中国组织工程研究 ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (17): 2781-2788.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.3170
• 组织构建循证医学 evidence-based medicine in tissue construction • 上一篇
中药、针刺、灸法和推拿等中医疗法治疗血瘀型腰椎间盘突出症的网状Meta分析
张冲锋1,李现林2,彭卫兵2,贾宏声1,蔡 磊1
- 1河南中医药大学,河南省郑州市 450000; 2河南中医药大学第一附属医院骨伤科,河南省郑州市 450000
Treating lumbar disc herniation of blood stasis type with Chinese herbs, acupuncture, moxibustion, and massage: a Bayesian network Meta-analysis
Zhang Chongfeng1, Li Xianlin2, Peng Weibing2, Jia Hongsheng1, Cai Lei1
- 1Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, the First Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450000, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
网状Meta分析:网状Meta分析分为经典频率学派和贝叶斯学派,频率学派发展最早,应用广泛,但近年来因贝叶斯方法引用后验概率,更加符合实际且估计值更加准确,目前越来越多应用贝叶斯的方法进行分析。此外传统Meta只能分析2种干预措施,网状Meta则能分析多种干预措施,对多种不同治疗方法进行疗效评估与排序,同时因其能够进行间接比较,也能弥补部分直接资料缺乏的研究。
腰椎间盘突出症:是临床常见病,其主要临床表现为腰部疼痛,单侧或双侧下肢放射性疼痛,严重者还会出现马尾神经症状。因其发病率高,给患者带来的痛苦大,在临床中常常被关注。
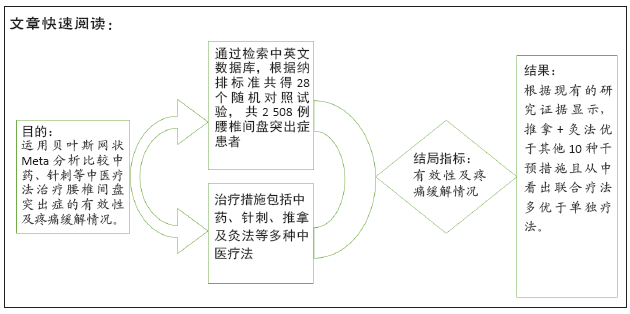
目的:中药、针刺及推拿等中医疗法在治疗腰椎间盘突出症方面有着不可替代的作用,但是由于其治疗方法的多样性且目前研究多为两两比较,尚缺乏多种措施之间的疗效比较。文章运用网状Meta分析方法评价中医疗法治疗血瘀型腰椎间盘突出症的有效率及疼痛缓解情况。
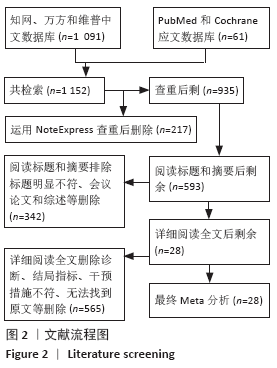
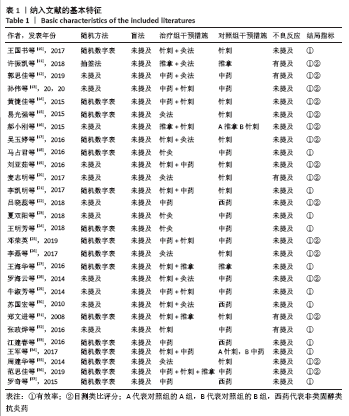
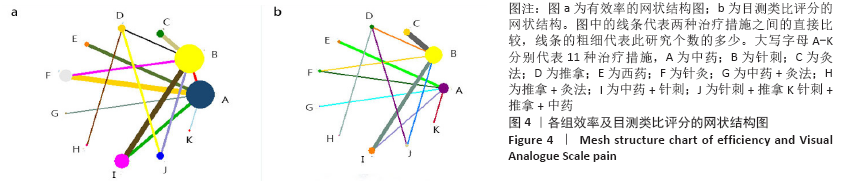
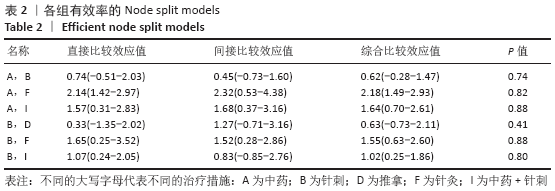
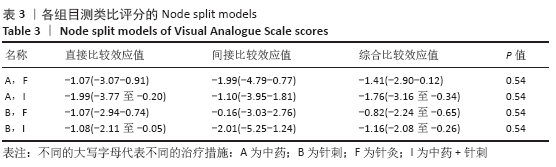
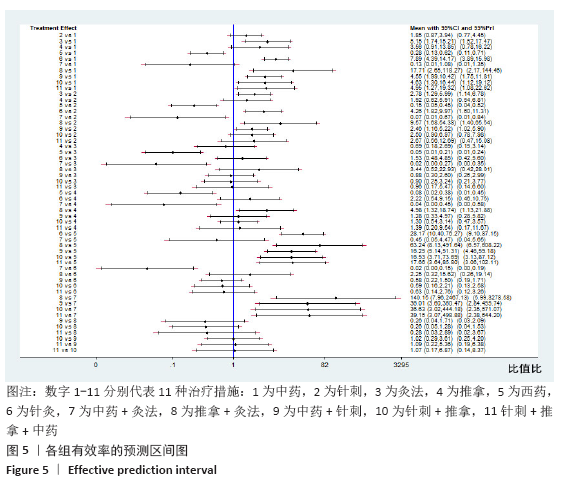
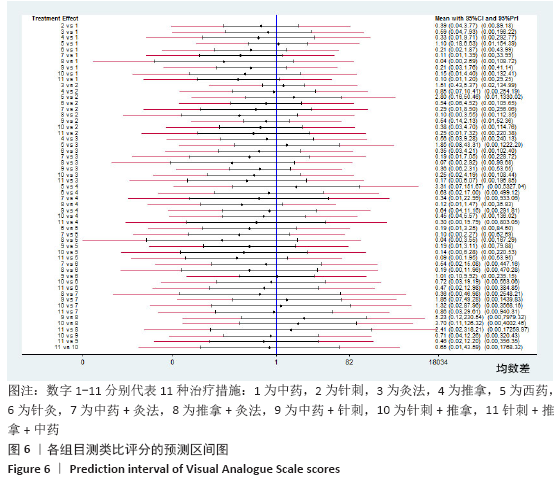
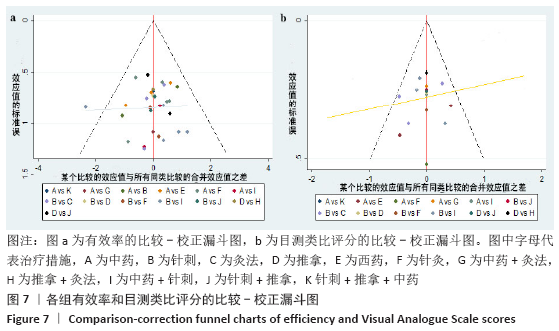
方法:检索中国期刊全文数据库、维普中文科技期刊全文数据库、万方数据期刊论文资源、PubMed、The Cochrane Library英文数据库中有关中医疗法治疗血瘀型腰椎间盘突出症的随机对照试验,检索日期为各数据库建立到2020年2月。由2名研究员根据设定好的标准独立筛选文献、数据提取及质量和风险偏倚评估。应用Stata 14.2软件绘制网状结构图、预测区间图及发表偏倚的比较-校正漏斗图,采用Ge MTC 0.14.3版本软件进行网状Meta分析。
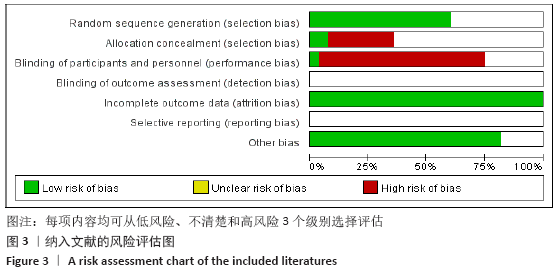
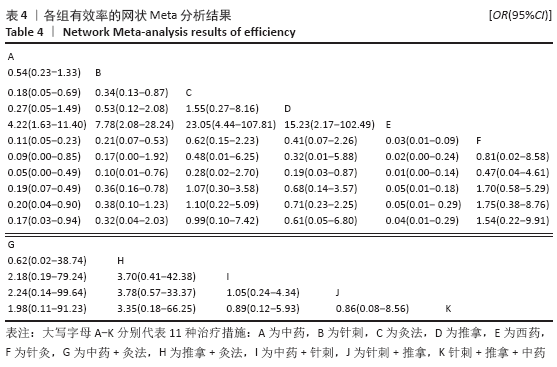
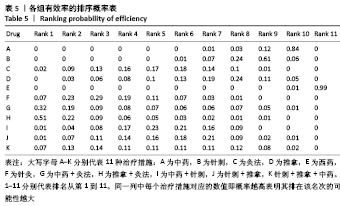
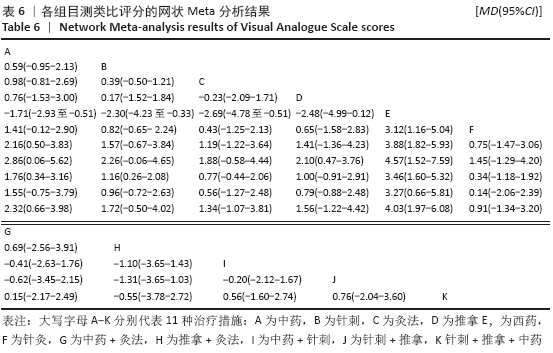
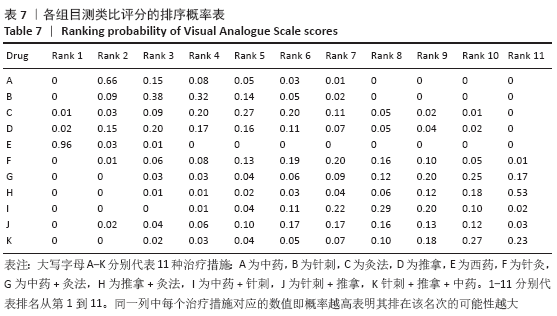
结果:①文章共纳入28个随机对照试验,合计2 508例腰椎间盘突出症患者,涉及中药、针刺、灸法、推拿、西药、针灸、中药+灸法、推拿+灸法、中药+针刺、针刺+推拿、针刺+推拿+中药11种治疗措施;②根据Cochrane偏倚风险工具评价结果,总结得到纳入的28篇文献中有21篇文章评价为高风险,7篇文章评价为不清楚;③网状Meta分析结果显示:在有效率上,其他治疗措施均优于西药,灸法、针灸、中药+灸法、推拿+灸法、中药+针刺、针刺+推拿、针刺+推拿+中药均优于中药,灸法、针灸、推拿+灸法、中药+针刺均优于针刺,推拿+灸法优于推拿;④目测类比评分上,其他治疗均优于西药,中药+灸法、推拿+灸法、中药+针刺、针刺+推拿+中药优于中药;⑤有效率从优到劣依次为推拿+灸法>中药+灸法>针灸>针刺+推拿+中药>中药+针刺>灸法>针刺+推拿>推拿>针刺>中药>西药;⑥目测类比评分从优到劣依次为推拿+灸法>针刺+推拿+中药>中药+灸法>中药+针刺>针灸>针刺+推拿>灸法>推拿>针刺>中药>西药。
结论:根据现有的研究证据显示,推拿+灸法优于其他10种干预措施且从中看出联合疗法多优于单独疗法,故确切的结果仍需要大量的随机对照试验来证明。
中图分类号: