| [1] 秦泗河.骨外固定技术的发展与创新[J].中医正骨, 2012, 24(9): 3-7.[2] 张永明.骨骼骨折固定和愈合的力学分析与研究[D]. 哈尔滨工业大学, 2009.[3] 秦泗河,葛建忠,郭保逢.Ilizarov技术在中国大陆20年(1991~2011年)[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2012,20(7):662-666.[4] 王成.新型动力型Hoffmann外固定器的生物力学及临床研究[D].苏州大学, 2005.[5] 秦泗河.加深对骨外固定概念的认识,提高骨外固定技术水平[J].中华骨科杂志, 2012, 32(3):197-198.[6] 秦泗河,曲龙.骨外固定技术的发展史与骨科自然重建理念的形成[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(16): 1262-1265.[7] 陈德旺.骨应力刺激仪叩击治疗促进下肢骨干骨折愈合的临床研究[D].福建中医药大学, 2011.[8] 丁真奇,高俊.叩击式骨应力刺激仪促进闭合性胫骨干骨折愈合[J].临床骨科杂志,2006, 9(4):289-292.[9] Burkhart TA, Andrews DM,Dunning CE.Finite element modeling mesh quality, energy balance and validation methods: a review with recommendations associated with the modeling of bone tissue.J Biomech.2016;46(9):1477-1488.[10] Ali AA,Cristofolini L,Schileo E,et al.Specimen-specific modeling of hip fracture pattern and repair.J Biomech.2016;47(2):536-543.[11] Moroz TK, Finlay JB, Rorabeck CH, et al.External skeletal fixation: choosing a system based on biomechanical stability.J Orthop Trauma.2015;2(4):284-296.[12] Wolf JW, White AA,PanjabiMM,etal.Comparison of cyclic loading versus constant compression in the treatment of lone bone fracture in rabbits.J Bone Joint Surg (Am).1981;63(5):805-808.[13] 王颖.机械振动疗法的新进展[J].中华理疗杂志,2001,24(6): 378-380.[14] 王颖.机械振动疗法及其在康复治疗中的应用[J].中国康复医学杂志,2004,19(8):633-636[15] Goodship A E,Kenwright J.Theinfiuence of induced micromovement upon the healing of experimental tibial fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br.1985;67(4):650-655.[16] 张建国,夏家骝.周期性载荷对实验性骨折愈合影响的图像分析[J].中华骨科杂志, 1995,4):220-223.[17] 申华,陈国振,王建国.振动应力促进骨重建最佳频率的生物力学实验研究[J].中华医学杂志,2000,80(10):795-796[18] 朱东,谷贵山,高甲子,等. 间歇1-7天高频低载振动对抗骨质疏松的实验研究[C]. 全国生物力学学术会议,2009.[19] 汪建, 赵滨, 杨士彩,等. 持续与间歇性低载荷振动对成骨细胞增殖及分化能力影响的实验研究[C].全国生物流变学学术会议,2015.[20] 袁泉.基于振动的截肢康复训练系统的开发研究[D].河北工业大学, 2011.[21] 胡志勇. 变参数偏心同步驱动颗粒振动康复仪研究[D]. 河北工业大学, 2014.[22] 周亮. 外固定术后骨伤病人的振动促进骨愈合技术研究[D].河北工业大学, 2016.[23] 江捍平,王大平,张成裕.骨延长术研究进展[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2004, 14(4):66-69.[24] 黄劲松.骨痂牵拉术延长肢体的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,1997,4(6):515-516.[25] Spiegelberg B,Parratt t,Dheerendra SK,et al. Ilizarov principles of deformity correction.Ann R CollSurg Engl.2010;92(2):101-105[26] J. Van Ham,P. Reynders-Frederix,R. Puers.An Autonomous Implantable Distraction Nail Controlled By An Inductive Power And Data Link[R].The 14th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems, Lyon, France, June 10-14, 2007[27] 苏佳灿,任可,张春才.应力对骨折愈合的影响及其作用机制[J].第二军医大学学报, 2001, 22(10):988-990.[28] Potsika VT, Grivas KN, Protopappas VC, et al.Application of an effective medium theory for modeling ultrasound wave propagation in healing long bones.Ultrasonics.2014;54(5):1219-1230.[29] Lin H, Samchukov ML, Birch JG, et al.Semi-automated intra- operative fluoroscopy guidance for osteotomy and external-fixator. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2006;1: 3811-13814.[30] A. Zuniga,A. Babakhanov,C. Mahajan,M. Nikish.Fracture Track Bone Healing Measurement through an External Fixator[R].2013 39th Annual Northeast Bioengineering Conference[31] Inal S, Taspinar F, Gulbandilar E, et al. Comparison of the biomechanical effects of pertrochanteric fixator and dynamic hip screw on an intertrochanteric femoral fracture using the finite element method.Int J Med Robot.2015;11(1):95-103.[32] Esan O, Ikem I C, Oginni LM, et al.Comparison of unreamed interlocking nail and external fixation in open tibia shaft fracture management.West Afr J Med.2014;33(1):16-20.[33] Augat P, Simon U, Liedert A, et al. Mechanics and mechanobiology of fracture healing in normal and osteoporotic bone. Osteoporos. Osteoporos Int. 2005;16 Suppl 2:S36-43. [34] Gorman SC, Kraus KH, Keating JH, et al.In vivo axial dynamization of canine tibial fractures using theSecuros external skeletal fixation system. Vet Comp Orthop Traumatol. 2005;18(4): 199-207.[35] Claes L, Blakytny R, Göckelmann M, et al.Early dynamization by reduced fixation stiffness does not improve fracture healing in a rat femoral osteotomy model. J Orthop Res. 2009;27(1):22-27. [36] Gilbert JA,Dahners LE,Atkinson MA.The effect of external fixation stiffness on early healing of transverse osteotomies. J Orthop Res. 1989;7(3):389-397. [37] Glatt V, Evans CH,Tetsworth K.A Concert between Biology and Biomechanics:The Influence of the Mechanical Environment on Bone Healing. Front Physiol. 2017;7:678. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。
文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。.jpg) 文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。
文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。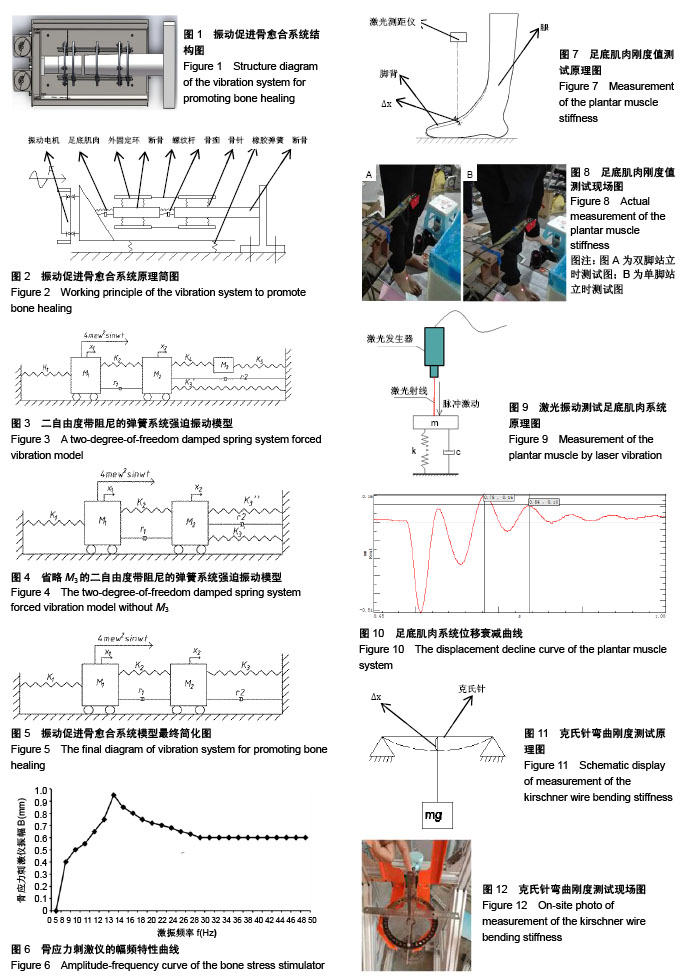
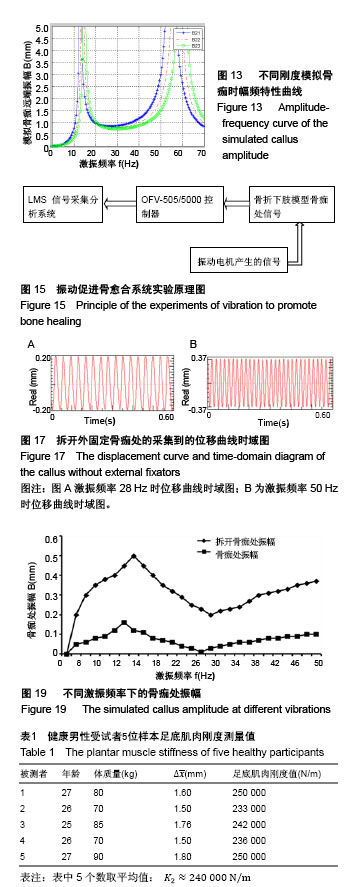
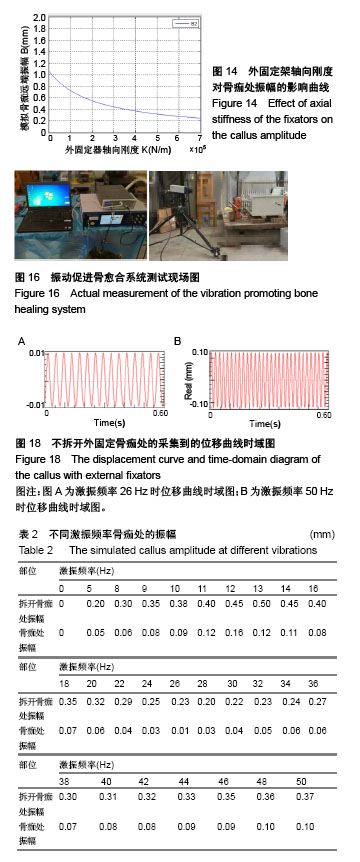
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。
文题释义:
参数辨识:是根据实验数据和建立的模型来确定一组参数值,使得由模型计算得到的数值结果能最好的拟合测试数据(曲线拟合问题),从而可以为生产过程进行预测,提供一定的理论指导。当计算得到的数值结果与测试值之间的误差较大时,就认为该数学模型与实际的过程不符或者差距较大,进而修改模型,重新选择参数。因此,参数辨识问题是一个逆问题,参数估计的好坏决定了用模型来解释实际问题的可信度。
骨应力刺激仪:应力刺激通过足底经肢体纵轴传导,能够在骨折端产生压应力,从而达到改善骨折处的生物学和生物力学环境,有效克服应力遮挡,促进骨折愈合的效果。