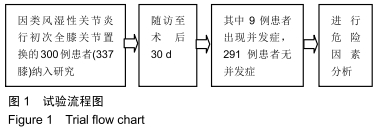
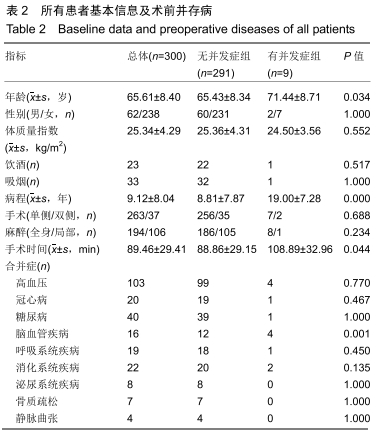
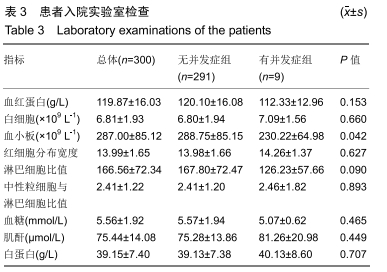
[1] BLEVINS JL, CHIU YF, LYMAN S, et al. Comparison of expectations and outcomes in rheumatoid arthritis versus osteoarthritis patients undergoing total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(9): 1946-1952.e2.
[2] YOSHIHARA H, YONEOKA D, MARGALIT A, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis patients undergoing total hip and knee arthroplasty have better in-hospital outcomes compared with non-rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2016;34(2): 270-275.
[3] CRAWFORD DA, ADAMS JB, BEREND KR, et al. Low complication rates in outpatient total knee arthroplasty. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019.
[4] PATEL H, KHOURY H, GIRGENTI D, et al. Burden of surgical site infections associated with arthroplasty and the contribution of staphylococcus aureus. Surg Infect. 2016;17(1):78.
[5] REEVES RA, SCHAIRER WW, JEVSEVAR DS. The national burden of periprosthetic hip fractures in the US: costs and risk factors for hospital readmission. Hip Int. 2019;29(5):550-557.
[6] BOHL DD, ONDECK NT, BASQUES BA, et al. What is the timing of general health adverse events that occur after total joint arthroplasty? Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2017;475(12):2952-2959.
[7] JOHNSON DJ, HARTWELL MJ, WEINER JA, et al. Which post-operative day after total joint arthroplasty are catastrophic events most likely to occur? Jarthroplasty. 2019.
[8] YOO JY, O'MALLEY MJ, MATSEN KO LJ, et al. Knee arthroplasty after subchondroplasty: early results, complications, and technical challenges. J Arthroplasty, 2016;31(10): 2188-2192.
[9] JOHNSON DJ, HARTWELL MJ, WEINER JA, et al. Which postoperative day after total joint arthroplasty are catastrophic events most likely to occur? J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(10):2466-2472.
[10] WARREN JA, SUNDARAM K, KAMATH AF, et al. Venous thromboembolism rates did not decrease in lower extremity revision total joint arthroplasty from 2008 to 2016. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(11): 2774-2779.
[11] TANG H, LI H, ZHANG S, et al. Postoperative complications causing readmission in 30 days after total knee arthroplasty: a retrospective nested case-control study of risk factors based on propensity score matching. J Knee Surg. 2019. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1692630.
[12] HART A, KHALIL JA, CARLI A, et al. Blood transfusion in primary total hip and knee arthroplasty. Incidence, risk factors, and thirty-day complication rates. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(23):1945-1951.
[13] BOTTLE A, PARIKH S, AYLIN P, et al. Risk factors for early revision after total hip and knee arthroplasty: National observational study from a surgeon and population perspective. PloS One. 2019;14(4): e0214855-e0214855.
[14] BAIER C, ADELMUND S, SCHWAB F, et al. Incidence and risk factors of surgical site infection after total knee arthroplasty: Results of a retrospective cohort study. Am J Infect Control.2019;47(10): 1270-1272.
[15] TAY KS, CHER EWL, ZHANG K, et al. Comorbidities have a greater impact than age alone in the outcomes of octogenarian total knee arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2017;32(11): 3373-3378.
[16] VAKHARIA RM, VAKHARIA AM, EHIOROBO JO, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis increases venous thromboemboli, readmissions, and costs of care after primary total knee arthroplasty: a matched-control analysis. J Arthroplasty. 2019. pii: S0883-5403(19)31003-4.
[17] CORDTZ R, ODGAARD A, KRISTENSEN LE, et al. Risk of medical complications following total hip or knee arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A register-based cohort study from Denmark. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2019. pii: S0049-0172(19)30281-1.
[18] VAKHARIA AM, COHEN-LEVY WB, VAKHARIA RM, et al. Perioperative complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis following primary total knee arthroplasty: an analysis of 102,898 patients. J Knee Surg. 2019;32(11):1075-1080.
[19] CANCIENNE JM, WERNER BC, BROWNE JA. Complications of primary total knee arthroplasty among patients with rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, and osteoarthritis. J Am Acad Orthop Surg. 2016;24(8): 567-574.
[20] SINGH JA, INACIO MC, NAMBA RS, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis is associated with higher ninety-day hospital readmission rates compared to osteoarthritis after hip or knee arthroplasty: a cohort study. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015;67(5):718-724.
[21] PUGELY AJ, CALLAGHAN JJ, MARTIN CT, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for 30-day readmission following elective primary total joint arthroplasty: analysis from the ACS-NSQIP. J Arthroplasty, 2013;28(9): 1499-1504.
[22] STUNDNER O, CHIU Y, SUN X, et al. Perioperative outcomes in patients with rheumatoid versus osteoarthritis for total hip arthroplasty: a population-based study. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2013; 31(6): 889-895.
[23] STUNDNER O, DANNINGER T, CHIU YL, et al. Rheumatoid arthritis vs osteoarthritis in patients receiving total knee arthroplasty: perioperative outcomes. J Arthroplasty. 2014; 29(2): 308-313.
[24] RAVI B, CROXFORD R, HOLLANDS S, et al. Increased risk of complications following total joint arthroplasty in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014;66(2): 254-263.
[25] SIU KT, NG FY, CHAN PK, et al. Bacteriology and risk factors associated with periprosthetic joint infection after primary total knee arthroplasty: retrospective study of 2543 cases. Hong Kong Med J. 2018;24(2):152-157.
[26] ALETAHA D, NEOGI T, SILMAN AJ, et al. 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62(9):2569-2581.
[27] BELMONT PJ, GOODMAN GP, WATERMAN BR, et al. Thirty-day postoperative complications and mortality following total knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2014;96(1): 20-26.
[28] DIXON W, WATSON K, LUNT M, et al. Rates of serious infection, including site-specific and bacterial intracellular infection, in rheumatoid arthritis patients receiving anti–tumor necrosis factor therapy: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54(8):2368-2376.
[29] HUNTER TM, BOYTSOV NN, ZHANG X, et al. Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in the United States adult population in healthcare claims databases, 2004–2014. Rheumatol Int. 2017;37(9): 1551-1557.
[30] MURPHY BPD, DOWSEY MM, SPELMAN T, et al. The impact of older age on patient outcomes following primary total knee arthroplasty. Bone Joint J. 2018;100-B(11):1463-1470.
[31] SEO JG, MOON YW, CHO BC, et al. Is total knee arthroplasty a viable treatment option in octogenarians with advanced osteoarthritis? Knee Surg Relat Res. 2015;27(4): 221-227.
[32] ROSS D, ERKOCAK O, RASOULI MR, et al. Operative time directly correlates with blood loss and need for blood transfusion in total joint arthroplasty. Arch Bone Joint Surg. 2019;7(3): 229-234.
[33] SODHI N, ANIS HK, GOLD PA, et al. Operative times can predict and are correlated with lengths-of-stay in primary total knee arthroplasty: a nationwide database study. J Arthroplasty. 2019;34(7): 1328-1332.
[34] GEORGE J, MAHMOOD B, SULTAN AA, et al. How fast should a total knee arthroplasty be performed? An analysis of 140,199 surgeries. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(8): 2616-2622.
[35] WANG L, SEOK S, KIM S, et al. The risk factors of postoperative delirium after total knee arthroplasty. J Knee Surg. 2017;30(6): 600-605.
[36] ZENG Y, SI H, WU Y, et al. The incidence of symptomatic in-hospital VTEs in Asian patients undergoing joint arthroplasty was low: a prospective, multicenter, 17,660-patient-enrolled cohort study. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2019; 27(4): 1075-1082.
[37] BROWN CH 4TH, FAIGLE R, KLINKER L, et al. The association of brain mri characteristics and postoperative delirium in cardiac surgery patients. Clin Ther. 2015; 37(12): 2686-2699.e2689.
[38] 马利阁,尹万乐,尤笑迎.全髋关节置换术后老年患者感染发生相关因素分析[J]. 中华老年医学杂志, 2018, 37(5): 550-553.
|