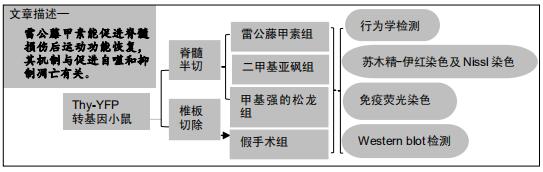
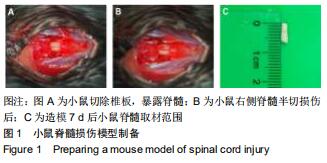
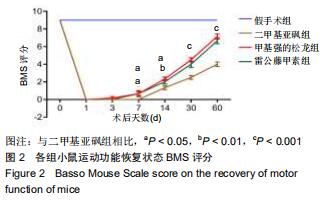
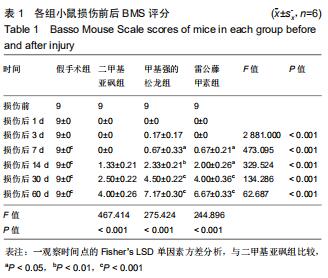
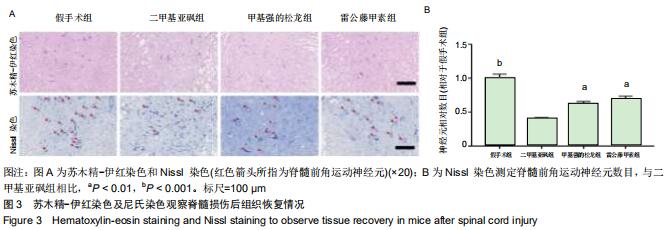
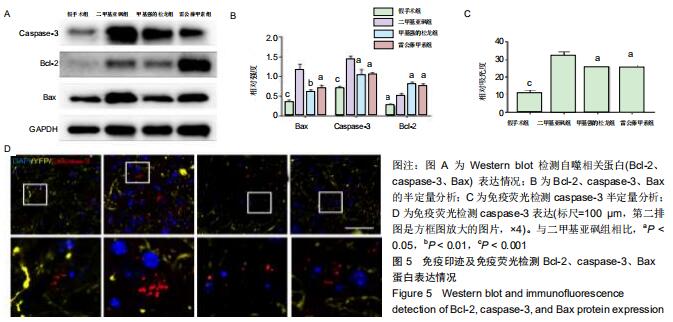
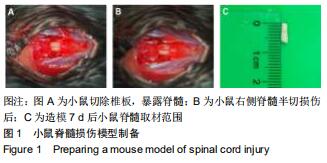
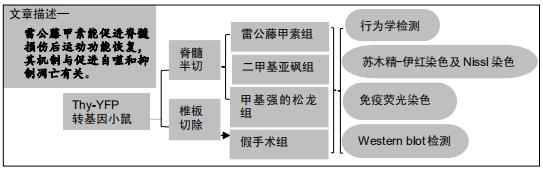
|
[1] ZHOU J, HUO X, BOTCHWAY BOA, et al. Beneficial Effects of Resveratrol-Mediated Inhibition of the mTOR Pathway in Spinal Cord Injury. Neural Plast. 2018;2018:7513748.
[2] GUO Y, WANG F, LI H, et al. Metformin Protects Against Spinal Cord Injury by Regulating Autophagy via the mTOR Signaling Pathway. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(5):1111-1117.
[3] RONG Y, LIU W, LV C, et al. Neural stem cell small extracellular vesicle- based delivery of 14-3-3t reduces apoptosis and neuroinflammation following traumatic spinal cord injury by enhancing autophagy by targeting Beclin-1. Aging (Albany NY).2019;11(18):7723-7745.
[4] LI Y, JONES JW, MC CHOI H, et al. cPLA2 activation contributes to lysosomal defects leading to impairment of autophagy after spinal cord injury. Cell Death Dis.2019;10(7):531.
[5] LI W, YANG Y, HU Z, et al. Neuroprotective effects of DAHP and Triptolide in focal cerebral ischemia via apoptosis inhibition and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway activation. Front Neuroanat. 2015;9:48.
[6] SU Z, YUAN Y, CAO L, et al. Triptolide Promotes Spinal Cord Repair by Inhibiting Astrogliosis and Inflammation. Glia.2010;58(8):901-915.
[7] SEIRA O,LIU J,ASSINCK P,et al.KIF2A characterization after spinal cord injury.Cell Mol Life Sci.2019;76(21):4355-4368.
[8] VIDAL PM, ULNDREAJ A, BADNER A, et al. Methylprednisolone treatment enhances early recovery following surgical decompression for degenerative cervical myelopathy without compromise to the systemic immune system. J Neuroinflammation. 2018;15(1):222
[9] TANG P, ZHANG Y, CHEN C, et al. In Vivo Two-Photon Imaging of Axonal Dieback, Blood Flow and Calcium Influx withMethylprednisolone Therapy after Spinal Cord Injury.Sci Rep. 2015;5:9691.
[10] DRUSCHEL C, SCHASER KD, SCHWAB JM. Current practice of methylprednisolone administration for acute spinal cord injury in Germany: a national survey. Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2013;38(11): E669-E677.
[11] LIN Y, LI C, LI J, et al. NEP1-40-modified human serum albumin nanoparticles enhance the therapeutic effect of methylprednisolone against spinal cord injury. J Nanobiotechnology.2019;17(1):12.
[12] TANG P, ZHANG Y, CHEN C, et al. In Vivo Two-Photon Imaging of Axonal Dieback, Blood Flow and Calcium Influx withMethylprednisolone Therapy after Spinal Cord Injury.Sci Rep. 2015;5:9691.
[13] ALLAHDADI KJ, DE SANTANA TA, SANTOS GC, et al. IGF-1 overexpression improves mesenchymal stem cell survival and promotes neurological recovery after spinal cord injury. Stem Cell Res Ther.2019;10(1):146.
[14] SILVA NA, SOUSA N, REIS RL, et al. From basics to clinical: a comprehensive review on spinal cord injury. Prog Neurobiol.2014;114: 25-57.
[15] WU J, LIPINSKI MM. Autophagy in Neurotrauma: Good, Bad, or Dysregulated. Cells. 2019;8(7). pii: E693.
[16] HU G, GONG X, WANG L, et al. Triptolide Promotes the Clearance of alpha-Synuclein by Enhancing Autophagy in Neuronal Cells.Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(3):2361-2372.
[17] ERLICH S, SHOHAMI E, PINKAS-KRAMARSKI R. Neurodegeneration Induces Upregulation of Beclin 1. Autophagy.2006;2(1):49-51.
[18] RONG Y, LIU W, WANG J, et al. Neural stem cell-derived small extracellular vesicles attenuate apoptosis and neuroinflammation after traumatic spinal cord injury by activating autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(5):340.
[19] RONG Y, LIU W, LV C, et al. Neural stem cell small extracellular vesicle-based delivery of 14-3-3t reduces apoptosis and neuroinflammation following traumatic spinal cord injury by enhancing autophagy by targeting Beclin-1. Aging (Albany NY).2019;11(18): 7723-7745.
[20] SARASWAT OHRI S, BANKSTON AN, MULLINS SA, et al. Blocking Autophagy in Oligodendrocytes Limits Functional Recovery after Spinal Cord Injury.J Neurosci. 2018;38(26):5900-5912.
[21] ZHAO H, CHEN S, GAO K, et al. Resveratrol protects against spinal cord injury by activating autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis mediated by the SIRT1/AMPK signaling pathway. Neuroscience.2017;348: 241-251.
[22] LI Z, CHEN T, CAO Y, et al. Pros and Cons: Autophagy in Acute Spinal Cord Injury. Neurosci Bull.2019;35(5):941-945.
|