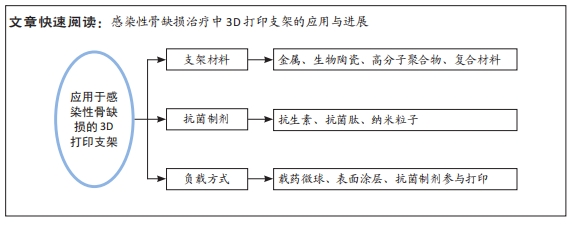
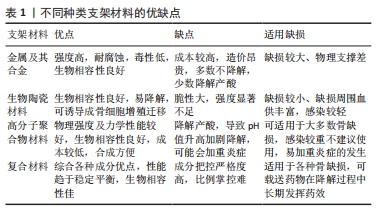
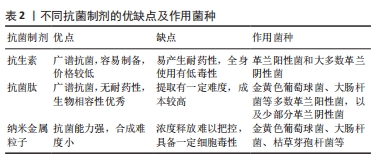
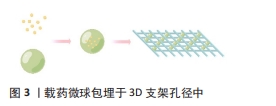
[1] SCHWARZ EM, PARVIZI J, GEHRKE T, et al. 2018 International consensus meeting on musculoskeletal infection: research priorities from the general assembly questions. J Orthop Res. 2019;37(5):997-1006.
[2] YANO MH, KLAUTAU GB, DA SILVA CB, et al. Improved diagnosis of infection associated with osteosynthesis by use of sonication of fracture fixation implants. J Clin Microbiol. 2014;52:4176-4182.
[3] IIKURA T, LEE SY, SAKAI Y, et al. Causative factors of fracture nonunion: the proportions of mechanical, biological, patient- dependent , and patient- independent factors. Orthop Sci. 2014;19(1):120-124.
[4] METSEMAKERS WJ, KUEHL R, MORIARTY TF, et al. Infection after fracture fixation: Current surgical and microbiological concepts. Injury. 2018;49(3): 511-522.
[5] 王进,葛建飞,郭开今,等.3D打印多孔材料应用于骨缺损修复的研究进展[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2019,12(7):556-560.
[6] ZHU W, MA X, GOU M, et al. 3D printing of functional biomaterials for tissue engineering. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2016;40:103-112.
[7] 贺超,王磊,李国远,等.3D打印在骨科的应用[J].中华骨科杂志,2017, 37(19):1235-1241.
[8] QIAO S, WU D, LI Z, et al. The combination of multi-functional ingredients-loaded hydrogels and three-dimensional printed porous titanium alloys for infective bone defect treatment. J Tissue Eng. 2020;11:2041731420965797.
[9] ZHOU W, YAN J, LI Y, et al. Based on the synergistic effect of Mg2+ and antibacterial peptides to improve the corrosion resistance, antibacterial ability and osteogenic activity of magnesium-based degradable metals. Biomater Sci. 2021; 9(3): 807-825.
[10] WANG H, SU K, SU L, et al. Comparison of 3D-printed porous tantalum and titanium scaffolds on osteointegration and osteogenesis. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2019;104:109908.
[11] ABDUL HALIM NA, HUSSEIN MZ, KANDAR MK. Nanomaterials-Upconverted Hydroxyapatite for Bone Tissue Engineering and a Platform for Drug Delivery. Int J Nanomedicine. 2021;16:6477-6496.
[12] KASTEN P, BEYEN I, BORMANN D, et al. The effect of two point mutations in GDF-5 on ectopic bone formation in a beta-tricalciumphosphate scaffold. Biomaterials. 2010;31(14):3878-3884.
[13] 吴重草,郇志广,朱钰方,等.3D打印HA微球支架的制备与表征[J].无机材料学报,2021,36(6):601-607.
[14] 段钢,陈宏亮,郭开今,等.3D打印β-磷酸三钙仿生骨支架修复兔股骨髁骨缺损[J].骨科临床与研究杂志,2020,5(4):243-250.
[15] EL-RASHIDY AA, ROETHER JA, HARHAUS L, et al. Regenerating bone with bioactive glass scaffolds: A review of in vivo studies in bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2017;62:1-28.
[16] BAINO F, VITALE-BROVARONE C. Mechanical properties and reliability of glass-eceramic foam scaffolds for bone repair. Mater Lett. 2014;(118):27-30.
[17] SEDDIGHIAN A, GANJI F, BAGHABAN-ESLAMINEJAD M, et al. Electrospun PCL scaffold modified with chitosan nanoparticles for enhanced bone regeneration. Prog Biomater. 2021;10(1):65-76.
[18] MOGHADDASZADEH A, SEDDIQI H, NAJMODDIN N, et al. Biomimetic 3D-printed PCL scaffold containing a high concentration carbonated-nanohydroxyapatite with immobilized-collagen for bone tissue engineering: enhanced bioactivity and physicomechanical characteristics. Biomed Mater. 2021;16(6). doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ac3147.
[19] BAI J, WANG H, GAO W, et al. Melt electrohydrodynamic 3D printed poly (ε-caprolactone)/polyethylene glycol/roxithromycin scaffold as a potential anti-infective implant in bone repair. Int J Pharm. 2020;576:118941.
[20] JIN S, XIA X, HUANG J, et al. Recent advances in PLGA-based biomaterials for bone tissue regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2021;127:56-79.
[21] SONG X, LI X, WANG F, et al. Bioinspired Protein/Peptide Loaded 3D Printed PLGA Scaffold Promotes Bone Regeneration. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022;10:832727.
[22] TURNBULL G, CLARKE J, PICARD F, et al. 3D bioactive composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Bioact Mater. 2017;3(3):278-314.
[23] RAJABI M, MCCONNELL M, CABRAL J, et al. Chitosan hydrogels in 3D printing for biomedical applications. Carbohydr Polym. 2021;260:117768.
[24] HERMENEAN A, CODREANU A, HERMAN H, et al. Chitosan-Graphene Oxide 3D scaffolds as Promising Tools for Bone Regeneration in Critical-Size Mouse Calvarial Defects. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):16641-16612.
[25] 郑扬,李危石,刘忠军.骨组织3D打印: 骨再生的未来[J].北京大学学报( 医学版),2015,47(2):203-206.
[26] BABILOTTE J, MARTIN B, GUDURIC V, et al. Development and characterization of a PLGA-HA composite material to fabricate 3D-printed scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2021;118:111334.
[27] YANG Y, CHU L, YANG S, et al. Dual-functional 3D-printed composite scaffold for inhibiting bacterial infection and promoting bone regeneration in infected bone defect models. Acta Biomater. 2018;79:265-275.
[28] WANG Y, WANG J, GAO R, et al. Biomimetic glycopeptide hydrogel coated PCL/nHA scaffold for enhanced cranial bone regeneration via macrophage M2 polarization-induced osteo-immunomodulation. Biomaterials. 2022; 285:121538.
[29] TRAMPUZ A, ZIMMERLI W. Diagnosis and treatment of infections associated with fracture-fixation devices. Injury. 2006;37: 59-66.
[30] WRIGHT GD. Antibiotic Adjuvants: Rescuing Antibiotics from Resistance. Trends Microbiol. 2016;24(11):862-871.
[31] 许刚,何纯青,张飞,等.低温3D打印复合万古霉素/PLGA/TCP骨修复材料的制备与性能评估[J].中国美容医学,2021,30(5):59-62.
[32] WANG M, LI H, YANG Y, et al. A 3D-bioprinted scaffold with doxycycline-controlled BMP2-expressing cells for inducing bone regeneration and inhibiting bacterial infection. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(5):1318-1329.
[33] CICUÉNDEZ M, DOADRIO JC, HERNÁNDEZ A, et al. Multifunctional pH sensitive 3D scaffolds for treatment and prevention of bone infection. Acta Biomater. 2018;65:450-461.
[34] 李善龙,从凯,尚剑,等.抗生素缓释载体在慢性骨髓炎治疗中的应用进展[J].临床与病理杂志,2021,41(4):934-941.
[35] 辛本凯,王会岩.抗菌肽在抗菌材料中的研究进展[J].吉林医药学院学报,2021,42(1):53-55.
[36] YAN Y, LI Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Advances of peptides for antibacterial applications. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2021;202:111682.
[37] LI C, XU X, GAO J, et al. 3D printed scaffold for repairing bone defects in apical periodontitis. BMC Oral Health. 2022;22(1):327.
[38] KARAMAT-ULLAH N, DEMIDOV Y, SCHRAMM M, et al. 3D Printing of Antibacterial, Biocompatible, and Biomimetic Hybrid Aerogel-Based Scaffolds with Hierarchical Porosities via Integrating Antibacterial Peptide-Modified Silk Fibroin with Silica Nanostructure. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021; 7(9):4545-4556.
[39] WANG L, HU C, SHAO L. The antimicrobial activity of nanoparticles:present situation and prospects for the future. Int J Nanomed. 2017;12:1227-1249.
[40] JANCZAK K, KOSMALSKA D, KACZOR D, et al. Bactericidal and Fungistatic Properties of LDPE Modified with a Biocide Containing Metal Nanoparticles. Materials (Basel). 2021;14(15):4228.
[41] TANG S, ZHENG J. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: Structural Effects. Adv Healthc Mater. 2018;7(13):e1701503.
[42] WENG W, LI X, NIE W, et al. One-Step Preparation of an AgNP-nHA@RGO Three-Dimensional Porous Scaffold and Its Application in Infected Bone Defect Treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2020;15:5027-5042.
[43] 张昌,任恩,庞鑫,等.光动力抗菌纳米制剂研究进展[J].中国激光, 2020,47(2):163-170.
[44] LI M, MA Z, ZHU Y, et al. Toward a Molecular Understanding of the Antibacterial Mechanism of Copper-Bearing Titanium Alloys against Staphylococcus aureus. Adv Healthc Mater. 2016;5(5):557-566.
[45] LU Y, LI L, ZHU Y, et al. Multifunctional Copper-Containing Carboxymethyl Chitosan/Alginate Scaffolds for Eradicating Clinical Bacterial Infection and Promoting Bone Formation. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2018;10(1): 127-138.
[46] LEYLAND NS, PODPORSKA-CARROLL J, BROWNE J, et al. Cu doped TiO2 anti-bacterial visible light active photocatalytic coatings to combat hospital-acquired infections. Sci Rep. 2016;6:24770.
[47] 李仕明,李永亮,毛傲飞,等.支架载药微纳结构的加工进展[J].激光杂志,2018,39(3):1-4.
[48] 谭浩,周建平,许燕,等.3D打印异烟肼载药微球支架及体外释药研究[J].燕山大学学报,2022,46(1):38-45.
[49] ZHOU Z, YAO Q, LI L, et al. Antimicrobial Activity of 3D-Printed Poly(ε-Caprolactone) (PCL) Composite Scaffolds Presenting Vancomycin-Loaded Polylactic Acid-Glycolic Acid (PLGA) Microspheres. Med Sci Monit. 2018;24: 6934-6945.
[50] HAN X, SUN M, CHEN B, et al. Lotus seedpod-inspired internal vascularized 3D printed scaffold for bone tissue repair. Bioact Mater. 2020;6(6):1639-1652.
[51] HESS U, SHAHABI S, TRECCANI L, et al. Co-delivery of cisplatin and doxorubicin from calcium phosphate beads/matrix scaffolds for osteosarcoma therapy. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2017;77:427-435.
[52] YANG Y, YANG S, WANG Y, et al. Anti-infective efficacy, cytocompatibility and biocompatibility of a 3D-printed osteoconductive composite scaffold functionalized with quaternized chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2016;46:112-128.
[53] ZHANG S, SHI X, MIAO Z, et al. 3D-Printed Polyurethane Tissue‐Engineering Scaffold with Hierarchical Microcellular Foam Structure and Antibacterial Properties. Adv Eng Mater. 2022;24(3):2101134.
[54] BUYUKSUNGUR S, ENDOGAN TANIR T, BUYUKSUNGUR A, et al. 3D printed poly(ε-caprolactone) scaffolds modified with hydroxyapatite and poly(propylene fumarate) and their effects on the healing of rabbit femur defects. Biomater Sci. 2017;5(10):2144-2158.
[55] SHAO J, MA J, LIN L, et al. Three-Dimensional Printing of Drug-Loaded Scaffolds for Antibacterial and Analgesic Applications. Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2019;25(4):222-231.
[56] YANG N, LIU Y. The Role of the Immune Microenvironment in Bone Regeneration. Int J Med Sci. 2021;18(16):3697-3707.
[57] LIU X, CHEN M, LUO J, et al. Immunopolarization-regulated 3D printed-electrospun fibrous scaffolds for bone regeneration. Biomaterials. 2021; 276:121037.
[58] HU W, CHEN Y, DOU C, et al. Microenvironment in subchondral bone: predominant regulator for the treatment of osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021;80(4):413-422.
[59] ERIKSEN EF. Cellular mechanisms of bone remodeling. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2010,11(4):219-227.
[60] SALHOTRA A, SHAH HN, LEVI B, et al. Mechanisms of bone development and repair. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2020;21(11):696-711. |