中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5198-5202.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2806
• 组织构建临床实践 clinical practice in tissue construction • 上一篇 下一篇
肾移植受者422例病原菌感染分析
郭 娟1,郑 珊2,谢 辉1,胡亚会1
郑州人民医院,1检验科,2肾移植科,河南省郑州市 450003
An analysis of pathogenic bacteria infection in 422 kidney transplant recipients
Guo Juan1, Zheng Shan2, Xie Hui1, Hu Yahui1
1Department of Laboratory Medicine, 2Department of Kidney Transplantation, People’s Hospital of Zhengzhou, Zhengzhou 450003, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文题释义:
肾移植术:将健康者的肾脏移植给有肾脏病变并丧失肾脏功能的患者。人体有左右2个肾脏,通常一个肾脏就可以支持正常的代谢需求,当慢性肾功能不全发展至终末期,可用肾移植方法治疗。肾移植因其供肾来源不同分为自体肾移植、同种异体肾移植和异种肾移植,习惯把同种异体肾移植简称为肾移植。
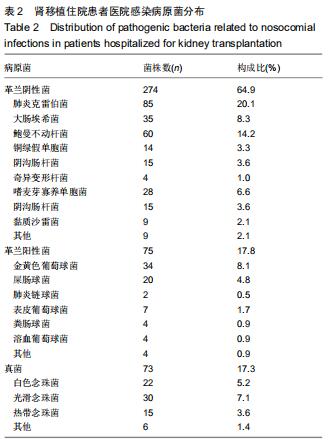
病原菌感染:为了预防肾移植手术后的排斥反应,一般都要常规使用免疫抑制剂。使用免疫抑制剂的过程中会使机体的免疫功能下降,而导致患者容易发生细菌、病毒、真菌、原虫等感染,其中最为常见的是细菌感染性疾病的发生。革兰阴性菌分离率较高的分别为肺炎克雷伯菌、鲍曼不动杆菌和大肠埃希氏菌,革兰阳性菌分离率较高的分别为金黄色葡萄球菌、屎肠球菌和表皮葡萄球菌。肾移植受者感染的致病菌以革兰阴性菌为主,其中大多数病原菌对多种抗生素耐药率偏高。
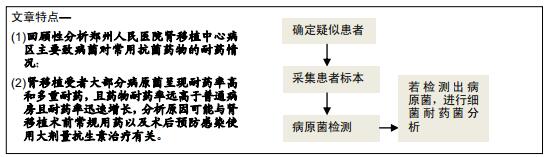
背景:了解肾移植受者细菌感染的类型和特点,分析肾移植术后医院感染病原菌分布及细菌耐药性变迁趋势,旨在为临床医生提供精准有效的治疗和防控措施,达到对肾移植受者临床合理使用抗菌药物的目的。
目的:探讨肾移植受者术后医院感染流行病学特点。
方法:对2014年8月至2019年8月在郑州人民医院肾移植中心术后发生病原菌感染的422例受者进行调查,包括标本类型、病原菌分布、病原菌耐药率等。该临床研究的实施符合郑州人民医院对研究的相关伦理要求。
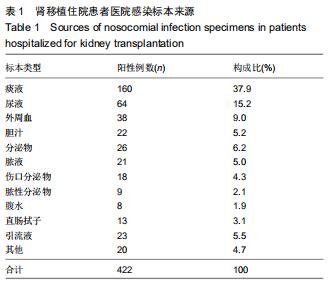
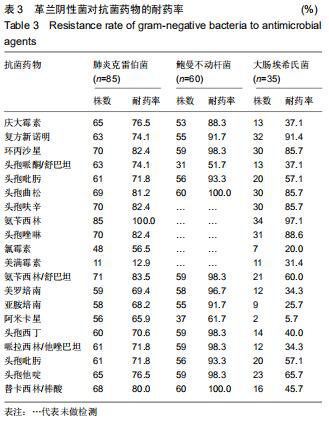
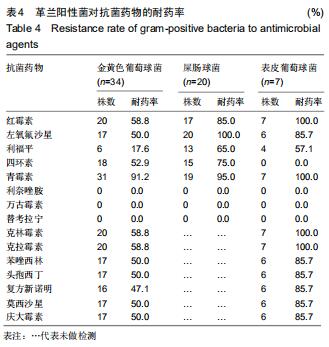
结果与结论:①肾移植受者发生病原菌感染阳性标本主要来自于痰液、尿液和外周血;②422株病原菌中革兰阴性菌274株(占64.9%),革兰阳性菌75株(占17.8%),真菌73株(占17.3%),其中革兰阴性菌分离率较高的分别为肺炎克雷伯菌、鲍曼不动杆菌和大肠埃希氏菌,革兰阳性菌分离率较高的是金黄色葡萄球菌、屎肠球菌和表皮葡萄球菌;③革兰阴性菌对多数抗菌药物的耐药率均较高,革兰阳性菌除了对万古霉素、替考拉宁和利奈唑胺完全敏感外,对其他抗菌药物有不同程度的耐药率;④结果表明,肾移植受者感染的致病菌以革兰阴性菌为主,其中大多数病原菌对多种抗生素耐药率偏高,有的已产生多重耐药性,应加强对肾移植受者耐药性的监管,合理使用抗菌药物。
ORCID: 0000-0001-6861-6619(郭娟)
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程中图分类号: