| [1] Li B, He X, Jia W, et al. Novel applications of metabolomics in personalized medicine: a mini-review. Molecules. 2017;22(7): 1173.[2] 吴清平,李玉冬,张菊梅.常见食源性致病菌代谢组学研究进展[J].微生物学通报,2016,43(3):609-618.[3] Wang P, Wu Y. Applications of metabonomics in pesticide toxicology. Curr Drug Metab. 2015;16(3):191-199.[4] Han B, Huang HZ, Li Z, et al. Therapeutic effects of Chinese medicine herb pair, Huzhang and Guizhi, on monosodium urate crystal-induced gouty arthritis in rats revealed by anti-inflammatory assessments and NMR-based metabonomics. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2016;2016:9398435.[5] 于正,梁繁荣.代谢组学在心血管疾病方面的研究进展[J].中国医学科学院学报,2012,34(4):413-417.[6] 楚淑芳,李惠林,刘德亮,等.2型糖尿病血瘀证患者血浆代谢组学特征[J].中医杂志,2017,58(8):664-668,672.[7] 彭琳秀,陈良慧,狄留庆,等.基于UPLC/LTQ-Orbitrap-MS技术的复方祖师麻片抗类风湿关节炎的血浆代谢组学研究[J].中草药, 2017,48(10):1964-1970.[8] Ni Y, Xie G, Jia W. Metabonomics of human colorectal cancer: new approaches for early diagnosis and biomarker discovery. J Proteome Res.2014;13(9):3857-3870.[9] 高仰贤,江蓉星.骨性关节炎发病机制的国内研究进展[J].中医正骨,2005,17(4):55-57.[10] 汪永忠,柳清,姜辉,等.基于气相色谱-飞行时间质谱技术的佐剂性关节炎大鼠尿液代谢组学的研究[J].色谱, 2016,34(6): 602-607.[11] Priori R, Scrivo R, Brandt J, et al. Metabolomics in rheumatic diseases: the potential of an emerging methodology for improved patient diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment efficacy. Autoimmun Rev.2013;12(10):1022-1030.[12] 孙明翠.痛风冲剂治疗急性痛风性关节炎的临床疗效观察及花生四烯酸代谢代谢组学分析[D].上海中医药大学,2007.[13] Denery JR, Nunes AK, and Dickerson TJ. Quality assurance procedures for mass spectrometry untargeted metabolomics: a review. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2011; 83 (3):1040–1047.[14] Begou O, Gika HG, Wilson ID, et al. Hyphenated MS-based targeted approaches in metabolomics. Analyst.2017;142(17): 3079-3100. [15] 张宁,于栋华,王宇,等.穿山龙抗急性痛风性关节炎的肾脏代谢组学研究[J].中华中医药杂志, 2017,32(05):2034-2039.[16] 刘树民,张宁,于栋华,等.穿山龙抗急性痛风性关节炎的肝脏代谢组学研究[J].中国中药杂志,2017;42(10):1971-1978.[17] Hugle T, Kovacs H, Heijnen IA, et al. Synovial fluid metabolomics in different forms of arthritis assessed by nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30(2):240-245.[18] 杨刚.基于UPLC/Q-TOF-MS的骨性关节炎软骨下骨硬化的代谢组学研究[D]. 重庆医科大学, 2016。[19] 袁博,王金海,方晓丽,等.热补针法对寒证类风湿关节炎模型家兔滑膜组织代谢物谱的影响[J].中国老年学杂志, 2017;37(4): 800-804.[20] 王斯婷,李晓娜,王皎,等.代谢组学及其分析技术[J].药物分析杂志, 2010,09(30):1792-1797.[21] 陆艳,周学平,谢彤.类风湿关节炎的代谢组学研究进展[J].中华中医药杂志, 2015,10:3585-3588.[22] 杜小正,袁博,王金海,等.热补针法对寒证类风湿关节炎模型家兔滑膜组织代谢物的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2017;24(2): 55-59.[23] Qi Y, Pi Z, Liu S, et al. Urinary metabonomics study of Wu-tou-tang and its co-decoction with Pinelliae Rhizoma in adjuvant-induced arthritis rats. Chin Chem Lett.2015;26(3): 387-390.[24] 颉旺军,蒲瑞生,方晓丽,等.颊针对类风湿关节炎家兔血浆代谢物表达的影响[J].中国中医药信息杂志, 2017,24(05):57-62.[25] 戴七一,覃学流,韩杰,等.基于1HNMR平台探讨揉髌手法对兔膝关节骨关节炎模型血清代谢组学的影响[J].广西中医药大学学报,2017,20(01):1-5.[26] 杨贵尊. 关节1号方对兔膝骨关节炎血清脂质代谢组学生化模式影响的初步研究[D]. 上海中医药大学,2011.[27] Zhai G, Wang-Sattler R, Hart DJ, et al. Serum branched-chain amino acid to histidine ratio: a novel metabolomic biomarker of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis.2010;69(6):1227-1231.[28] Walsh DA, McWilliams DF, Turley MJ, et al. Angiogenesis and nerve growth factor at the osteochondral junction in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Rheumatology.2010; 49(10):1852-1861.[29] Wen S, Liu Y, Yin H, et al. Effect of acupuncture on rats with acute gouty arthritis inflammation: a metabonomic method for profiling of both urine and plasma metabolic perturbation. Am J Chin Med.2011;39 (2):287-300.[30] 郭苏健,姚博,赵延龙,等.类风湿关节炎的中医药治疗优势[J].中华中医药学刊, 2017,7:1769-1771.[31] 陈永新,李涛,孙世光. 蚁参蠲痹胶囊治疗类风湿关节炎的系统评价与Meta分析[J]. 中医杂志, 2017(09):756-758.[32] Lu WW, Zhang JM, Lv ZT, et al. Update on the clinical effect of acupuncture therapy in patients with gouty arthritis: systematic review and meta-analysis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2016,2016:9451670.[33] 汪永忠,柳清,姜辉,等.基于气相色谱-飞行时间质谱技术的佐剂性关节炎大鼠尿液代谢组学的研究[J].色谱, 2016,34(6): 602-607.[34] 马俊杰,王小龙,刘会平.不同证型非小细胞肺癌患者肿瘤组织代谢组学研究[J].中国中西医结合杂志,2015,35(06):659-663.[35] van Wietmarschen HA, Dai W, van der Kooij AJ, et al. Characterization of rheumatoid arthritis subtypes using symptom profiles, clinical chemistry and metabolomics measurements. Plos One. 2012;7:e443319.[36] 崔扬,郭慧,匡海学,等.代谢组学技术在中医证型研究中的应用概述[J].中华中医药学刊,2017;32(2):672-673.[37] 柳青,汪永忠,姜辉,等.基于GC_TOF_MS研究威灵仙总皂苷对佐剂性关节炎大鼠血清代谢谱的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2016, 41(12):2321-2327.[38] 范仕成,高悦,张慧贞,等.非靶向和靶向代谢组学在药物靶点发现中的应用[J].药学进展, 2017,4:263-269.[39] 汪思媛,赵星阳,徐玮蔚,等.基于质谱技术的细胞代谢组学研究进展[J].中国细胞生物学学报,2017,8:1130-1134.[40] 陈艳华,张瑞萍,宋咏梅,等.基于快速高分辨液相色谱串联质谱技术的代谢组学尿液分析方法的建立[J].分析化学, 2011;39(2): 173-177.[41] 胡钢锋,肖鲁伟,童培建.关节液代谢组学在类风湿关节炎诊断及寒热证候分型中的应用[J].中医正骨,2015,27(1):5-8.[42] 朱航,蓝文贤,刘买利.代谢组学研究中样本间区分度的简易评判方法[J].分析化学, 2013,7:1000-1005.[43] 任向楠,梁琼麟.基于质谱分析的代谢组学研究进展[J].分析测试学报,2017,2:161-169.[44] Guan TY, Liang Y, Li CZ, et al. Recent development in liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry and allied topics for traditional Chinese medicine research. Chin J Nat Med. 2011;5(9):385-389.[45] Li J, Ren L, Sun G, et al. Gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) and its application in metabonomics. 2013:29:434-446.[46] 熊喜悦,盛小奇,王华,等.代谢组学气相色谱-质谱分析方法中样品衍生化技术的新进展[J]. 化学通报, 2015,07:602-607.[47] Guo HT, Niu XY,2, Gu Y, et al. Differential amino acid, carbohydrate and lipid metabolism perpetuations involved in a subtype of rheumatoid arthritis with Chinese medicine cold pattern.Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(10): 1757.[48] 郭慧,崔扬,王秋红,等.基于代谢组学技术的中药复方研究近况[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2017(1):213.[49] 王荔,刘晓慧.丹红注射液不良反应360例文献分析[J].中国药房, 2016,17:2352-2354.[50] 刘清平,孙骏炜,李楠,等.益肾蠲痹丸致不良反应的文献分析[J].中国药房,2017,28(5):618-620.[51] 李金洋,李军,王君明,等.雷公藤配伍减毒的研究进展及对策[J].中华中医药杂志,2017,2:676-679. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
非靶向代谢组学:在有限的研究和背景知识的基础上,对生物体内源性代谢物进行全面系统的、无偏向的代谢组学分析,从而找出差异代谢物。目前,非靶向代谢组学分析在疾病诊断与治疗机制研究等领域广泛应用,可以为疾病治疗机制或者疾病发病机制研究的瓶颈问题提供新的思路。
靶向代谢组学:针对特定的代谢物进行的有偏向的代谢组学分析。在非靶向代谢组学发现差异代谢物后,再进行靶向代谢组学进行系统的确证。
文题释义:
非靶向代谢组学:在有限的研究和背景知识的基础上,对生物体内源性代谢物进行全面系统的、无偏向的代谢组学分析,从而找出差异代谢物。目前,非靶向代谢组学分析在疾病诊断与治疗机制研究等领域广泛应用,可以为疾病治疗机制或者疾病发病机制研究的瓶颈问题提供新的思路。
靶向代谢组学:针对特定的代谢物进行的有偏向的代谢组学分析。在非靶向代谢组学发现差异代谢物后,再进行靶向代谢组学进行系统的确证。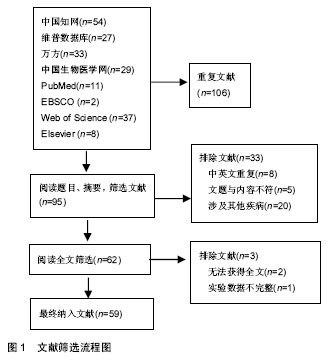

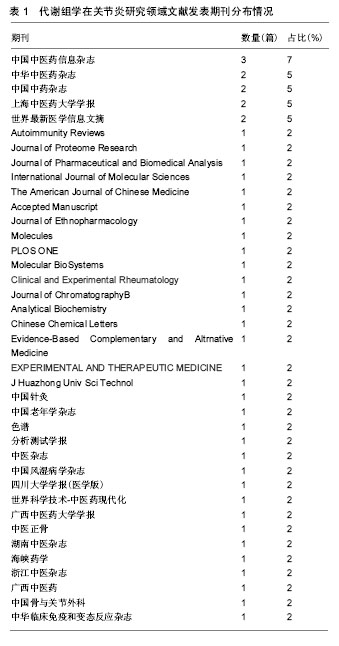
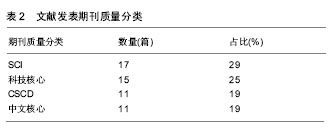

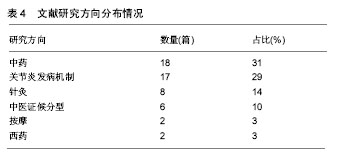

.jpg) 文题释义:
非靶向代谢组学:在有限的研究和背景知识的基础上,对生物体内源性代谢物进行全面系统的、无偏向的代谢组学分析,从而找出差异代谢物。目前,非靶向代谢组学分析在疾病诊断与治疗机制研究等领域广泛应用,可以为疾病治疗机制或者疾病发病机制研究的瓶颈问题提供新的思路。
靶向代谢组学:针对特定的代谢物进行的有偏向的代谢组学分析。在非靶向代谢组学发现差异代谢物后,再进行靶向代谢组学进行系统的确证。
文题释义:
非靶向代谢组学:在有限的研究和背景知识的基础上,对生物体内源性代谢物进行全面系统的、无偏向的代谢组学分析,从而找出差异代谢物。目前,非靶向代谢组学分析在疾病诊断与治疗机制研究等领域广泛应用,可以为疾病治疗机制或者疾病发病机制研究的瓶颈问题提供新的思路。
靶向代谢组学:针对特定的代谢物进行的有偏向的代谢组学分析。在非靶向代谢组学发现差异代谢物后,再进行靶向代谢组学进行系统的确证。