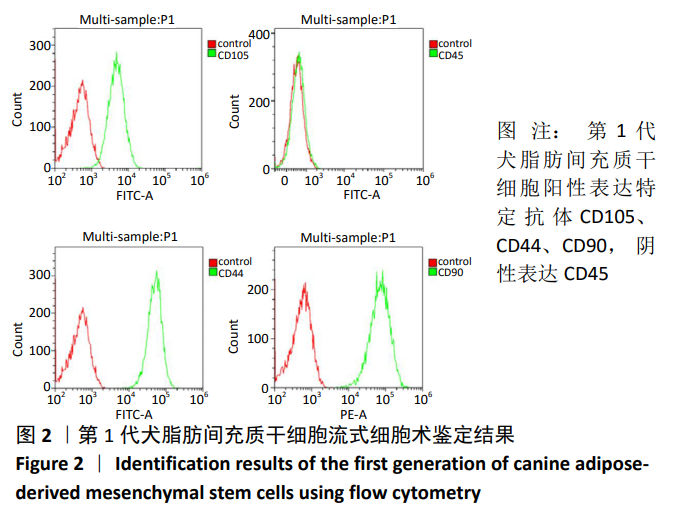
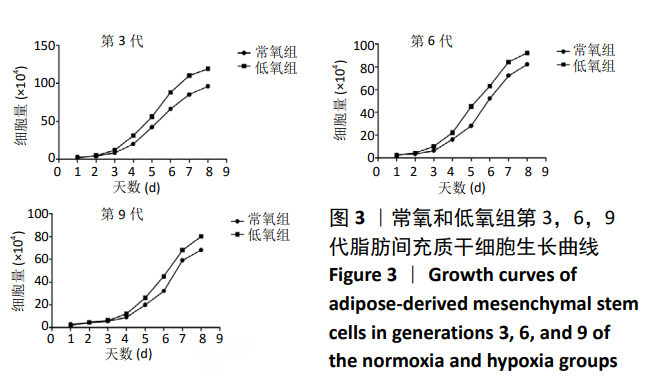
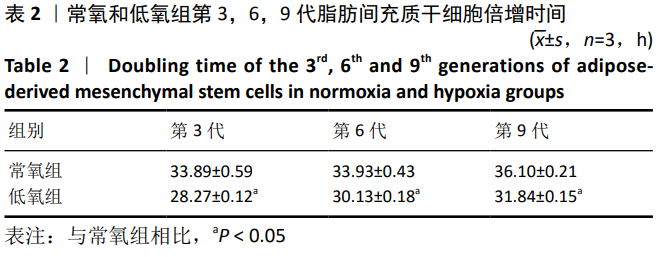
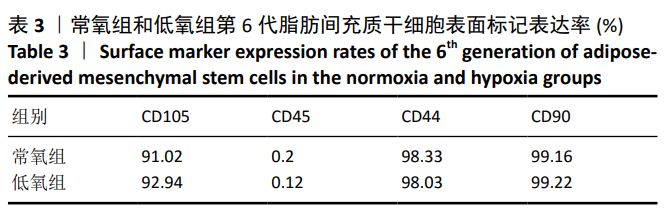
[1] WANG JM, GU Y, PAN CJ, et al. Isolation, culture and identification of human adipose-derived stem cells. Exp Ther Med. 2017;13(3): 1039-1043.
[2] FOUBERT P, GONZALEZ AD, TEODOSESCU S, et al. Adipose-Derived Regenerative Cell Therapy for Burn Wound Healing: A Comparison of Two Delivery Methods. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2016; 5(7):288-298.
[3] SHEYKHHASAN M, QOMI RT, GHIASI M. Fibrin Scaffolds Designing in order to Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Differentiation to Chondrocytes in the Presence of TGF-β3. Int J Stem Cells. 2015;8(2):219-227.
[4] SAMBERG M, STONE R 2ND, NATESAN S, et al. Platelet rich plasma hydrogels promote in vitro and in vivo angiogenic potential of adipose-derived stem cells. Acta Biomater. 2019;87:76-87.
[5] DUSCHER D, MAAN ZN, LUAN A, et al. Ultrasound-assisted liposuction provides a source for functional adipose-derived stromal cells. Cytotherapy. 2017;19(12):1491-1500.
[6] 刘琴,王丽平,陈芳,等.脂肪干细胞分离研究进展[J].华南国防医学杂志, 2018,32(4): 281-285.
[7] 王倩,刘羿,张雨,等.低氧条件下人脂肪间充质干细胞分泌多种细胞因子的水平[J].中国组织工程研究, 2019,23(29): 4681-4687.
[8] ZHAO L, JOHNSON T, LIU D. Therapeutic angiogenesis of adipose-derived stem cells for ischemic diseases. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2017;8(1): 125.
[9] RYLOVA JV, ANDREEVA ER, GOGVADZE VG, et al. Etoposide and hypoxia do not activate apoptosis of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells in vitro. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2012;154(1):141-144.
[10] CHUNG HM, WON CH, SUNG JH. Responses of adipose-derived stem cells during hypoxia: enhanced skin-regenerative potential. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2009;9(12):1499-1508.
[11] REN ML, PENG W, YANG ZL, et al. Allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells with low immunogenicity constructing tissue-engineered bone for repairing bone defects in pigs. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(12):2711-2721.
[12] CHOI J, MINN KW, CHANG H. The efficacy and safety of platelet-rich plasma and adipose-derived stem cells: an update. Arch Plast Surg. 2012;39(6):585-592.
[13] 王立维,赵渝,黄旭,等.氧体积分数变化与大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及迁移[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(19): 3442-3446.
[14] SIMON MC, KEITH B. The role of oxygen availability in embryonic development and stem cell function. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2008;9(4): 285-296.
[15] 刘林奇,鲁峰,王量,等.低氧预处理对人脂肪来源干细胞增殖和分化潜能影响的研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志, 2015,26(4): 231-234.
[16] STUBBS SL, HSIAO ST, PESHAVARIYA HM, et al. Hypoxic preconditioning enhances survival of human adipose-derived stem cells and conditions endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(11):1887-1896.
[17] YAMAMOTO Y, FUJITA M, TANAKA Y, et al. Low oxygen tension enhances proliferation and maintains stemness of adipose tissue-derived stromal cells. Biores Open Access. 2013;2(3):199-205.
[18] KIM JH, SONG SY, PARK SG, et al. Primary involvement of NADPH oxidase 4 in hypoxia-induced generation of reactive oxygen species in adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2012;21(12):2212-2221.
[19] KIM JH, PARK SH, PARK SG, et al. The pivotal role of reactive oxygen species generation in the hypoxia-induced stimulation of adipose-derived stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(10):1753-1761.
[20] 陈犹白,陈聪慧, QIXU ZHANG, 等.脂肪干细胞表型和标记物的研究进展[J].中国美容医学, 2016,25(3): 91-100.
[21] LE BLANC K, FRASSONI F, BALL L, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of steroid-resistant, severe, acute graft-versus-host disease: a phase II study. Lancet. 2008;371(9624):1579-1586.
[22] GUSTAFSSON MV, ZHENG X, PEREIRA T, et al. Hypoxia requires notch signaling to maintain the undifferentiated cell state. Dev Cell. 2005;9(5):617-628.
[23] 杨记农,姜亦瑶,袁超,等.不同氧体积分数下脂肪间充质干细胞和脐带间充质干细胞的旁分泌能力[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(21): 3322-3327.
[24] LEE HM, JOO BS, LEE CH, et al. Effect of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 on the Differentiation of Adipose-derived Stem Cells into Osteoblasts and Adipocytes. J Menopausal Med. 2015;21(2):93-103.
[25] ISAKSON M, DE BLACAM C, WHELAN D, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Cutaneous Wound Healing: Current Evidence and Future Potential. Stem Cells Int. 2015;2015:831095.
[26] 罗冬章,罗惠娜,詹小舒,等.猫4种不同来源间充质干细胞的生物学特性比较[J].生物技术通报, 2019,35(7): 39-45.
[27] VALORANI MG, MONTELATICI E, GERMANI A, et al. Pre-culturing human adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells under hypoxia increases their adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation potentials. Cell Prolif. 2012;45(3):225-238.
[28] XU L, SUN X, CAO K, et al. Hypoxia induces osteogenesis in rabbit adipose-derived stem cells overexpressing bone morphogenic protein-2. Oral Dis. 2014;20(5):430-439.
[29] FOTIA C, MASSA A, BORIANI F, et al. Prolonged exposure to hypoxic milieu improves the osteogenic potential of adipose derived stem cells. J Cell Biochem. 2015;116(7):1442-1453.
[30] KIM JH, KIM SH, SONG SY, et al. Hypoxia induces adipocyte differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells by triggering reactive oxygen species generation. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(1):32-40.
|