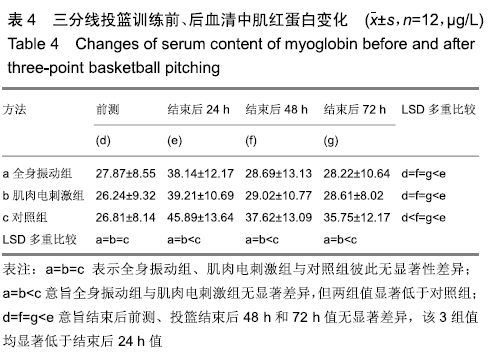
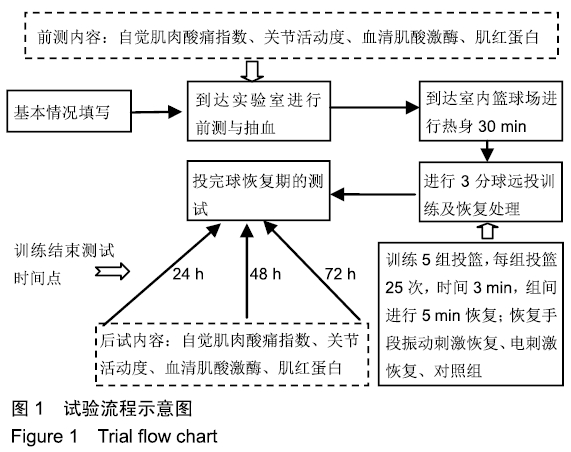
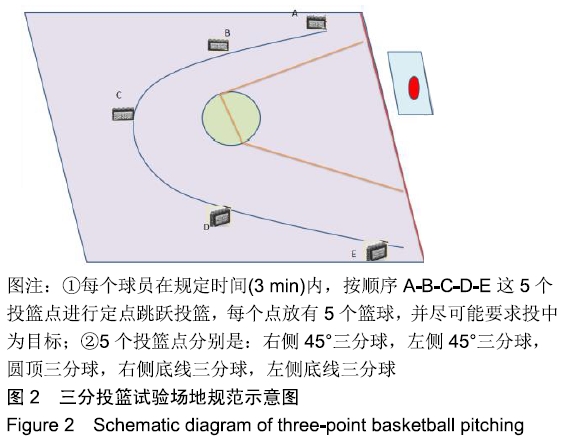
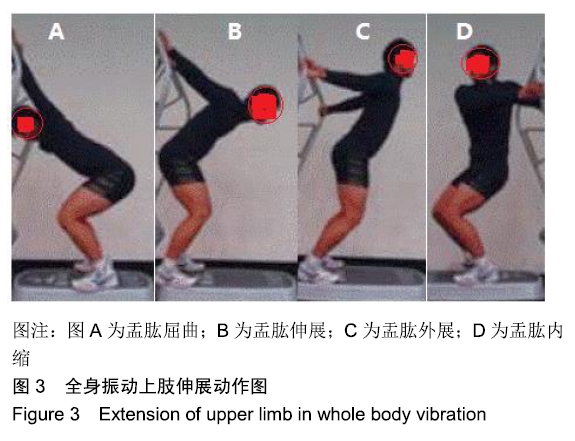
[1] 张学领.中国男子职业篮球联赛常规赛和季后赛绩效表现的回归分析[J].中国体育科技,2018,52(2):129-134.
[2] 曹中旺. 篮球竞技双方攻守能力评价实证研究—以2015-2016赛季CBA总决赛为例[J].吉林体育学院学报,2016,32(5):79-83.
[3] MULAZIMOGLU O, YANAR S, EVCIL AT, et al. Examining the effect of fatigue on shooting accuracy in young basketball players. The Anthropologist. 2017;27:77-80.
[4] BOWMAN TG, HART JM, MCGUIRE BA,et al. A functional fatiguing protocol and deceleration time of the shoulder from an internal rotation perturbation.J Athl Train. 2006;41(3): 275-279.
[5] LIAO YS, WANG LH. Effect of upper extremity fatigue on baseball throwing. Quarterly of Chinese Physical Education. 2010;24(3):116-123.
[6] LAUDNER KG, SELKOW NM, BURKE NC,et al. Decreased blood flow in the throwing arm of professional baseball pitchers.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2014;23(12):1753-1756.
[7] TUFANO JJ, BROWN LE, COBURN JW,et al. Effect of aerobic recovery intensity on delayed-onset muscle soreness and strength.J Strength Cond Res. 2012;26(10):2777-2782.
[8] ERICKSON BJ, SGORI T, CHALMERS PN, et al.The Impact of Fatigue on Baseball Pitching Mechanics in Adolescent Male Pitchers.Arthroscopy. 2016;32(5):762-771.
[9] CROTIN RL, BHAN S, RAMSEY DK,et al.An inferential investigation into how stride length influences temporal parameters within the baseball pitching delivery.Hum Mov Sci. 2015;41:127-135.
[10] DAVIS WJ, WOOD DT, ANDREWS RG,et al. Elimination of delayed-onset muscle soreness by pre-resistance cardioacceleration before each set. J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(1):212-225.
[11] LUO J, MCNAMARA B, MORAN K.The use of vibration training to enhance muscle strength and power.Sports Med. 2005;35(1): 23-41.
[12] ALGHADIR AH, ANWER S, ZAFAR H,et al. Effect of localised vibration on muscle strength in healthy adults: a systematic review. Physiotherapy.2018;104(1):18-24.
[13] BEMBEN DA, PALMER IJ, BEMBEN MG, et al.Effects of combined whole-body vibration and resistance training on muscular strength and bone metabolism in postmenopausal women. Bone.2010;47(3):650-656.
[14] SANDS WA, MCNEAL JR, STONE MH,et al. The effect of vibration on active and passive range of motion in elite female synchronized swimmers. Eur J Sport Sci. 2008;8(4):217-223.
[15] COCHRANE DJ, STANNARD SR, SARGEANT AJ, et al. The rate of muscle temperature increase during acute whole-body vibration exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol. 2008;103(4):441-448.
[16] AMINIAN-FAR A, HADIAN MR, OLYAEI G, et al.Whole-body vibration and the prevention and treatment of delayed-onset muscle soreness.J Athl Train. 2011;46(1):43-49.
[17] DABBS NC, BLACK CD, GARNER JC,et al.Effects of whole body vibration on muscle contractile properties in exercise induced muscle damaged females.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2016;30:119-125.
[18] DI GIMINIANI R, MASEDU F, TIHANYI J, et al.The interaction between body position and vibration frequency on acute response to whole body vibration.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2013;23(1):245-251.
[19] RHIBI F, CHTOUROU H,ZRIBI A ,et al. Effect of the electrostimulation during the tapering period compared to the exponential taper on anaerobic performances and rating of perceived exertion. Science & Sports.2016;31(4):93-100.
[20] MINDER PM, NOBLE JG, ALVES-GUERREIRO J, et al. Interferential therapy: Lack of effect upon experimentally induced delayed onset muscle soreness.Clin Physiol Funct Imaging. 2002; 22(5):339-347.
[21] DEFRODA SF, GOYAL D, PATEL N, et al. Shoulder Injuries in the Overhead Throwing Athlete.Curr Sports Med Rep. 2018; 17(9): 308-314.
[22] TRIPP BL, BOSWELL L, GANSNEDER BM,et al.Functional fatigue decreases 3-dimensional multijoint position reproduction acuity in the overhead-throwing athlete.J Athl Train. 2004; 39(4):316-320.
[23] ERICKSON BJ, SGORI T, CHALMERS PN, et al.The Impact of Fatigue on Baseball Pitching Mechanics in Adolescent Male Pitchers.Arthroscopy. 2016;32(5):762-771.
[24] WARREN CD, BROWN LE, LANDERS MR, et al. Effect of three different between-inning recovery methods on baseball pitching performance. J Strength Cond Res. 2011;25(3): 683688.
[25] TESSITORE A, MEEUSEN R, PAGANO R,et al.Effectiveness of active versus passive recovery strategies after futsal games.J Strength Cond Res. 2008;22(5):1402-1412.
[26] YAMAUCHI T, HASEGAWA S, NAKAMURA M, et al.Effects of two stretching methods on shoulder range of motion and muscle stiffness in baseball players with posterior shoulder tightness: a randomized controlled trial.J Shoulder Elbow Surg.2016;25(9):1395-1403.
[27] WU BH, YEH NC, WU CC. Effects of whole body vibration and static stretching on attenuation of delayed onset of muscle soreness following eccentric exercise.Sports & Exercise Research. 2011;13(4):470-478.
[28] WU BH, CHEN CL, KUO KB. Effects of whole body vibration training as a recovery method on delayed onset muscle soreness after eccentric exercise.Sports & Exercise Research. 2014;16(1):71-81.
[29] KINSER AM, RAMSEY MW, O’BRYANT HS,et al.Vibration and stretching effects on flexibility and explosive strength in young gymnasts. Med Sci Sports Exerc.2008;40(1):133-140.
[30] GÓMEZ-BRUTON A, GONZÁLEZ-AGÜERO A, Matute-Llorente A, et al.Effects of Whole Body Vibration on Tibia Strength and Structure of Competitive Adolescent Swimmers: A Randomized ControlledTrial.PM&R. 2018;10(9): 889-897.
[31] KARATRANTOU K, GERODIMOS V, DIPLA K, et al. Whole-body vibration training improves flexibility, strength profile of knee flexors, and hamstrings-to-quadriceps strength ratio in females.J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(5):477-481.
[32] CHENG CF, LEE CL,YANG YS. Acute effect of vibration exercise on grip strength and physiological recovery from high intensity intermittent grip exercise. Sports & Exercise Research.2010;12(3):98-105.
[33] SANTOS I, RAHAL S, SANTOS A, et al.Whole-body vibration on leg muscles thermography and femoral resistive index of in adult healthy dogs.Res Vet Sci. 2019;122:118-123.
[34] RHEA MR, BUNKER D, MARÍN PJ, et al. Effect of iTonic whole-body vibration on delayed-onset muscle soreness among untrained individuals.J Strength Cond Res. 2009; 23(6):1677-1682.
[35] ALGHADIR AH, ANWER S, ZAFAR H, et al. Effect of localised vibration on muscle strength in healthy adults: a systematic review. Physiotherapy.2018;104(1):18-24.
[36] THOMPSON C, BÉLANGER M. Effects of vibration in inline skating on the Hoffmann reflex, force, and proprioception.Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002;34(12):2037-2044.
[37] FERNANDES IA, KAWCHUK G, BHAMBHANI Y,et al.Does whole-body vibration acutely improve power performance via increased short latency stretch reflex response?.J Sci Med Sport. 2013;16(4):360-364. |