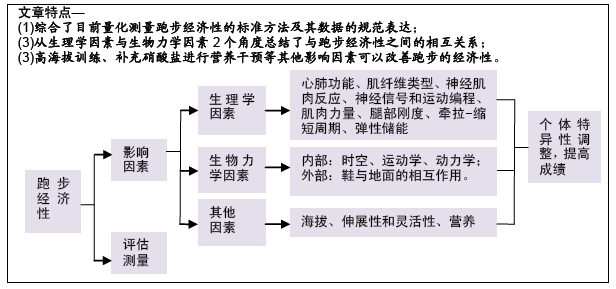
2.1 跑步经济性的测量方法 跑步经济性由给定运行速度下所需的能量决定,并表示为给定运行速度下的次最大摄氧量[3-5],该值反映了跑步时的代谢、心肺、生物力学和神经肌肉反应等。因此,跑步经济性的测量可能是有缺陷的,因为它由多个变量确定,这些变量可能是基于摄氧量,也可能不是基于摄氧量。在对跑步经济性概念有基本了解的情况下,就能描述与特定跑步速度相关的稳态摄氧量,并提供了一种方法来比较个体与他人之间、不同条件下个体自身之间的经济性。
2.1.1 跑步经济性的测量 量化测量跑步经济性的标准方法是在跑步机上以各种恒定速度运行时测量跑步者的稳态摄氧量,且持续足够长的时间以达到生理稳态。通常如果跑步机运行速度低于乳酸阈时,研究中使用的持续运行时间为3-15 min[9],同时通过考虑其他生理参数来验证是否达到稳态条件,如检验血乳酸浓度是否与基线水平相似,并且呼吸商(RER)<1 [3]。传统上,个体之间跑步经济性的比较通过在给定相同的运行速度下每分钟每千克体质量的摄氧量[mL/(kg·min)],或表达为每千克体质量运行1 km的总摄氧量[mL/(kg·min)] [10]。最常用的参考速度是16 km/h(268 m/min=4.47 m/s),表示每跑1 km用时 3 min 44 s,在其他研究中也采用从12-21 km/h不等的速度[3-4]。然而,简单地测量给定速度下的摄氧量来评估跑步经济性的方法并没有考虑到不同速度下基质使用的差异,因此一些研究将跑步经济性表明为热量单位成本[kcal/(kg·km)][11]。
2.1.2 规范数据表达 从迄今为止的研究来看,由于运动方案、气体分析设备、数据处理技术和最大有氧能力的差异,很难准确地将跑步经济性划分为差、良好和优秀3个等级。在承认这些潜在局限性的前提下,对现有文献中不同水准跑步者在16 km/h速度下运行的稳态摄氧量值进行分析,发现在16 km/h运行速度下最低的稳态摄氧量属于一个东非跑者,数值为39.0 mL/(kg·min),其完成1 500 m仅需3 min 35 s,但他的最大摄氧量仅为63 [mL/(kg·min)[10]。跑步经济性相对于最大摄氧量称为相对强度,这是一个重要的概念,因为训练有素的跑步者都表现出与他们各自最大摄氧量几乎相等的百分比,这取决于跑步的距离[12]。
2.1.3 跑步经济测量的可靠性 由于在实际的场地上运行(即在训练和比赛期间)难以获得代谢数据,因此跑步经济性的测量通常在实验室中的跑步机上进行,并使用各种气体分析系统(即呼吸分析仪)进行分析[13]。然而在实验室测试期间排除了空气和风阻力的干扰,所以将在跑步机上得到的数据转移到实际场地上时需要谨慎[4-5]。具体而言,可能会发现实际场地上随着速度的增加,空气和风阻力的影响变得更明显[5]。此外,在跑步机上跑步的技术不同于在地面上跑步,其中腿部肌肉被更大程度地使用以产生向前推进的水平和垂直力。尽管跑步机可产生轻微倾斜的梯度(-1%)用于增加补偿性的能量需求,但综合上述原因,实验室跑步机测试期间收集的数据可能低估了地面运行期间的真实能量需求[14]。近年来研究者比较了跑步机与室外田径场地带来的不同的生理适应,发现二者存在很强的相关性,为跑步机在训练与测量中的可靠性提供了强有力的证据[14]。
2.2 影响跑步经济性的生理学因素 改善跑步经济可能是由于肌肉氧化能力的提高,运动单位补充模式的相关变化,相同运动强度下通气量、心率的降低和跑步技术的改进。在训练之后,与碳水化合物作为基质的代谢相比,脂肪代谢再合成ATP需要更多氧气。目前研究发现跑步经济与肌肉弹性可能相关,实验室最近的观察结果表明在16.0 km/h速度下运行的氧气成本与26名国际男性长跑运动员的下肢灵活性(通过坐姿伸展进行测量)呈负相关,即“僵硬”的跑步者更为经济[15]。导致这些结果的一种解释是在牵拉-缩短活动的向心阶段硬度更高的肌肉和肌腱能够更好地储存弹性能量,并且这种储存的能量可以在跑步时释放出来,从而降低了运动的氧气成本[15]。
2.2.1 代谢和心肺效率 在改善跑步经济性的背景下,代谢和心肺呼吸效率是指在给定的工作输出下更好地使用氧气,增加能量产生的过程,其中心肺功能(心率、每分钟通气量)、体温调节(核心温度)和基质代谢(肌肉收缩效率、线粒体效率)的波动与跑步经济性的变化有关[16]。
(1)心肺功能:PATE等[17]提出,心肺功能测量值(心率、每分钟通气量)的变化是导致次最大和最大运动期间跑步经济性变化的部分原因。THOMAS等[18]发现在训练有素的女性跑步者的5 km比赛中,肺通气量的变化与需氧量的变化之间存在相关性(r=0.79,P < 0.05)。研究还发现跑步经济性的改善和肺通气量的减少之间存在相关性(r=0.77,P < 0.000 1)。与先前的研究类似,每分钟通气量的增加是与跑步经济性增加相关的唯一量度(r=0.64,P < 0.05)。虽然这2个变量在几项研究中本身并不意味着因果关系,然而随着训练引起的每分钟通气量减少,呼吸成本随之降低,表明通气适应可能确实在改善跑步经济性中起作用。
(2)核心温度:关于核心温度和跑步经济性关系之间的研究并没有统一的结论。在一些研究中,较高的核心温度导致在高热条件给定速度下的稳态摄氧量增加[19],其原因可能是循环增强、汗液蒸发、肺通气量和氧化磷酸化效率降低导致代谢需求增加[19]。GRIMBY[20]发现核心温度增加1.3 ℃会使稳态摄氧量增加5.5%。相比之下,其他研究结果表明在高温运动期间并没有发生变化或稳态摄氧量减少[21],这表明更高的核心温度增强了肌肉的机械效率,其程度等于或大于循环增强、汗液蒸发、肺通气量和氧化磷酸化效率降低的程度。
2.2.2 肌纤维类型 研究表明,人类存在一系列肌纤维类型,并且各自都表现出它们自己的代谢特征。实际上,肌纤维的结构和组成似乎影响跑步经济性[22]。ⅡA型肌纤维比ⅡX型肌纤维更具氧化性,并且具有与Ⅰ型纤维更相似的功能特性。因此,ⅡA型纤维的增加导致肌肉氧化能力增强,并且有助于改善跑步经济性。虽然没有研究肌纤维类型与跑步经济性之间的遗传性联系,但运动员可能会根据其Ⅰ型和Ⅱ型肌纤维的组成而表现出不同的经济性[22]。
2.2.3 神经肌肉反应 神经肌肉反应也是跑步经济性的重要方面。神经肌肉系统之间的相互作用是所有运动的基础,此系统有效地将心肺呼吸能力转化为力学并表现为运动能力。现代研究表明,有氧因子并不是影响耐力表现的唯一变量。GREEN等[23]认为机械收缩时的任何失效都可能妨碍氧气的充分利用,这表明在某些情况下使用氧气的能力可能不是限制耐力性能的最重要因素。基本上神经肌肉反应可以分为2类:改善跑步运动的神经信号和运动编程、改善肌肉力量。
(1)神经信号和运动编程:高性能跑步是一种技巧,需要精确计算身体的几乎所有主要的肌肉和关节,才能在移动中转换肌肉力量,需要练习以提高活动的效率。运动学习研究表明,任务的持续练习可以更加熟练地控制运动,其内在原因是肌肉活动的幅度和持续时间减少,肌肉共激活降低,运动变异性减少[24]。近期证据表明,休闲跑步者与训练有素的跑步者相比,表现出更大的个体差异(即步幅之间的差异)、更大的种群差异(即运动员之间肌肉补充的差异)、更广泛和更多变的肌肉共激活,肌肉活动持续时间更长[25]。一些研究发现训练可以引起跑步经济性的积极变化。跑步似乎会引起对运动编程和运动募集的适应,这对于良好的跑步经济性来说至关重要。BONACCI等[26]主张训练后对运动募集的适应性是一种学习效果。学习特定的肌肉招募模式,这种模式通过提高任务效率(例如提高生物力学和神经肌肉效率),从而提高运动成绩。
(2)肌肉力量:有人提出,耐力表现不仅可能受到有氧能力的限制,还可能受到与神经肌肉系统的“肌肉力量”因素的限制。同样,在拥有相似的最大摄氧量的高强度训练耐力跑步者的同质分组中,10 km和5 km跑步速度更快的运动员显示出更高的相对肌肉预激活。此外,在恒速运行期间,跑步经济性与站立期平均接触时间之间存在显著相关性,表明肌肉力量在确定训练有素跑者的跑步性能中起重要作用[27]。
2.2.4 腿部刚度 较短的站立接触时间和更大的肌肉预激活可能代表腿部肌肉刚度的增加,从而导致从制动阶段到地面接触的推进阶段可以更快过渡。DALLEAU等[28]通过证明跑步经济性与推进腿的刚度相关,突出了神经肌肉因素的重要性,增大腿部的刚度能改善跑步经济性。ARAMPATZIS等[29]证实了这一发现,在3组共28名长跑运动员中,最经济的跑步者具有最高的肌腱刚度。肌肉共激活能调节跑步期间的腿部刚度,并且可以通过储存的弹性能量来改变跑步经济性,并没有额外的代谢成本。增加的肌腱刚度表明能量储存的增加和运动时下肢肌肉输出的重新分布,这可能导致跑步经济性的改善。研究还显示肌腱单位的刚度随着跑步速度的增加而增加。
2.2.5 牵拉-缩短周期 KYROLAINEN等[30]发现随着跑步速度的增加,肌肉预激活和地面反作用力以及力的生成速率也随之增加。预激活肌肉是牵拉-缩短周期的重要功能。牵拉-缩短周期是在高速离心收缩之后紧接高速向心收缩的组合。牵拉-缩短周期的肌肉功能增强了向心收缩,同时预激活肌肉活动的增加被认为是一种承受更高的冲击负荷[30]。最近的一项研究表明,离心收缩与向心收缩时股外侧肌活动的比例越大,能获得更好的跑步经济[31]。
2.2.6 弹性储能 离心收缩与向心收缩之间的平衡可能会影响跑步经济性,因为存储弹性能量的离心收缩比释放能量的向心收缩成本更低[32]。有证据表明,跑步时的机械效率远超肌肉将化学能转化为动能的效率[32]。因此,在跑步的离心收缩期间存储的弹性能量在随后的同心收缩期间被释放,对跑步时向前推进作出重大贡献。可惜目前没有数据可以量化这2种收缩的相对能量成本,也没有设计出一种方法来区分离心收缩和肌腱拉伸[32]。
2.3 总结影响跑步经济性的生物力学因素 一些可改变的生物力学因素可能会影响跑步经济性,这些生物力学因素可以分为内部或外部2种因素。内在因素是指个人身体上的生物力学因素,可以进一步分为时空因素(与步态周期变化或阶段有关的参数,例如与地面的接触时间和步幅);运动学因素(运动模式,如下肢关节角度);动力学因素(增加运动的力,如地面反作用力)。涉及的外在因素包括鞋与地面的相互作用(包括鞋类和跑步表面)。
2.3.1 时空因素 步幅频率和步幅长度是相互依赖的,如果运行速度恒定,增加步幅长度或步幅频率将导致另一个参数的减少。跑步者似乎自然地选择经济上最佳的(或非常接近最佳的)步幅频率或步幅长度,这种先天潜意识的运行生物力学调整被称为自我优化。研究发现,训练有素的跑步者计算出的最佳步幅频率或步幅长度平均比他们的首选频率快3%或长度短3%。这些结果表明,有一个最佳的步幅“范围”,训练有素的跑步者可以在不损害其跑步经济性的情况下采用。与非疲劳状态相比,在疲劳状态下训练有素的跑步者会降低他们的步幅频率,并产生一个新的优选步幅频率,类似于在疲劳状态下达到的最佳步幅频率。这些结果意味着训练有素的跑步者可以动态地自我优化跑步生物力学,从而影响生理状态。对于新手跑步者,目前建议更多关注跑步者的步幅参数(步幅频率和步幅长度)以优化运动技术并最终提高性能[33]。
与步幅频率和步幅长度类似,垂直振荡也是影响跑步经济性的时空因素之一。研究表明,降低垂直振荡可以略微改善跑步经济性,但前提是身体质心的(CoM)绝对高度不变[34]。通过降低和支撑体质量相关的代谢成本,减少垂直位移可能会改善跑步经济性[34]。此外,它可以使跑步者更有机械效率,因为身体质心的位移减少会降低机械能成本。从跑步者的性别来看,女性跑步者的垂直摆动幅度低于男性,但关于女性是否比男性更经济,研究结果之间存在矛盾[35]。ERIKSSON等[36]论证了利用视觉和听觉反馈可以成功降低垂直振荡,跑步者发现改变垂直振荡比改变步频更自然。这意味着研究人员没有尝试确定跑步者是否具有最佳的垂直振荡幅度,或者是否仅仅通过降低他们的垂直振荡来提高跑步经济性。
足部与地面接触的时间与其跑步经济性之间的联系尚不明确。一些研究未能发现地面接触时间与跑步经济性之间的任何关系[37],一些研究发现更好的跑步经济性与较长的地面接触时间有关,而另一些发现则与之相反[38]。有人建议足部与地面接触的时间短会导致代谢成本升高,因为需要力量的快速产生,这意味着募集了代谢成本高的快速肌肉纤维。同时较长的地面接触时间也可能会导致较高的代谢成本,因为力的缓慢产生意味着跑步者减速时制动阶段会更长[38]。虽然这2种观点似乎都有道理,但最近SANTOS-CONCEJERO等[38]发现相同速度下优秀运动员与地面接触的时间缩短了约10.0%,同时氧气消耗也降低8.9%。
2.3.2 下肢动力学因素 在交叉比较研究中,一些运动参数被认为与较好的跑步经济性有关:较大的跖屈速度、较大的初始接触时水平脚跟速度、较大的大腿与垂直方向的最大伸展角、大的膝盖伸展角、较小的站立时膝关节的活动范围、较小的制动时髋部弯曲度、较小的髋关节在制动时的屈曲峰值、较小的膝关节在摆动时的屈曲速度、站姿时更大的背屈幅度和更快的背屈速度、更大的初始接触时角度[39]。在个体内的比较发现,较晚出现的背屈峰值、在初始接触时较慢的外翻速度和更少的膝关节屈曲都与改善的跑步经济性相关[39]。
从交叉和个体内比较研究中得到一项拥有强有力证据支持对跑步经济性有利的运动学变量是脚趾离开时较小的腿部延伸。有证据表明,当跑步者离开地面时可以通过减少跖骨弯曲或减少膝关节伸展来达到这个目的,见图2[40]。髋部伸展也可能起到一定作用,但研究通常集中在膝关节和踝关节角度上。更少的腿伸展可以产生更大的推进力,MOORE等[39]提出通过潜在地允许腿伸肌在力-长度曲线上以更有利的位置操作,并获得更高的齿轮比率(地面反作用力(GRF)力矩臂与肌肉-肌腱力矩臂)。这2种策略都可以最大限度地提高推进力。先前的研究表明,腿转动惯量的降低,降低了腿在摆动阶段的机械需求,也降低了步行的代谢需求。因此,在跑步时可能存在类似的关系,但这需要进一步研究。

足部着地模式被认为是影响跑步经济性的一个可修改的因素,一些研究人员认为最经济的着地模式是前脚着地[40],然而结果显示在慢速、中等速度和快速跑步时后足和中足着地没有差异。另一些研究表明在低速跑步时后脚着地要比中脚着地更经济[41]。根据目前的文献,足部着地对跑步经济性的影响似乎可以忽略不计,只有习惯性的后足着地才有可能通过改变足部着地模式而使跑步经济性恶化。
2.3.3 躯干和上肢动力学因素 与下肢生物力学相比,跑步经济性与躯干生物力学和上肢生物力学之间的关系往往被忽视。在跑步过程中摆动臂起着重要的作用,因为它有助于减小垂直振荡,反向作用下肢的垂直角动量,并最大限度地减少头部、肩部和躯干的旋转[42]。通过将手放在头顶上来消除手臂摆动可能损害跑步经济性[42],而将手放在背后或抱在胸前却没有一致的结果[42]。然而,没有证据表明个体可以通过改变手臂运动学来改善跑步经济性,从而改善跑步表现。根据目前的证据,鼓励个体在跑步时保持自然的手臂摆动。
根据WILLIAMS等[43]的发现,有人提出在跑步期间前倾躯干可以改善跑步经济性。然而,也有研究表明前倾躯干对跑步经济性有害。此发现也可能是其他原因导致的,如生物力学变化可能是由于2种情况之间的运行时间差异导致的肌肉疲劳产生,这意味着肌肉疲劳可能导致稳态摄氧量增加。
对于女性跑步者,乳房运动学也有可能影响跑步经济性和跑步生物力学。有证据表明,乳房运动学可以影响运动动力学[44],通过乳房支撑和下肢生物力学,特别是膝关节角度和步长的变化影响躯干倾斜。但也有学者发现跑步经济性并不存在性别差异,高水平耐力跑者却比休闲耐力跑者表现出更好的经济性[45]。
2.3.4 鞋与地面的相互作用因素 穿着传统的跑步运动鞋跑步与赤脚跑步或穿着轻便的运动鞋相比是对改善跑步经济性不利的,因为增加了鞋的质量。最近分析表明,小于440 g(每双)的鞋质量是不影响跑步经济的,但大于440 g的鞋会对跑步经济性有负面影响[46]。然而,由于使用的评价方法不同,关于鞋的质量对跑步经济性影响的证据是模棱两可的。其他鞋的特性,如刚度、舒适度和缓冲,可能会影响跑步经济性。换鞋也可以改变脚下的缓冲水平,FREDERICK等[47]提出了“缓冲成本”假设,指出在跑步时积极缓冲身体可能会产生更高的代谢成本。因此,具有有限缓冲或无缓冲(例如赤脚)的鞋将导致个体必须使用下肢肌肉来主动缓冲身体并导致摄氧量的增加。FRANZ等[48]提供了一些支持这一观点的证据,他们发现穿着质量增加的鞋子跑步时比赤脚跑步需要更少的代谢能量。因此,即使增加的鞋质量相似,在没有缓冲的情况下跑步比有缓冲的情况下跑步有更高的代谢需求。
此外,对于良好的跑步经济性,似乎存在“最佳”缓冲表面。赤足跑步时,10 mm的缓冲表面对跑步经济性而言,比没有缓冲表面或20 mm的缓冲表面更有益[49]。在考虑自然跑步的地形环境时,PINNINGTON等[50]发现在草地上跑步引起的摄氧量比在沙地上运行时低。这可能是由于沙子的阻尼效应,导致在站姿期间完成的机械功增加。因此,在吸收能量较小的表面上跑步时将改善跑步者的跑步经济性。
2.4 其他影响跑步经济性的因素 除了上述的影响跑步经济性的生理学或生物力学因素之外,还有其他的一些因素也可以影响跑步经济性。对海拔高度产生高原适应的结果可以改善氧的输送和利用,潜在的改善跑步经济性。其他的因素,如拉伸和灵活性的发展,似乎有一个最佳的灵活性要求,以最大限度地防止运动伤害。一些营养干预也受到关注,如膳食硝酸盐对减少运动期间的氧气需求有明显影响。
2.4.1 海拔高度 许多运动员会进行某种形式的高原训练,以获得生理适应和跑步性能上的微小改善。最近一项Meta分析结果表明,对高训练强度和中训练强度的运动员使用自然和人工海拔暴露的不同方案后,其性能提升了1%-4%[51]。性能的改善主要归因于血液学参数的增加导致最大有氧能力的增加[52]。
有人提出高海拔暴露后跑步经济性改善差异的机制与缺氧暴露后血红蛋白质量和浓度变化的差异有关。虽然用于增加总血红蛋白质量的缺氧情况目前已明确,但这不适用于跑步经济性。BURTSCHER等[53]研究在5周的时间内缺氧暴露的持续时间仅为30 h,这不足以显著增加总血红蛋白质量,但足以改善跑步经济性。作者确实报告了血红蛋白浓度和血细胞比容的小幅增加,与跑步经济性的改善密切相关。LEVINE等[52]报道适度训练的中等海拔(2 500 m)和低海拔(1 250 m)训练的跑步者在返回海平面后,增加红细胞量(9%)以及改善最大摄氧量(平均5%)和跑步经济性(2%-5%)。文献表明跑步者的海拔暴露对跑步经济性没有不利影响,并且有充分证据表明它可能导致跑步经济性在回到海平面上时的改善。许多在高海拔暴露后未发现跑步经济性改善的研究是在接近竞赛季节时进行的,这强调了时间和训练阶段对跑步经济性高度暴露有效性的重要性。
2.4.2 伸展性和灵活性 关于拉伸或灵活性对跑步经济性的影响似乎存在相反的研究结果。一些研究人员已经确定了灵活性和跑步经济性之间的反比关系;也就是说,较低的灵活性与更好的跑步经济性相关[54]。GLEIM等[54]在3-12 km/h的速度范围内对100名男性和女性受试者进行躯干和下肢柔韧性测试,发现那些在测试中表现出较低灵活性的人更为经济。具体而言,在足部与地面接触时身体躯干和臀部区域的横向和前部平面的不灵活性可以稳定骨盆,减少过度的运动范围和较高的代谢并稳定肌肉[54]。此外,研究表明具有较强或较硬肌肉结构的跑步者在其下肢存储更多的弹性能量,导致次最大跑动速度下的稳态摄氧量较低[54]。相比之下,其他研究未能支持反向关系的存在,反驳了灵活性是距离运行性能的重要组成部分[55]。改善髋部柔韧性、肌筋膜平衡和由于伸展引起的骨盆对称性被认为可以增强神经肌肉的平衡和收缩,从而导致摄氧量的降低和跑步经济性的改善。这些结果证实了一般的观点,即为了获得最佳的运行性能,需要提高灵活性。
2.4.3 营养干预 一些营养干预因为在运动中减少跑步者的有氧需求而受到关注,其中最显著的是膳食硝酸盐。现已知可以通过饮食方式增加硝酸盐(NO3-)和亚硝酸盐(NO2-)的组织浓度。绿叶蔬菜,如生菜、菠菜、芹菜和甜菜根特别富含硝酸盐。膳食硝酸盐补充剂的使用,增加了循环血浆亚硝酸盐并且因此降低NO-浓度以降低运动的氧需求(即提高代谢效率和跑步经济性)[56]。
虽然迄今为止只有一项研究表明补充硝酸盐后的跑步经济性水平有所提高[57],但有报道称其他几种运动包括骑自行车、步行等对氧的需求有所降低[57],工作效率提高。BAILEY等[56]研究中添加硝酸盐后稳态摄氧量下降幅度约为5%,持续3-6 d。在急性硝酸盐补充后也有类似的稳态摄氧量减少的报道。VANHATALO等[58]报告了甜菜根汁摄入仅2.5 h后,稳态摄氧量明显减少。
虽然膳食硝酸盐似乎是一种有前景的增效助剂,但还需要进一步研究,以确定其对训练程度不同的长跑运动员和不同比赛项目的影响范围。未来的研究还应该检查使用其他营养干预来增强跑步经济性的功效。