中国组织工程研究 ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (16): 2545-2552.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1212
• 骨与关节综述 bone and joint review • 上一篇 下一篇
脊柱矫形后近端交界性后凸的发生及预防策略
戴建军1,邢文华2
- 1内蒙古医科大学研究生学院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000;2内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000
-
出版日期:2019-06-08发布日期:2019-06-08 -
通讯作者:邢文华,博士,主任医师,内蒙古医科大学第二附属医院,内蒙古自治区呼和浩特市 010000 -
作者简介:戴建军,男,1992年生,山东省临沂市人,汉族,内蒙古医科大学在读硕士,主要从事脊柱外科研究。 -
基金资助:国家自然科学基金资助项目(81460344),项目负责人:邢文华|内蒙古自然科学基金资助项目(2018MS08095),项目负责人:邢文华
Development and prevention strategy of proximal junctional kyphosis after scoliosis surgery
Dai Jianjun1, Xing Wenhua2
- 1Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China; 2the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China
-
Online:2019-06-08Published:2019-06-08 -
Contact:Xing Wenhua, MD, Chief physician, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
About author:Dai Jianjun, Master candidate, Graduate School of Inner Mongolia Medical University, Hohhot 010000, Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81460344 (to XWH)| the Natural Science Foundation of Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, No. 2018MS08095 (to XWH)
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg)
中图分类号:
引用本文
戴建军,邢文华. 脊柱矫形后近端交界性后凸的发生及预防策略[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2019, 23(16): 2545-2552.
Dai Jianjun, Xing Wenhua. Development and prevention strategy of proximal junctional kyphosis after scoliosis surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(16): 2545-2552.
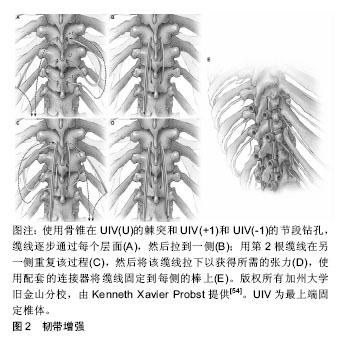
旨在增强韧带的技术被证明是有效的,因为在近端交界性后凸畸形和近端交界性失败的发病机制中,后韧带复合体的破坏被认为是一个重要的因素。韧带增强的目的是为UIV,UIV+1和UIV-1水平提供强度,同时还减少了这些节段的交界区应力,并加强后韧带复合体。这种技术显示早期近端交界性后凸畸形有显著减少,但是需要长期的数据。

| [1] Lowe TG, Kasten MD. An analysis of sagittal curves and balance after Cotrel-Dubousset instrumentation for kyphosis secondary to Scheuermann’s disease: a review of 32 patients. Spine. 1994;19: 1680-1685.[2] Lee GA, Betz RR, Clements DH 3rd, et al. Proximal kyphosis after posterior spinal fusion in patients with idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 1999;24: 795-799.[3] Glattes RC, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity following long instrumented posterior spinal fusion: incidence, outcomes and risk factor analysis. Spine. 2005; 30: 1643-1649.[4] Hostin R, McCarthy I, O’Brien M, et al. Incidence, mode, and location of acute proximal junctional failures after surgical treatment of adult spinal defor-mity.Spine.2013;38: 1008-1015.[5] O?Shaughnessy BA, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Does a long-fusion "T3-sacrum" portend a worse outcome than a short-fusion "T10-sacrum" in primary surgery for adult scoliosis? Spine.2012;37: 884-890.[6] Bridwell KH,Lenke LG,Cho SK, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in primary adult deformity surgery: evaluation of 20 degrees as a critical angle. Neurosurgery. 2013;72: 899-906.[7] Helgeson MD, Shah SA, Newton PO, et al. Evaluation of proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis following pedicle screw, hook, or hybrid instrumentation. Spine. 2010;35:177-181.[8] Sacramento-Domínguez C, Vayas-Díez R, Coll-Mesa L, et al. Reproducibility measuring the angle of proximal junctional kyphosis using the first or the second vertebra above the upper instrumented vertebrae in patients surgically treated for scoliosis. Spine. 2009;34: 2787-2791.[9] Rastegar F,Contag A,Daniels A, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis: inter- and intra-observer reliability of radiographic measurements in adult spinal deformity. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2017. doi: 10.1097/BRS.0000000000002261.[10] Kim HJ,Lenke LG,Shaffrey CI, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis as a distinct form of adjacent segment pathology after spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review.Spine. 2012;37: S144-164.[11] Hart RA,McCarthy I,Ames CP, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure. Neurosurg. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2013;24(2):213-218.[12] Yagi M, Rahm M, Gaines R, et al. Characterization and surgical outcomes of proximal junctional failure in surgically treated patients with adult spinal deformity. Spine. 2014;39: E607-614.[13] Raman T,Miller E,Martin CT, et al. The effect of prophylactic vertebroplasty on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following posterior spinal fusion in adult spinal deformity: a 5-year follow-up study. Spine J. 2017;17: 1489-1498.[14] Kim YJ, Bridwell KH, Lenke LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity after segmental posterior spinal instru- mentation and fusion: minimum five-year follow-up. Spine. 2008; 33:2179-2184. [15] Yagi M, Akilah KB, Boachie-Adjei O. Incidence, risk factors and classification of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis.Spine.2011;36: E60-68.[16] Maruo K,Ha Y,Inoue S, et al. Predictive factors for proximal junctional kyphosis in long fusions to the sacrum in adult spinal deformity.Spine. 2013;38: E1469-1476.[17] Sebaaly A,Sylvestre C,El Quehtani Y, et al. Incidence and risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: results of a multicentric study of adult scoliosis. Clin Spine Surg. 2018; 31: E178-E183.[18] Nicholls FH,Bae J,Theologis AA, et al. Factors associated with the development of and revision for proximal junctional kyphosis in 440 consecutive adult spinal deformity patients. Spine.2017; 42: 1693-1698.[19] Luo M,Wang P,Wang W, et al. Upper thoracic versus lower thoracic as site of upper instrumented vertebrae for long fusion surgery in adult spinal deformity: a meta-analysis of proximal junctional kyphosis. World Neurosurg. 2017; 102: 200-208.[20] Liu Fe,Wang T,Yang SD, et al. Incidence and risk factors for proximal junctional kyphosis: a meta-analysis.Eur Spine J. 2016;25: 2376-2383.[21] Lafage R,Schwab F,Glassman S,et al. Age-adjusted alignment goals have the potential to reduce PJK.Spine. 2017;42: 1275-1282.[22] Yagi M,King AB,Boachie-Adjei O. Incidence, risk factors, and natural course of proximal junctional kyphosis: surgical outcomes review of adult idiopathic scoliosis. Minimum 5 years of follow-up. Spine. 2012;37: 1479-1489.[23] Wang J,Zhao Y,Shen B, et al. Risk factor analysis of proximal junctional kyphosis after posterior fusion in patients with idiopathic scoliosis.Injury. 2010; 41: 415-420.[24] Kim HJ,Bridwell KH,Lenke LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis results in inferior SRS pain subscores in adult deformity patients. Spine. 2013;38: 896-901.[25] Anderson AL, McIff TE, Asher MA, et al. The effect of posterior thoracic spine anatomical structures on motion segment flexion stiffness.Spine. 2009;34: 441-446.[26] Arlet V,Aebi M, Junctional spinal disorders in operated adult spinal deformities: present understanding and future perspectives. Eur Spine J. 2013;22 Suppl 2:S276-295.[27] Han S, Hyun SJ, Kim KJ, et al. Rod stiffness as a risk factor of proximal junctional kyphosis after adult spinal deformity surgery: comparative study between cobalt chrome multiple-rod constructs and titanium alloy two-rod constructs. Spine. Spine J. 2017;17(7): 962-968.[28] Lau D,Clark AJ,Scheer JK, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and failure after spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review of the literature as a background to classification development.Spine. 2014;39: 2093-2102.[29] Kim HJ,Bridwell KH,Lenke LG, et al. Patients with proximal junctional kyphosis requiring revision surgery have higher postoperative lumbar lordosis and larger sagittal balance corrections. Spine. 2014;39: E576-580.[30] Lafage R,Schwab F,Challier V, et al. Defining spino-pelvic alignment thresholds: should operative goals in adult spinal deformity surgery account for age? Spine. 2016; 41: 62-68.[31] Kim HJ, Iyer S. Proximal junctional kyphosis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24: 318-326.[32] Lau D, Clark AJ, Scheer JK, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis and failure after spinal deformity surgery: a systematic review of the literature as a background to classification development. Spine. 2014; 39(25):2093-2102.[33] Park SJ, Lee CS, Chung SS, et al. Different risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure following long instrumented fusion to the sacrum for adult spinal deformity: survivorship analysis of 160 patients. Neurosurgery. 2017; 80: 279-286.[34] Kim DK, Kim JY, Kim DY, et al. Risk factors of proximal junctional kyphosis after multilevel fusion surgery: more than 2 years follow-up data. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2017; 60: 174-180.[35] Yagi M,Fujita N,Tsuji O, et al. Low bone-mineral density is a significant risk for proximal junctional failure after surgical correction of adult spinal deformity: a propensity score-matched analysis. Spine. 2018; 43: 485-491.[36] Diebo BG, Jalai CM, Challier V, et al. Novel index to quantify the risk of surgery in the setting of adult spinal deformity: a study on 10,912 patients from the nationwide inpatient sample. Clin Spine Surg. 2017;30: E993-E999.[37] Scheer JK,Osorio JA,Smith JS, et al. Development of validated computer-based preoperative predictive model for proximal junction failure (pjf) or clinically significant pjk with 86% accuracy based on 510 asd patients with 2-year follow-up. Spine. 2016; 41: E1328-E1335.[38] Lange T, Schulte TL, Gosheger G, et al. Effects of multilevel posterior ligament dissection after spinal instrumentation on adjacent segment biomechanics as a potential risk factor for proximal junctional kyphosis: a biomechanical study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018; 19(1): 57.[39] Scheer JK, Lafage R, Schwab FJ, et al. Under correction of sagittal deformities based on age-adjusted alignment thresholds leads to worse health-related quality of life whereas over correction provides no additional benefit. Spine. 2018; 43: 388-393.[40] Lafage R, Bess S, Glassman S,et al. Virtual modeling of postoperative alignment after adult spinal deformity surgery helps predict associations between compensatory spinopelvic alignment changes, overcorrection, and proximal junctional kyphosis. Spine. 2017;42: E1119-E1125.[41] Masevnin S, Ptashnikov D, Michaylov D, et al. Risk factors for adjacent segment disease development after lumbar fusion. Asian Spine J. 2015; 9(2): 239-244.[42] Lafage R, Line BG, Gupta S, et al. Orientation of the upper-most instrumented segment influences proximal junctional disease following adult spinal deformity surgery. Spine. 2017;42: 1570-1577.[43] Martin CT, Skolasky RL,Mohamed AS, et al. Preliminary results of the effect of prophylactic vertebroplasty on the incidence of proximal junctional complications after posterior spinal fusion to the low thoracic spine. Spine Deform. 2013;1: 132-138.[44] Kebaish KM,Martin CT,O'Brien JR, et al. Use of vertebroplasty to prevent proximal junctional fractures in adult deformity surgery: a biomechanical cadaveric study. Spine J. 2013;13: 1897-1903.[45] Theologis AA,Burch S. Prevention of acute proximal junctional fractures after long thoracolumbar posterior fusions for adult spinal deformity using 2-level cement augmentation at the upper instrumented vertebra and the vertebra 1 level proximal to the upper instrumented vertebra. Spine. 2015; 40: 1516-126.[46] Ghobrial GM,Eichberg DG,Kolcun JPG, et al. Prophylactic vertebral cement augmentation at the uppermost instrumented vertebra and rostral adjacent vertebra for the prevention of proximal junctional kyphosis and failure following long-segment fusion for adult spinal deformity. Spine J. 2017; 17: 1499-1505.[47] Watanabe K,Lenke LG,Bridwell KH, et al. Proximal junctional vertebral fracture in adults after spinal deformity surgery using pedicle screw constructs: analysis of morphological features. Spine. 2010; 35: 138-145.[48] Verlaan JJ,Oner FC,Slootweg PJ, et al. Histologic changes after vertebroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004;86-A(6):1230-1238.[49] Kim YJ,Bridwell KH,Lenke LG, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adolescent idiopathic scoliosis following segmental posterior spinal instrumentation and fusion: minimum 5-year follow-up. Spine. 2005; 30: 2045-2050.[50] Pahys JM,Vivas AC,Samdani AF, et al. Assessment of proximal junctional kyphosis and shoulder balance with proximal screws versus hooks in posterior spinal fusion for adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2018;43: E1322-E1328.[51] Clements DH,Betz RR,Newton PO, et al. Correlation of scoliosis curve correction with the number and type of fixation anchors. Spine. 2009;34: 2147-2150.[52] Newton PO,Yaszay B,Upasani VV, et al. Preservation of thoracic kyphosis is critical to maintain lumbar lordosis in the surgical treatment of adolescent idiopathic scoliosis. Spine. 2010;35: 1365-1370.[53] Hassanzadeh H, Gupta S, Jain A, et al. Type of anchor at the proximal fusion level has a significant effect on the incidence of proximal junctional kyphosis and outcome in adults after long posterior spinal fusion. Spine Deform. 2013;1(4): 299-305.[54] Safaee MM, Deviren V, Dalle Ore C, et al. Ligament augmentation for prevention of proximal junctional kyphosis and proximal junctional failure in adult spinal deformity. J Neurosurg Spine. 2018;28: 512-519.[55] Pham MH, Tuchman A, Smith L,et al. Semitendinosus graft for interspinous ligament reinforcement in adult spinal deformity. Orthopedics. 2017; 40: e206-e210.[56] Zaghloul KM, Matoian BJ, Denardin NB, et al. Preventing proximal adjacent level kyphosis with strap stabilization. Orthopedics. 2016;39: e794-7999.[57] Zhao J, Yang M, Yang Y, et al. Proximal junctional kyphosis in adult spinal deformity: a novel predictive index. Eur Spine J. 2018;27: 2303-2311.[58] Zhu ZZ , Chen X , Qiu Y, et al. Adding satellite rods to standard 2-rod construct with the use of duet screws: an effective technique to improve surgical outcomes and preventing proximal junctional kyphosis in posterior-only correction of scheuermann kyphosis. Spine. 2017.[59] Hart R, McCarthy I, O?brien M, et al. Identification of decision criteria for revision surgery among patients with proximal junctional failure after surgical treatment of spinal deformity. Spine. 2013;38: E1223-1227. |
| [1] | 赵春涛, 卿明松, 余浪波, 彭笳宸. 运动学对线和机械力学对线指导全膝关节置换效果的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(9): 1435-1442. |
| [2] | 涂鹏程, 郭 杨, 马 勇, 潘娅岚, 郑苏阳, 王礼宁, 吴承杰, 过俊杰. 威灵仙提取物可促进体外牵张应力环境下软骨细胞表型的维持[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1182-1187. |
| [3] | 张 聪, 赵 岩, 杜小宇, 杜欣瑞, 庞廷娟, 付怡凝, 张 浩, 张步洲, 李筱贺, 王利东. 青少年特发性脊柱侧凸腰主弯患者腰椎-骨盆的生物力学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1155-1161. |
| [4] | 许国峰, 李学斌, 唐一钒, 赵 寅, 周盛源, 陈雄生, 贾连顺. 人黄韧带细胞骨化发生过程中的自噬[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(8): 1174-1181. |
| [5] | 林 明, 潘金勇, 张惠荣. 敲除NIPBL基因可下调小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞增殖及成骨分化能力[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(7): 1002-1008. |
| [6] | 岑妍慧, 夏 猛, 贾 微, 罗伟生, 林 江, 陈松林, 陈 炜, 刘 鹏, 黎明星, 李景云, 李曼莉, 艾丁丁, 蒋云霞. 黄芩素能下调诱捕受体3表达抑制肝癌干细胞的生物学行为[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(7): 1023-1029. |
| [7] | 和雨洁, 王海燕, 李志军, 李筱贺, 蔡永强, 戴丽娜, 许阳阳, 王一丹, 徐雪彬. 学龄期儿童胸椎经“椎弓根-肋骨”单元内固定的数字化测量[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [8] | 刘 群, 孙东东, 高丽兰, 何志江, 孙明林. 经皮椎体后凸成形后再发骨折相关因素的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(6): 976-984. |
| [9] | 严 舒, 卢 岩, 欧阳昭连. 中国组织工程领域2013至2018年国家自然科学基金资助项目分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(5): 731-735. |
| [10] | 宋世雷, 陈跃平, 章晓云. PI3K/AKT信号通路调控股骨头坏死的相关机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 408-415. |
| [11] | 孙 健, 方 超, 高 飞, 魏来福, 钱 军. 长节段与短节段内固定治疗退变性脊柱侧弯疗效与并发症的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [12] | 高阳阳, 车先达, 韩鹏飞, 梁 斌, 李鹏翠. 透视引导与机器人辅助椎弓根置钉效果的荟萃分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 446-452. |
| [13] | 张 健, 王小健, 秦德安, 赵中涛, 梁庆元, 安奇君, 宋洁富. 脊柱矫形后发生近端交界性后凸危险因素的荟萃分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(3): 460-468. |
| [14] | 梁晨亮, 赵振群, 刘万林. OPG/RANKL/RANK信号通路在骨巨细胞瘤发病机制中的作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(23): 3723-3729. |
| [15] | 许阳阳, 张 凯, 李志军, 张云凤, 苏宝科, 王 星, 王利东, 王一丹, 和雨洁, 李 琨, 王海燕, 李筱贺. 12-15岁青少年腰椎椎弓根螺钉置入最佳选择的形态学分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(21): 3321-3328. |
1.1 资料来源 计算机检索PubMed数据库,检索词为“Proximal junctional kyphosis,PJK”。检索文献时限为1994年1月至2018年10月,检索语言设定为英文,检索文献类型包括研究原著、综述、论著、经验交流、国际会议及荟萃分析等。
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
为了减少近端交界性后凸畸形的发生制定了有效的预防策略。在UIV和UIV+1处使用椎体成形术可以缓冲轴向压力,并将压力传播到其他节段,减少了UIV+1的应力,进而预防近端交界性后凸畸形的发生。椎体成形术具有较好的临床表现,但这种技术有一定的局限性。骨水泥有可能阻断椎体内血供,减少邻近椎间盘的营养供应,从而加速退行性疾病的发生。其也有可能导致相邻节段的骨折和塌陷。在UIV中使用骨钩代替椎弓根螺钉是另一种公认的近端交界性后凸畸形预防策略。后方韧带复合体的损伤是近端交界性后凸畸形的一大危险因素,骨钩可减少周围肌肉和小关节的显露,保护后方韧带复合体,增强脊柱稳定性,因此在UIV上使用骨钩可降低近端交界性后凸畸形的发生。 中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
.jpg)