| [1]Morrison WA. Progress in tissueengineering of soft tissue and organs. Surgery. 2009;145(2):127-130.
[2]Jaklenec A, Stamp A, Deweerd E, et al. Progress in the tissue engineering and stem cell industry "are we there yet?". Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2012;18(3):155-166.
[3]Martino S, D'Angelo F, Armentano I, et al. Stem cell-biomaterial interactions for regenerative medicine. Biotechnol Adv. 2012;30(1):338-351.
[4]Bhat S, Kumar A. Cell proliferation on three-dimensional chitosan-agarose-gelatin cryogel scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. J Biosci Bioeng. 2012;114(6):663-670.
[5]Mahmoudifar N, Doran PM. Osteogenic differentiation and osteochondral tissue engineering using human adipose- derived stem cells. Biotechnol Prog. 2013;29(1):76-185.
[6]Wang W, Cao B, Cui L, et al. Adipose tissue engineering with human adipose tissue-derived adult stem cells and a novel porous scaffold. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2013; 101(1):68-75.
[7]Declercq HA, De Caluwé T, Krysko O, et al. Bone grafts engineered from human adipose-derived stem cells in dynamic 3D-environments. Biomaterials. 2013;34(4): 1004-1017.
[8]Kwan MD, Sellmyer MA, Quarto N, et al. Chemical control of FGF-2 release for promoting calvarial healing with adipose stem cells. J Biol Chem. 2011;286(13):11307-11313.
[9]Kang JM, Han M, Park IS, et al. Adhesion and differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells on a substrate with immobilized fibroblast growth factor. Acta Biomater. 2012;8(5):1759-1767.
[10]Kotulák T, Drápalová J, Kopecký P, et al. Increased circulating and epicardial adipose tissue mRNA expression of fibroblast growth factor-21 after cardiacsurgery: possible role in postoperative inflammatory response and insulin resistance. Physiol Res. 2011;60(5):757-767.
[11]徐扬阳,姜南,杨柳,等.重组人碱性成纤维细胞生长因子对人脂肪干细胞分化为脂肪细胞的影响[J].中华医学美学美容杂志,2013, 19(2):134-137.
[12]Von Heimburg D, Hemmrich K,Zachariah S,et al. Oxygen consumption in undifferentiated versus differentiated adipogenic mesenchymal precursor cells. Respir Physiol Neurobiol. 2005;146(2-3):107-116.
[13]Beahm EK,Walton RL,Patrick Jr CW. Progress in adipose tissue construct development. Clin Plast Surg. 2003;30(4): 547-558.
[14]刘琳,张亚,周云,等.脂肪源干细胞向血管内皮细胞的分化[J].中国组织工程研究,2013,17(23):4224-4231.
[15]Strem BM, Hedrick MH. The growing importance of fat in regenerative medicine. Trends Biotechnol. 2005;23(2):64-66.
[16]Strem BM, Hicok KC, Zhu M, et al. Multipotential differentiation of adipose tissue-derived stem cells. Keio J Med. 2005;54(3):132-141.
[17]Handel M1, Hammer TR, Hoefer D. Adipogenic differentiation of scaffold-bound human adipose tissue-derived stem cells (hASC) for soft tissue engineering. Biomed Mater. 2012;7(5): 054107.
[18]Matsumoto D, Sato K, Gonda K, et al. Cell-assisted lipotransfer: supportive use of human adipose-derived cells for soft tissue augmentation with lipoinjection. Tissue Eng. 2006;12(12):3375-3382.
[19]Neofytou EA, Chang E, Patlola B, et al. Adipose tissue-derived stem cells display a proangiogenic phenotype on 3D scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2011; 98(3):383-393.
[20]Hemmrich K, Van de Sijpe K, Rhodes NP, et al. Autologous in vivo adipose tissue engineering in hyaluronan-based gels--A pilot study. J Surg Res. 2008;144(1):82-88.
[21]Eppley BL, Sidner RA, PIatis JM, et al. Bioactivation of free-fat transfers:a potential new approach to improving graft survival. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1992;90(6):1022-1030.
[22]Tabata Y, Miyao M, Inamoto T,et al. De novo formation of adipose tissue by controlled release of basic fibroblast growth factor. Tissue Eng. 2000;6(3):279-289.
[23]黎洪棉,高建华,吴涛,等. 脂肪干细胞与外源性血管内皮生长因子及纤维蛋白胶复合物体内构建血管化组织工程脂肪[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(40):7480-7484. |
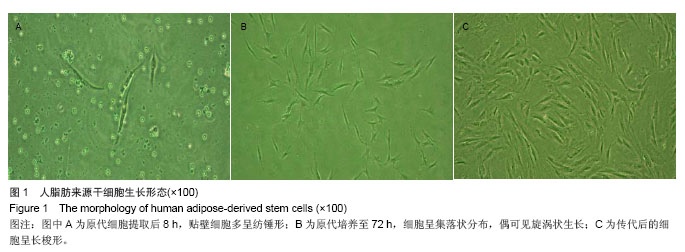

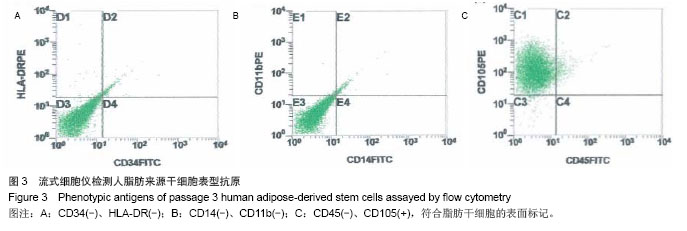
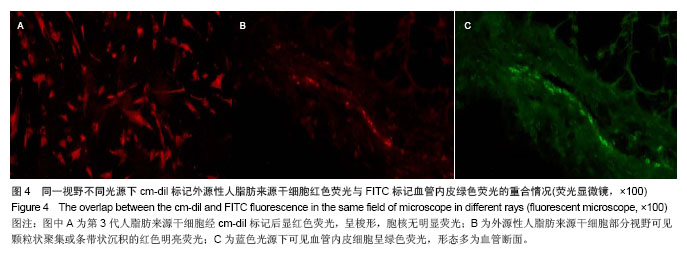
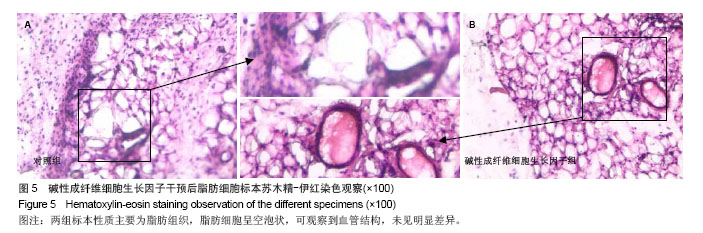
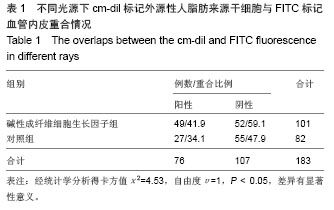
.jpg)