| [1]Mizumura K,Taguchi T.Delayed onset muscle soreness: Involvement of neurotrophic factors.J Physiol Sci.2016;66(1):43-52.[2]Selmi O,Ouerghi N,Khalifa WB,et al.Influence of Stress, Fatigue, Sleep and Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness on Perceived Physical Enjoyment Exertion during Small Sided Games. Iran J Public Health. 2018;47(3): 449-450.[3]蒋全睿,李武,刘小卫,等.按法对肱二头肌延迟性肌肉酸痛志愿者血清T-AOC和CK-MM水平的影响[J].针灸推拿医学(英文版), 2018,16(2):89-95.[4]Koutris M,Türker KS,van Selms MKA,et al.Delayed-onset muscle soreness in human masticatory muscles increases inhibitory jaw reflex responses. J Oral Rehabil.2018;45(6):430-435.[5]Imtiyaz S,Veqar Z,Shareef MY.To Compare the Effect of Vibration Therapy and Massage in Prevention of Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness(DOMS). J Clin Diagn Res.2014;8(1):133-136.[6]Koh HW,Cho SH,Kim CY,et al.Effects of vibratory stimulations on maximal voluntary isometric contraction from delayed onset muscle soreness.J Phys Ther Sci.2013;25(9):1093-1095.[7]Wheeler AA,Jacobson BH.Effect of whole-body vibration on delayed onset muscular soreness, flexibility, and power.J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(9):2527-2532.[8]Lau WY,Nosaka K. Effect of Vibration Treatment on Symptoms Associated with Eccentric Exercise Induced Muscle Damage. Am J Phys Med Rehabil.2011;90(8):648-657.[9]黄美欢,曹建国,贠国俊,等.肌内效贴在脑瘫儿童康复中的应用进展[J].中国康复医学杂志,2016, 31(1):102-105.[10]Lee YS,Bae SH,Hwang JA,et al.The effects of kinesio taping on architecture, strength and pain of muscles in delayed onset muscle soreness of biceps brachii. J Phys Ther Sci.2015;27(2):457-459.[11]Bae SH,Lee YS, Kim GD,et al.The Effects of Kinesio-taping Applied to Delayed Onset Muscle Soreness on Changes in Pain. IJPBST.2014;6(3): 133-142.[12]Haksever B,Kinikli GL,Tunay VB,et al. Effect of kinesiotaping intervention on knee muscle strength and delayed onset muscle soreness pain following eccentric fatigue training.Fizyoterapi Rehabilitasyon. 2016;27(1): 12-18.[13]张国海,王人卫.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛和肌肉功能恢复的影响[J].体育科学,2017,37(12):46-51.[14]Rhea MR,Bunker D,Marín PJ,et al.Effect of iTonic whole-body vibration on delayed-onset muscle soreness among untrained individuals.J Strength Cond Res.2009;23(23):1677-1682.[15]Pinto NS.Effectiveness of a protocol involving acute whole-body vibration exercises in an adult and health individual with delayed-onset muscle soreness observed after running: a case report.J Med Med Sci. 2011; 2(1):612-617.[16]董启正.肌内效贴对运动性膝关节延迟性肌肉酸痛的作用[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(3):367-371.[17]吴新华,蒋云飞,程亮,等.优秀男子跳远运动员下肢关节等速肌力特征的分析[J].成都体育学院学报, 2013,39(10):86-89.[18]李静雅,程亮.不同频率全身振动训练对老年女性平衡能力、下肢肌力和位置觉的影响[J].体育学刊, 2018, 25(2):128-134.[19]王富鸿,张金梅,程亮,等.等速训练对前交叉韧带重建运动员膝关节肌力和位置觉的影响[J].环境与职业医学, 2018,35(8):716-720.[20]杨雪清,程亮.篮球运动员躯干和下肢等速肌力分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(12):1835-1840.[21]Cardinale M,Bosco C.The use of vibration as an exercise intervention. Exerc Sport Sci Rev. 2003;31(1):3-7.[22]Cardinale M,Soiza RL,Leiper JB,et al.Hormonal responses to a single session of wholebody vibration exercise in older individuals.BrJ Sports Med.2010;44(4):284-288.[23]宋法明,刘北湘.全身振动介入静态伸展对离心运动后延迟性肌肉酸痛的影响研究[J].山东体育学院学报, 2017, 33(1):74-79.[24]Cochrane DJ,Stannard SR,Sargeant AJ,et al.The rate of muscle temperature increase during acute whole-body vibration exercise.Eur J Appl Physiol.2008;103(4):441-448.[25]Bakhtiary AH,Safavifarokhi Z,Aminianfar A.Influence of vibration on delayed onset of muscle soreness following eccentric exercise. Br J Sports Med.2007;41(3):145-148. [26]Souza SE,Christensen SW,Hirata RP,et al.Blood flow after contraction and cuff occlusion is reduced in subjects with muscle soreness after eccentric exercise.Scand J Med Sci Sports.2018;28(1):29-39. [27]龙志.肌内效贴对延迟性肌肉酸痛的疼痛缓解效果研究及其机制探讨[D].上海:上海体育学院,2016. [28]Hsu YH,Chen WY, Lin HC,et al.The effects of taping on scapular kinematics and muscle performance in baseball players with shoulder impingement syndrome.J Electromyogr Kinesiol. 2009;19(6):1092-1099.[29]Omoigui S.The Biochemical Origin of Pain-Proposing a new law of Pain: The origin of all Pain is Inflammation and the Inflammatory Response PART 1 of 3–A unifying law of pain.Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(1):70-82.[30]Nosaka K.The effect of kinesio taping on muscular micro-damage following eccentric exercises//15th Annual Kinesio Taping Int Symposium Rev,1999:70-73. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。
文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。.jpg) 文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。
文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。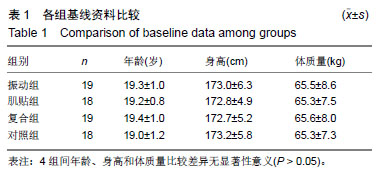
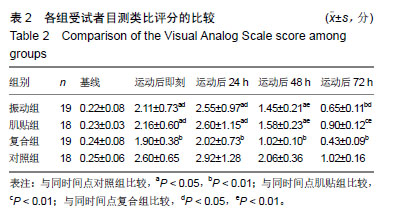
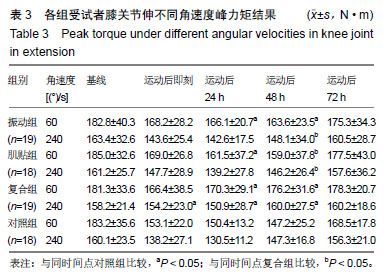
.jpg) 文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。
文题释义:
延迟性肌肉酸痛:是指机体从事大运动量,特别是开始一项新运动、运动项目改变或运动强度突然增加后一段时间内出现的肌肉酸痛现象,其是一种特殊类型的运动性肌肉疲劳,可能是产生超量恢复的基础条件。延迟性肌肉酸痛一般出现在运动后12-24 h,24-48 h达高峰,3-7 d可自行缓解并消失。
峰力矩:指在等速肌力测试中,受试者关节在整个等速运动范围内所输出的最大力矩值,能反映被测试关节力量,研究发现60 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表绝对力,240 (°)/s的峰力矩能代表爆发力。