中国组织工程研究 ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (32): 5191-5196.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0540
• 组织构建实验造模 experimental modeling in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
针刺对一次离心运动模型大鼠白细胞介素6表达的影响
白胜超1,陈圣菊1,王 博1,吴 迎1,尚画雨2
- 1北京体育大学运动人体科学学院,北京市 100084;2成都体育学院运动医学与健康学院,四川省成都市 610041
Effect of acupuncture on the expression level of interleukin-6 in rats after a single eccentric exercise
Bai Sheng-chao1, Chen Sheng-ju1, Wang Bo1, Wu Ying1, Shang Hua-yu2
- 1Sport Science College, Beijing Sport University, Beijing 100084, China; 2School of Sports Medicine and Health College, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。
文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。
.jpg) 文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。
文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。摘要
背景:白细胞介素6是一种细胞因子,其来源广泛,在运动后骨骼肌能够大量产生并对运动功能恢复起到重要作用;运动后进行骨骼肌针刺能够改善骨骼肌的超微结构,降低损伤程度,促进功能恢复。目前尚未见到针刺对运动后白细胞介素6影响的报道。
目的:探究针刺干预对一次离心运动后大鼠白细胞介素6的影响。
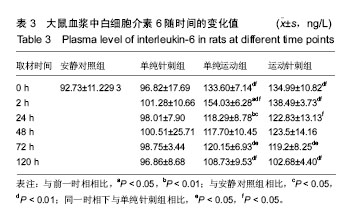
方法:114只雄性SD大鼠,随机分为:安静对照组(n=6)、单纯运动组(n=36)、单纯针刺组(n=36)、运动针刺组(n=36)。单纯运动组和运动针刺组均在坡度-16°的跑台上进行一次离心运动,单纯针刺组和运动针刺组进行小腿三头肌的斜刺。各组处理后,除安静组直接取材,其余3组分别在干预后0,2,24,48,72,120 h时间点取材,每个时间点6只。Western Blot法分别检测比目鱼肌、股直肌白细胞介素6的蛋白表达;ELISA法检测血浆中白细胞介素6水平。
结果与结论:①单纯针刺处理后,比目鱼肌和股直肌中白细胞介素6蛋白表达以及血浆中白细胞介素6水平均无明显变化(P > 0.05);②一次离心运动后,比目鱼肌、股直肌和血浆中白细胞介素6均出现不同程度升高,且比目鱼肌与股直肌间白细胞介素6表达无明显差异(P > 0.05);③运动后针刺能明显下调比目鱼肌白细胞介素6蛋白峰值表达(P < 0.05),而股直肌和血浆中白细胞介素6表达无明显变化(P > 0.05);④结果表明,对骨骼肌进行直接针刺干预不能引起白细胞介素6明显变化,骨骼肌在离心运动后会分泌较多的白细胞介素6,同时进行针刺干预能够降低针刺部位白细胞介素6的峰值量;针刺能够在局部对白细胞介素6产生明显作用,对于其他部位的骨骼肌和血浆未能产生显著效果。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7152-7676(白胜超)
中图分类号:

.jpg) 文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。
文题释义:
离心运动:运动时骨骼肌进行收缩,在产生张力的同时起止点相互远离被迫拉长,这种运动方式被称为离心运动,也被称为退让工作,在运动的过程中肌肉做负功,一些情况下离心运动方式可以起到保护作用,例如高处下跳时股四头肌的离心收缩。
白细胞介素6:一种糖基化蛋白,相对分子质量在22 000-27 000,带28个信号序列,作为一种细胞因子具有较多的生物学功能,能够刺激细胞生长、促进细胞增殖分化、协同其他因子发挥作用等,其来源广泛包括骨骼肌细胞、中性粒细胞、T细胞、B细胞、造骨细胞等众多类型细胞。