: the clinical impact. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2017;21(5): 616-629.[46] De Smet AA, Norris MA, Fisher DR. Magnetic resonance imaging of myositis ossificans: analysis of seven cases. Skeletal Radiol. 1992;21(8):503-507.[47] Wang Q, Zhang P, Li P, et al. Ultrasonography monitoring of trauma-induced heterotopic ossification: guidance for rehabilitation procedures. Front Neurol. 2018; 9: 771.[48] Van den Wyngaert T, Paycha F, Strobel K, et al. SPECT/CT in postoperative painful hip arthroplasty. Semin Nucl Med. 2018;48: 425-438.[49] Dobrindt O, Amthauer H, Krueger A, et al. Hybrid SPECT/ CT for the assessment of a painful hip after uncemented total hip arthroplasty. BMC Med Imaging. 2015;15: 18.[50] Vasileiadis GI, Sioutis IC, Mavrogenis AF, et al. COX-2 inhibitors for the prevention of heterotopic ossification after THA. Orthopedics. 2011;34(6): 467.[51] Joice M,Vasileiadis GI,Amanatullah DF. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for heterotopic ossification prophylaxis after total hip arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(7):915-922.[52] Rumi MN, Deol GS, Bergandi JA, et al. Optimal timing of preoperative radiation for prophylaxis against heterotopic ossification. A rabbit hip model. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(2): 366-373.[53] Morcos M, Smith K, Tanzer M. The effect of late radiotherapy on the progression of heterotopic ossification following total hip arthroplasty. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol. 2018;28(6): 1125-1131. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: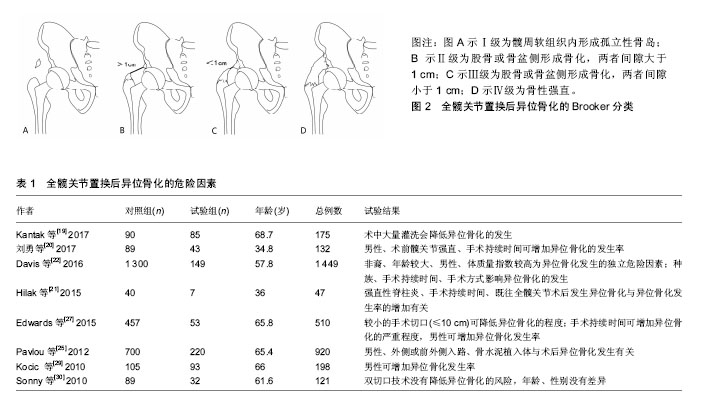

.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
文题释义: