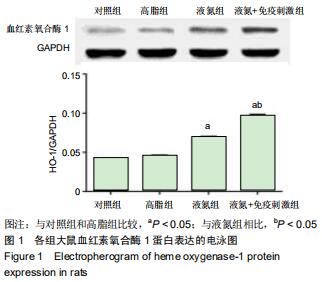
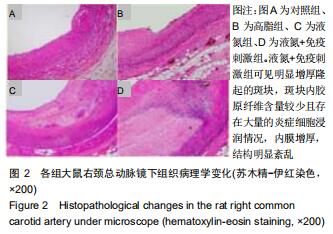
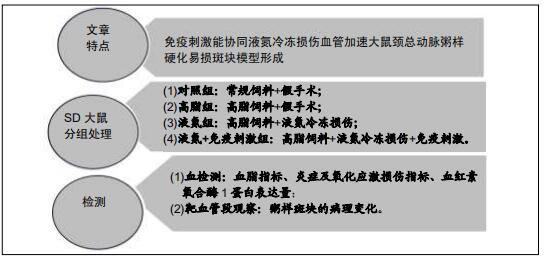
|
[1] NAHAPETYAN H, MOULIS M, GROUSSET E, et al. Altered mitochondrial quality control in Atg7-deficient VSMCs promotes enhanced apoptosis and is linked to unstable atherosclerotic plaque phenotype. Cell death disease.2019;10(2):119.
[2] GABRIONE F,OBERTI L,NARDONE M, et al. Why patients with cardiovascular risks go to dentists. Is there sufficient evidence of influence of periodontal therapy on cardiovascular disease? Journal of biological regulators and homeostatic agents.2019; 33(null):113-119.
[3] SPARTALIS M,SPARTALIS E,ATHANASIOU A,et al.The role of the endothelium in premature atherosclerosis: Molecular mechanisms. Current medicinal chemistry. 2020;27(7): 1041-1051.
[4] WU MY, LI CJ, HOU M, et al. New Insights into the Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Atherosclerosis. 2017; 18(10):2034.
[5] KATTOOR AJ, POTHINENI NVK, PALAGIRI D, et al. Oxidative Stress in Atherosclerosis.Current atherosclerosis reports.2017; 19(11):42.
[6] 黄爱良,黄荣志,黄小倩,等.动脉粥样硬化动物模型构建的方法与现状[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(27):4423-8.
[7] MEHRAD H, MOKHTARI-DIZAJI M, GHANAATI H. Developing a rabbit model of neointimal stenosis and atherosclerotic fibrous plaque rupture. The journal of Tehran Heart Center.2011;6(3): 117-125.
[8] 张安邦,黄昕,李令根,等.复合方法制备SD大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2015,21(3):282-5.
[9] 王双双,王丽丽,杨升华,等.改良液氮冻伤法建立易损动脉粥样硬化斑块模型[J].中国老年学杂志,2014,34(21):6082-6085.
[10] CHAUDHARY R, WALDER KR, HAGEMEYER CE, et al. Psammomys obesus: a Natural Diet-Controlled Model for Diabetes and Cardiovascular Diseases.Curr Atheroscler Rep. 2018;20(9):46.
[11] JIANG L,TU Y,KIMURA RH,et al.64Cu-labeled divalent cystine knot peptide for imaging carotid atherosclerotic plaques.J Nucl Med.2015; 56(6) :939-944.
[12] HINIKARIDOU A, ANDIA ME, INDERMUEHLE A, et al. Vascular remodeling and plaque vulnerability in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis: comparison of delayed-enhancement MR imaging with an elastin-specific contrast agent and unenhanced black-blood MR imaging.Radiology.2014;271(2):390-399.
[13] SUN X, CAO W, CUI JJ, et al. An animal model of atherosclerotic plaque disruption and thrombosis in rabbit using pharmacological triggering to plaques induced by perivascular collar placement. Cardiovasc Pathol.2013;22(4):264-269.
[14] SCHURGERS LJ, JOOSEN IA, LAUFER EM, et al. Vitamin K-antagonists accelerate atherosclerotic calcification and induce a vulnerable plaque phenotype.PLoS One.2012;7(8):e43229.
[15] CHEN L, LI X, LI C, et al. Chinese Herbal Cardiotonic Pill Stabilizes Vulnerable Plaques in Rabbits by Decreasing the Expression of Adhesion Molecules.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016;68(3):215-222.
[16] CIMMINO G, LOFFREDO FS, MORELLO A, et al. Immune- Inflammatory Activation in Acute Coronary Syndromes: A Look into the Heart of Unstable Coronary Plaque.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2017;13(2):110-117.
[17] LU JX, GUO C, OU WS, et al. Citronellal prevents endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis in rats.2019;120(3):3790-800.
[18] WANG SS, HU SW,ZHANG QH, et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Stabilize Atherosclerotic Vulnerable Plaque by Anti-Inflammatory Properties.PloS one.2015;10(8):e0136026.
[19] SUNG KC, KANG SM, CHO EJ, et al. Ferritin is independently associated with the presence of coronary artery calcium in12033 men. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.2012;32:2525- 2530.
[20] 张安邦,黄昕,李令根,等.复合方法制备SD大鼠动脉粥样硬化模型[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志,2015,21(3):282-285.
[21] MURY P, CHIRICO EN, MURA M, et al. Oxidative Stress and Inflammation, Key Targets of Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression and Vulnerability: Potential Impact of Physical Activity. Sports medicine (Auckland, NZ).2018;48(12):2725-2741.
[22] EL-ASHMAWY HM, SELIM FO, HOSNY TAM, et al. Association of low serum Meteorin like (Metrnl) concentrations with worsening of glucose tolerance, impaired endothelial function and atherosclerosis. Diabetes research and clinical practice.2019;150: 57-63.
[23] LI F, SUN XJ, XIE H, et al. The relationship between chronic periodontitis and the instability of carotid atherosclerotic plaque by serum level of MMP-9, MCP-1 and MMP-7.Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue. 2015 Oct;24(5):589-593.
[24] DAI R, DONG J, LI W, et al. Antibody to oxidized low-density lipoprotein inhibits THP1 cells from apoptosis by suppressing NF-κB pathway activation. Cardiovascular diagnosis and therapy. 2019;9(4):355-361.
[25] MORENO PR. Vulnerable plaque: definition, diagnosis, and treatment. Cardiol Clin. 2010;28(1):1-30.
[26] HANSSON GK, LIBBY P, TABAS I. Inflammation and plaque vulnerability. J Intern Med.2015;278(5): 483-493.
|