中国组织工程研究 ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (32): 5203-5212.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2808
• 共识与指南Consensus and guidelines • 上一篇 下一篇
成人心脏外科术后脑损伤诊治的中国专家共识
中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会心脏重症脑保护学组,中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会神经重症护理与康复学组
-
收稿日期:2020-01-19修回日期:2020-01-21接受日期:2020-03-09出版日期:2020-11-18发布日期:2020-09-27 -
通讯作者:韩宏光,解放军北部战区总医院,辽宁省沈阳市 110024
Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of postoperative brain injury in adult cardiac surgery
Cerebral Protection in Cardiac Intensive Care Group, Neural Regeneration and Repair Committee, Chinese Research Hospital Association,Neural Intensive Nursing and Rehabilitation Group, Neural Regeneration and Repair Committee, Chinese Research Hospital Association
-
Received:2020-01-19Revised:2020-01-21Accepted:2020-03-09Online:2020-11-18Published:2020-09-27 -
Contact:Han Hongguang, General Hospital of Northern Theater Command, Shenyang 110024, Liaoning Province, China
摘要:
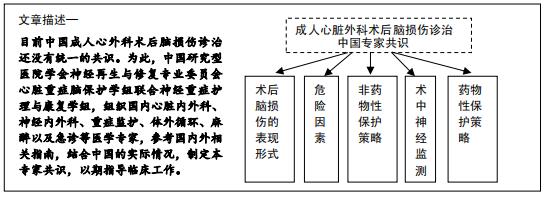
背景:脑损伤作为成人心脏外科术后一种严重的并发症,发病率依然较高,是除心功能不全以外导致心脏外科手术患者预后不良的最主要因素之一。
目的:为减少心脏外科手术后脑卒中并发症,建立相关方面的诊治规范。
方法:为了降低成人心脏外科术后脑损伤的发生率,减少神经系统并发症,中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会心脏重症脑保护学组联合神经重症护理与康复学组,组织国内心脏内外科、神经内外科、重症监护、体外循环、麻醉以及急诊等医学专家,参考国内外相关指南,结合中国的实际情况,从成人心脏外科术后脑损伤的表现形式、危险因素、非药物性保护策略、术中神经监测以及药物性保护策略等方面,旨在促进患者脑神经功能康复角度进行撰写,经多次讨论最终成稿,制定该专家共识,以期指导临床工作。
结果与结论:为了降低成人心脏手术后脑损伤的发生率,减少神经系统并发症,需要采用个性化、以患者为中心的方法来管理那些可改变的脑损伤危险因素,采用包括术中栓塞的预防,血压、血糖、体温的管理,以及针对术后神经炎性反应药物治疗等方法,达到改善手术效果、提高患者生活质量的目的。然而,目前仍需要进一步的研究,尤其是高质量的以结果为导向的随机对照试验,以进一步提高脑损伤处理策略的证据支持。
ORCID: 0000-0002-0850-5922(韩宏光)中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会心脏重症脑保护学组, 中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会神经重症护理与康复学组. 成人心脏外科术后脑损伤诊治的中国专家共识[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(32): 5203-5212.
Cerebral Protection in Cardiac Intensive Care Group, Neural Regeneration and Repair Committee, Chinese Research Hospital Association, Neural Intensive Nursing and Rehabilitation Group, Neural Regeneration and Repair Committee, Chinese Research Hospital Association. Chinese expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of postoperative brain injury in adult cardiac surgery[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(32): 5203-5212.
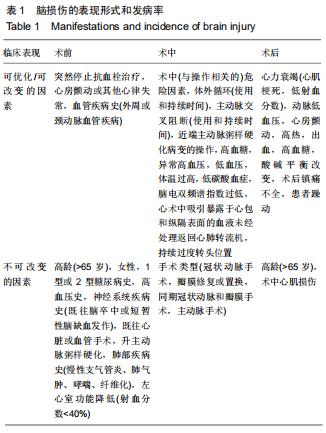
大多数脑损伤的危险因素(例如年龄、既往病史等)是不可改变的,而某些因素(例如栓塞、低血压、高血糖、高体温、手术方法等)是可优化、可改变的,见表1。围术期脑保护的目的是干预可改变的危险因素,进一步减少成人心脏外科术后的脑损伤的发生。脑保护措施可分为药物性和非药物性。非药物性策略最大限度地减少栓子的产生,通过血压、红细胞压积以及良好的温度管理来保护大脑;而药物性策略主要通过各种药物的炎症抑制作用,达到脑保护的目的。
|
[1] BERGER M, TERRANDO N, SMITH SK, et al. Neurocognitive Function after Cardiac Surgery: From Phenotypes to Mechanisms. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(4): 829-851.
[2] VLISIDES PE, MASHOUR GA, DIDIER TJ, et al. Recognition and Management of Perioperative Stroke in Hospitalized Patients. A A Case Rep. 2016;7(3): 55-56.
[3] GAUDINO M, RAHOUMA M, DI MAURO M, et al. Early Versus Delayed Stroke After Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(13): e012447.
[4] SANTARPINO G, MOSCARELLI M. Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction: A Forgotten Part of the Quality of Life. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108(5): 1583.
[5] LIU Y, CHEN K, MEI W. Neurological complications after cardiac surgery: anesthetic considerations based on outcome evidence. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2019;32(5):563-567.
[6] RAFFA GM, AGNELLO F, OCCHIPINTI G, et al. Neurological complications after cardiac surgery: a retrospective case-control study of risk factors and outcome. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2019;14(1):23.
[7] VEDEL AG, HOLMGAARD F, RASMUSSEN LS, et al. High-Target Versus Low-Target Blood Pressure Management During Cardiopulmonary Bypass to Prevent Cerebral Injury in Cardiac Surgery Patients: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Circulation. 2018;137(17):1770-1780.
[8] SUN LY, CHUNG AM, FARKOUH ME, et al. Defining an Intraoperative Hypotension Threshold in Association with Stroke in Cardiac Surgery. Anesthesiology. 2018;129(3):440-447.
[9] KNIPP SC, MATATKO N, WILHELM H, et al. Cognitive outcomes three years after coronary artery bypass surgery: relation to diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. Ann Thorac Surg. 2008;85(3):872-879.
[10] LOBERMAN D, CONSALVI C, HEALEY A, et al. Adverse Cerebral Outcomes after Coronary Artery Bypass Surgery-More Than a Decade of Experience in a Single Center. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;66(6): 452-456.
[11] KEELING B, HALKOS ME. The modern Hydra: Perioperative stroke and cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;155(2): 507.
[12] HOGUE CW JR, PALIN CA, ARROWSMITH JE. Cardiopulmonary bypass management and neurologic outcomes: an evidence-based appraisal of current practices. Anesth Analg.2006;103(1):21-37.
[13] PATEL N, MINHAS JS, CHUNG EM. The Presence of New MRI Lesions and Cognitive Decline After Cardiac Surgery: A Systematic Review. J Card Surg. 2015;30(11):808-812.
[14] NEWMAN MF, MATHEW JP, GROCOTT HP, et al. Central nervous system injury associated with cardiac surgery. Lancet. 2006;368(9536): 694-703.
[15] HUSEBRÅTEN IM, FIANE AE, RINGDAL M, et al. Measurement of gaseous microemboli in the prime before the initiation of cardiopulmonary bypass. Perfusion. 2018;33(1):30-35.
[16] MITZ MA. CO2 biodynamics: a new concept of cellular control.J Theor Biol.1979;80(4):537-551.
[17] WEBB WR, HARRISON LH JR, HELMCKE FR, et al. Carbon dioxide field flooding minimizes residual intracardiac air after open heart operations. Ann Thorac Surg. 1997;64(5):1489-1491.
[18] MARTENS S, THEISEN A, BALZER JO, et al. Improved cerebral protection through replacement of residual intracavital air by carbon dioxide: a porcine model using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;127(1):51-56.
[19] MARTENS S, DIETRICH M, WALS S, et al. Conventional carbon dioxide application does not reduce cerebral or myocardial damage in open heart surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2001;72(6):1940-1944.
[20] SVENARUD P, PERSSON M, VAN DER LINDEN J. Effect of CO2 insufflation on the number and behavior of air microemboli in open-heart surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Circulation. 2004; 109(9):1127-1132.
[21] PERSSON M, VAN DER LINDEN J. De-airing of a cardiothoracic wound cavity model with carbon dioxide: theory and comparison of a gas diffuser with conventional tubes. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2003;17(3): 329-335.
[22] VAN DER ZEE MP, KOENE BM, MARIANI MA. Fatal air embolism during cardiopulmonary bypass: analysis of an incident and prevention measures. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2014;19(5):875-877.
[23] NEEMA PK, PATHAK S, VARMA PK, et al. Case 2--2007: Systemic air embolization after termination of cardiopulmonary bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2007;21(2):288-297.
[24] NEWMAN MF, GROCOTT HP, MATHEW JP, et al. Report of the substudy assessing the impact of neurocognitive function on quality of life 5 years after cardiac surgery. Stroke. 2001;32(12): 2874-2881.
[25] DÁVILA-ROMÁN VG, MURPHY SF, NICKERSON NJ, et al. Atherosclerosis of the ascending aorta is an independent predictor of long-term neurologic events and mortality. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1999; 33(5):1308-1316.
[26] TUNICK PA, PEREZ JL, KRONZON I. Protruding atheromas in the thoracic aorta and systemic embolization. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115(6): 423-427.
[27] WAREING TH, DAVILA-ROMAN VG, BARZILAI B, et al. Management of the severely atherosclerotic ascending aorta during cardiac operations[J]. A strategy for detection and treatment. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1992;103(3): 453-462.
[28] KATZ ES, TUNICK PA, RUSINEK H, et al. Protruding aortic atheromas predict stroke in elderly patients undergoing cardiopulmonary bypass: experience with intraoperative transesophageal echocardiography. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1992;20(1): 70-77.
[29] RIBAKOVE GH, KATZ ES, GALLOWAY AC, et al. Surgical implications of transesophageal echocardiography to grade the atheromatous aortic arch. Ann Thorac Surg. 1992;53(5):758-61; discussion762-763.
[30] URBANSKI PP, SABIK JF, BACHET JE. Cannulation of an arch artery for hostile aorta. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2017;51(1):2-9.
[31] HEDAYATI N, SHERWOOD JT, SCHOMISCH SJ, et al. Axillary artery cannulation for cardiopulmonary bypass reduces cerebral microemboli. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004;128(3): 386-390.
[32] PAPPA M, THEODOSIADIS N, TSOUNIS A, et al. Pathogenesis and treatment of post-operative cognitive dysfunction. Electron Physician. 2017;9(2):3768-3775.
[33] CARRIER M, DENAULT A, LAVOIE J, et al. Randomized controlled trial of pericardial blood processing with a cell-saving device on neurologic markers in elderly patients undergoing coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2006;82(1):51-55.
[34] JEWELL AE, AKOWUAH EF, SUVARNA SK, et al. A prospective randomised comparison of cardiotomy suction and cell saver for recycling shed blood during cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2003;23(4):633-636.
[35] RUBENS FD, BOODHWANI M, MESANA T, et al. The cardiotomy trial: a randomized, double-blind study to assess the effect of processing of shed blood during cardiopulmonary bypass on transfusion and neurocognitive function. Circulation. 2007;116(11 Suppl):I89-197.
[36] YASUKAWA T, MANABE S, HIRAOKA D, et al. Safety and efficacy of a simple cardiotomy suction system as a blood salvage procedure during off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery. J Artif Organs. 2019; 22(3):194-199.
[37] SELNES OA, GOTTESMAN RF, GREGA MA, et al. Cognitive and neurologic outcomes after coronary-artery bypass surgery. N Engl J Med. 2012;366(3):250-257.
[38] LO COCO D, LOPEZ G, CORRAO S. Cognitive impairment and stroke in elderly patients. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2016;12:105-116.
[39] 李双磊,吴远斌,龚志云,等.心脏骤停患者心肺复苏后神经系统的维护[J].中国体外循环杂志,2019,17(4):249-251,256.
[40] BLÁHA J, MRÁZ M, KOPECKÝ P, et al. Perioperative Tight Glucose Control Reduces Postoperative Adverse Events in Nondiabetic Cardiac Surgery Patients. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015;100(8): 3081-3089.
[41] KNAAK C, WOLLERSHEIM T, MÖRGELI R, et al. Risk Factors of Intraoperative Dysglycemia in Elderly Surgical Patients. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(5):665-674.
[42] NAVARATNARAJAH M, REA R, EVANS R, et al. Effect of glycaemic control on complications following cardiac surgery: literature review. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2018;13(1):10.
[43] MOGHISSI ES, KORYTKOWSKI MT, DINARDO M, et al. American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Diabetes Association consensus statement on inpatient glycemic control. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(6):1119-1131.
[44] GOLD JP, CHARLSON ME, WILLIAMS-RUSSO P, et al. Improvement of outcomes after coronary artery bypass. A randomized trial comparing intraoperative high versus low mean arterial pressure. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.1995;110(5):1302-1311; discussion 1311-1314.
[45] SIEPE M, PFEIFFER T, GIERINGER A, et al. Increased systemic perfusion pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with less early postoperative cognitive dysfunction and delirium. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2011;40(1):200-207.
[46] WESSELINK EM, KAPPEN TH, VAN KLEI WA, et al. Intraoperative hypotension and delirium after on-pump cardiac surgery. Br J Anaesth. 2015;115(3):427-433.
[47] HORI D, BROWN C, ONO M, et al. Arterial pressure above the upper cerebral autoregulation limit during cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with postoperative delirium. Br J Anaesth. 2014;113(6):1009-1017..
[48] HORI D, NOMURA Y, ONO M, et al. Optimal blood pressure during cardiopulmonary bypass defined by cerebral autoregulation monitoring. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2017;154(5):1590-1598.e2.
[49] MURKIN JM, FARRAR JK, TWEED WA, et al. Cerebral autoregulation and flow/metabolism coupling during cardiopulmonary bypass: the influence of PaCO2. Anesth Analg. 1987;66(9):825-832.
[50] JOSHI B, ONO M, BROWN C, et al. Predicting the limits of cerebral autoregulation during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg.2012; 114(3):503-510.
[51] GOTTESMAN RF. Asymptomatic Carotid Stenosis in Cardiac Surgery Patients: Is Less More? Stroke.2017;48(10):2650-2651.
[52] GROGAN K, STEARNS J, HOGUE CW. Brain protection in cardiac surgery. Anesthesiol Clin. 2008;26(3):521-538.
[53] NAYLOR AR, BOWN MJ. Stroke after cardiac surgery and its association with asymptomatic carotid disease: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg. 2011;41(5):607-624.
[54] MORESOLI P, HABIB B, REYNIER P, et al. Carotid Stenting Versus Endarterectomy for Asymptomatic Carotid Artery Stenosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Stroke. 2017;48(8): 2150-2157.
[55] MCDONAGH DL, BERGER M, MATHEW JP, et al. Neurological complications of cardiac surgery. Lancet Neurol.2014;13(5):490-502.
[56] NEJIM B, DAKOUR ARIDI H, LOCHAM S, et al. Carotid artery revascularization in patients with contralateral carotid artery occlusion: Stent or endarterectomy? J Vasc Surg. 2017;66(6):1735-1748.e1.
[57] MASABNI K, RAZA S, BLACKSTONE EH, et al. Does preoperative carotid stenosis screening reduce perioperative stroke in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass grafting?. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2015;149(5):1253-1260.
[58] TOMAI F, PICCOLI A, CASTRIOTA F, et al. Long-Term Outcomes of Coronary and Carotid Artery Disease Revascularization in the FRIENDS Study. J Interv Cardiol.2019;2019:8586927.
[59] IRQSUSI M, VANNUCCHI A, BECKERS J, et al. Early Results of Surgical Simultaneous Therapy for Significant Carotid Artery Stenosis and Heart Disease. Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2018;66(3):261-265..
[60] STARKE RM. Optimal management of patients with asymptomatic carotid stenosis. Neurology. 2017,88(21):1988-1989.
[61] ABBOTT AL, BRUNSER AM, GIANNOUKAS A, et al. Misconceptions regarding the adequacy of best medical intervention alone for asymptomatic carotid stenosis. J Vasc Surg.2019;71(1):257-269.
[62] Authors/Task Force members, WINDECKER S, KOLH P, et al. 2014 ESC/EACTS Guidelines on myocardial revascularization: The Task Force on Myocardial Revascularization of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS)Developed with the special contribution of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions (EAPCI). Eur Heart J. 2014;35(37): 2541-2619.
[63] DHIR A, TEMPE DK. Anemia and Patient Blood Management in Cardiac Surgery-Literature Review and Current Evidence. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.2018;32(6):2726-2742.
[64] RANUCCI M, DI DEDDA U, CASTELVECCHIO S, et al. Impact of preoperative anemia on outcome in adult cardiac surgery: a propensity-matched analysis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;94(4): 1134-1141.
[65] KARKOUTI K, DJAIANI G, BORGER MA, et al. Low hematocrit during cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with increased risk of perioperative stroke in cardiac surgery. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;80(4): 1381-1387.
[66] PAONE G, LIKOSKY DS, BREWER R, et al. Transfusion of 1 and 2 units of red blood cells is associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Ann Thorac Surg.2014;97(1):87-93; discussion 93-94.
[67] BAHRAINWALA ZS, GREGA MA, HOGUE CW, et al. Intraoperative hemoglobin levels and transfusion independently predict stroke after cardiac operations. Ann Thorac Surg, 2011;91(4):1113-1118.
[68] MARISCALCO G, BIANCARI F, JUVONEN T, et al. Red blood cell transfusion is a determinant of neurological complications after cardiac surgery. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015;20(2):166-171.
[69] KIM J, WEIGAND M, PALMER AF, et al. Single cell analysis of aged RBCs: quantitative analysis of the aged cells and byproducts. Analyst. 2019;144(3):935-942.
[70] Society of Thoracic Surgeons Blood Conservation Guideline Task Force, FERRARIS VA, BROWN JR, et al. 2011 update to the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists blood conservation clinical practice guidelines. Ann Thorac Surg.2011;91(3):944-982.
[71] HORI D, EVERETT AD, LEE JK, et al. Rewarming Rate During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Is Associated With Release of Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;100(4):1353-1358.
[72] GEOCADIN RG, WIJDICKS E, ARMSTRONG MJ, et al. Practice guideline summary: Reducing brain injury following cardiopulmonary resuscitation: Report of the Guideline Development, Dissemination, and Implementation Subcommittee of the American Academy of Neurology. Neurology.2017;88(22):2141-2149.
[73] CARIOU A, PAYEN JF, ASEHNOUNE K, et al. Targeted temperature management in the ICU: Guidelines from a French expert panel. Anaesth Crit Care Pain Med.2018;37(5):481-491.
[74] MENG L, WANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Heterogeneity and Variability in Pressure Autoregulation of Organ Blood Flow: Lessons Learned Over 100+ Years. Crit Care Med.2019;47(3):436-448.
[75] LEWIS C, PARULKAR SD, BEBAWY J, et al. Cerebral Neuromonitoring During Cardiac Surgery: A Critical Appraisal With an Emphasis on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2018;32(5):2313-2322.
[76] ENGELMAN R, BAKER RA, LIKOSKY DS, et al. The Society of Thoracic Surgeons, The Society of Cardiovascular Anesthesiologists, and The American Society of ExtraCorporeal Technology: Clinical Practice Guidelines for Cardiopulmonary Bypass-Temperature Management During Cardiopulmonary Bypass. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2015;29(4):1104-1113.
[77] GROCOTT HP, MACKENSEN GB, GRIGORE AM, et al. Postoperative hyperthermia is associated with cognitive dysfunction after coronary artery bypass graft surgery. Stroke. 2002;33(2):537-541.
[78] KIVINIEMI T, MALMBERG M, BIANCARI F, et al. Thromboembolisms related to post-operative electrical cardioversions for atrial fibrillation in patients with surgical aortic valve replacement. Eur Heart J Qual Care Clin Outcomes.2018;4(2):120-125.
[79] GAUDINO M, ANGIOLILLO DJ, DI FRANCO A, et al. Stroke After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting and Percutaneous Coronary Intervention: Incidence, Pathogenesis, and Outcomes. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019;8(13):e013032.
[80] JACKSON JC, MOZAFFARIAN D, GRAVES AJ, et al. Fish Oil Supplementation Does Not Affect Cognitive Outcomes in Cardiac Surgery Patients in the Omega-3 Fatty Acids for Prevention of Post-Operative Atrial Fibrillation (OPERA) Trial. J Nutr.2018;148(3): 472-479.
[81] MARIANI J, DOVAL HC, NUL D, et al. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids to prevent atrial fibrillation: updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Am Heart Assoc. 2013;2(1):e005033.
[82] KUHN EW, SLOTTOSCH I, WAHLERS T, et al. WITHDRAWN: Preoperative statin therapy for patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2016;(5):CD008493.
[83] WANG X, YAO L, GE L, et al. Pharmacological interventions for preventing post-operative atrial fibrillation in patients undergoing cardiac surgery: a network meta-analysis protocol. BMJ Open.2017; 7(12):e018544..
[84] BUDERA P, STRAKA Z, OSMANČÍK P, et al. Comparison of cardiac surgery with left atrial surgical ablation vs. cardiac surgery without atrial ablation in patients with coronary and/or valvular heart disease plus atrial fibrillation: final results of the PRAGUE-12 randomized multicentre study. Eur Heart J.2012;33(21):2644-2652.
[85] REDDY VY, DOSHI SK, SIEVERT H, et al. Percutaneous left atrial appendage closure for stroke prophylaxis in patients with atrial fibrillation: 2.3-Year Follow-up of the PROTECT AF (Watchman Left Atrial Appendage System for Embolic Protection in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation) Trial. Circulation.2013;127(6):720-729.
[86] FEDOROW C, GROCOTT HP. Cerebral monitoring to optimize outcomes after cardiac surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol.2010; 23(1): 89-94.
[87] Guarracino F. Cerebral monitoring during cardiovascular surgery. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol. 2008;21(1):50-54.
[88] SAIDI N, MURKIN JM. Applied neuromonitoring in cardiac surgery: patient specific management. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.2005; 9(1):17-23.
[89] POLITO A, RICCI Z, DI CHIARA L, et al. Cerebral blood flow during cardiopulmonary bypass in pediatric cardiac surgery: the role of transcranial Doppler--a systematic review of the literature. Cardiovasc Ultrasound.2006;4:47.
[90] GROCOTT HP, AMORY DW, LOWRY E, et al. Transcranial Doppler blood flow velocity versus 133Xe clearance cerebral blood flow during mild hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. J Clin Monit Comput.1998; 14(1):35-39.
[91] WANG X, JI B, YANG B, et al. Real-time continuous neuromonitoring combines transcranial cerebral Doppler with near-infrared spectroscopy cerebral oxygen saturation during total aortic arch replacement procedure: a pilot study. ASAIO J.2012; 58(2):122-126.
[92] SELIM M. Perioperative stroke. N Engl J Med. 2007;356(7):706-713.
[93] SALAZAR JD, WITYK RJ, GREGA MA, et al. Stroke after cardiac surgery: short- and long-term outcomes. Ann Thorac Surg.2001; 72(4):1195-1201; discussion 1201-1202.
[94] MURKIN JM. Applied neuromonitoring and improving CNS outcomes. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.2005;9(2):139-142.
[95] SLOAN MA. Prevention of ischemic neurologic injury with intraoperative monitoring of selected cardiovascular and cerebrovascular procedures: roles of electroencephalography, somatosensory evoked potentials, transcranial Doppler, and near-infrared spectroscopy. Neurol Clin.2006;24(4):631-645.
[96] SHAABAN ALI M, HARMER M, LATTO I. Jugular bulb oximetry during cardiac surgery. Anaesthesia.2001;56(1):24-37.
[97] MACMILLAN CS, ANDREWS PJ. Cerebrovenous oxygen saturation monitoring: practical considerations and clinical relevance. Intensive Care Med.2000;26(8):1028-1036.
[98] SCHELL RM, COLE DJ. Cerebral monitoring: jugular venous oximetry. Anesth Analg. 2000;90(3):559-566.
[99] NAKAJIMA T, OHSUMI H, KURO M. Accuracy of continuous jugular bulb venous oximetry during cardiopulmonary bypass. Anesth Analg. 1993;77(6):1111-1115.
[100] CROUGHWELL ND, FRASCO P, BLUMENTHAL JA, et al. Warming during cardiopulmonary bypass is associated with jugular bulb desaturation. Ann Thorac Surg.1992;53(5):827-832.
[101] CROUGHWELL ND, NEWMAN MF, BLUMENTHAL JA, et al. Jugular bulb saturation and cognitive dysfunction after cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg.1994;58(6):1702-1708.
[102] COOK DJ, OLIVER WC JR, ORSZULAK TA, et al. A prospective, randomized comparison of cerebral venous oxygen saturation during normothermic and hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.1994;107(4):1020-1028; discussion 1028-1029.
[103] MARCUSE LV, BRONSTER DJ, FIELDS M, et al. Evaluating the obtunded patient after cardiac surgery: the role of continuous electroencephalography. J Crit Care.2014;29(2):316.e1-5.
[104] AVIDAN MS, ZHANG L, BURNSIDE BA, et al. Anesthesia awareness and the bispectral index. N Engl J Med.2008;358(11):1097-1108.
[105] RAMPIL IJ. A primer for EEG signal processing in anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 1998;89(4):980-1002.
[106] MYLES PS, LESLIE K, MCNEIL J, et al. Bispectral index monitoring to prevent awareness during anaesthesia: the B-Aware randomised controlled trial. Lancet.2004;363(9423):1757-1763.
[107] VASUNILASHORN SM, NGO L, INOUYE SK, et al. Cytokines and Postoperative Delirium in Older Patients Undergoing Major Elective Surgery. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2015;70(10):1289-1295.
[108] HOVENS IB, VAN LEEUWEN BL, NYAKAS C, et al. Prior infection exacerbates postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aged rats. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2015;309(2):R148-159.
[109] SALAMEH A, DHEIN S, DÄHNERT I, et al. Neuroprotective Strategies during Cardiac Surgery with Cardiopulmonary Bypass. Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(11). pii: E1945.
[110] BHAMIDIPATI D, GOLDHAMMER JE, SPERLING MR, et al. Cognitive Outcomes After Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting. J Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth.2017;31(2):707-718.
[111] LORD JM, MIDWINTER MJ, CHEN YF, et al. The systemic immune response to trauma: an overview of pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet.2014;384(9952):1455-1465.
[112] ABRAHAMOV D, LEVRAN O, NAPARSTEK S, et al. Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption After Cardiopulmonary Bypass: Diagnosis and Correlation to Cognition. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017;104(1):161-169.
[113] MERINO JG, LATOUR LL, TSO A, et al. Blood-brain barrier disruption after cardiac surgery. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol.2013;34(3):518-523..
[114] STEINBERG BE, SUNDMAN E, TERRANDO N, et al. Neural Control of Inflammation: Implications for Perioperative and Critical Care. Anesthesiology.2016;124(5):1174-1189.
[115] NTALOUKA MP, ARNAOUTOGLOU E, TZIMAS P. Postoperative cognitive disorders: an update. Hippokratia.2018;22(4):147-154.
[116] GLUMAC S, KARDUM G, SODIC L, et al. Effects of dexamethasone on early cognitive decline after cardiac surgery: A randomised controlled trial. Eur J Anaesthesiol.2017;34(11):776-784.
[117] MARDANI D, BIGDELIAN H. Prophylaxis of dexamethasone protects patients from further post-operative delirium after cardiac surgery: A randomized trial. J Res Med Sci. 2013;18(2):137-143.
[118] OTTENS TH, DIELEMAN JM, SAUËR AM, et al. Effects of dexamethasone on cognitive decline after cardiac surgery: a randomized clinical trial. Anesthesiology. 2014;121(3):492-500.
[119] DIELEMAN JM, NIERICH AP, ROSSEEL PM, et al. Intraoperative high-dose dexamethasone for cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA.2012;308(17):1761-1767.
[120] WANG X, XUE Q, YAN F, et al. Ulinastatin as a neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory agent in infant piglets model undergoing surgery on hypothermic low-flow cardiopulmonary bypass. Paediatr Anaesth. 2013;23(3):209-216.
[121] QIU Y, LIN J, YANG Y, et al. Lack of Efficacy of Ulinastatin Therapy During Cardiopulmonary Bypass Surgery. Chin Med J (Engl).2015; 128(23):3138-3142.
[122] SAYED S, IDRISS NK, SAYYEDF HG, et al. Effects of propofol and isoflurane on haemodynamics and the inflammatory response in cardiopulmonary bypass surgery. Br J Biomed Sci. 2015;72(3):93-101.
[123] BAKI ED, ALDEMIR M, KOKULU S, et al. Comparison of the effects of desflurane and propofol anesthesia on the inflammatory response and s100β protein during coronary artery bypass grafting. Inflammation. 2013;36(6):1327-1333.
[124] BILOTTA F, STAZI E, ZLOTNIK A, et al. Neuroprotective effects of intravenous anesthetics: a new critical perspective. Curr Pharm Des. 2014;20(34):5469-5475.
[125] KANBAK M, SARICAOGLU F, AVCI A, et al. Propofol offers no advantage over isoflurane anesthesia for cerebral protection during cardiopulmonary bypass: a preliminary study of S-100beta protein levels. Can J Anaesth.2004;51(7):712-717.
[126] SEDRAKYAN A, TREASURE T, ELEFTERIADES JA. Effect of aprotinin on clinical outcomes in coronary artery bypass graft surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2004;128(3):442-448.
[127] STAMOU SC, REAMES MK, SKIPPER E, et al. Aprotinin in cardiac surgery patients: is the risk worth the benefit?. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2009;36(5):869-875.
[128] HÉBERT PC, FERGUSSON DA, HUTTON B, et al. Regulatory decisions pertaining to aprotinin may be putting patients at risk. CMAJ. 2014;186(18):1379-1386.
[129] BENEDETTO U, ALTMAN DG, GERRY S, et al. Safety of Perioperative Aprotinin Administration During Isolated Coronary Artery Bypass Graft Surgery: Insights From the ART (Arterial Revascularization Trial). J Am Heart Assoc. 2018;7(5). pii: e007570.
[130] TIAN Z, DONG C, FUJITA A, et al. Expression of heat shock protein HSP-70 in the retrosplenial cortex of rat brain after administration of (R,S)-ketamine and (S)-ketamine, but not (R)-ketamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav.2018;172:17-21. [131] NAGELS W, DEMEYERE R, VAN HEMELRIJCK J, et al. Evaluation of the neuroprotective effects of S(+)-ketamine during open-heart surgery. Anesth Analg.2004;98(6):1595-1603.
[132] HUDETZ JA, IQBAL Z, GANDHI SD, et al. Ketamine attenuates post-operative cognitive dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.2009;53(7):864-872.
[133] LENG T, GAO X, DILGER JP, et al. Neuroprotective effect of lidocaine: is there clinical potential? Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol.2016; 8(1):9-13.
[134] FUJITANI T, ADACHI N, MIYAZAKI H, et al. Lidocaine protects hippocampal neurons against ischemic damage by preventing increase of extracellular excitatory amino acids: a microdialysis study in Mongolian gerbils. Neurosci Lett.1994;179(1-2):91-94.
[135] WANG D, WU X, LI J, et al. The effect of lidocaine on early postoperative cognitive dysfunction after coronary artery bypass surgery. Anesth Analg.2002;95(5):1134-1141, table of contents.
[136] KLINGER RY, COOTER M, BISANAR T, et al. Intravenous Lidocaine Does Not Improve Neurologic Outcomes after Cardiac Surgery: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Anesthesiology. 2019;130(6):958-970.
[137] SALAMEH A, EINENKEL A, KÜHNE L, et al. Hippocampal Neuroprotection by Minocycline and Epigallo-Catechin-3-Gallate Against Cardiopulmonary Bypass-Associated Injury. Brain Pathol. 2015;25(6):733-742.
[138] DRABEK T, JANATA A, WILSON CD, et al. Minocycline attenuates brain tissue levels of TNF-α produced by neurons after prolonged hypothermic cardiac arrest in rats. Resuscitation. 2014;85(2):284-291.
[139] HAN XY, LIU H, LIU CH, et al. Synthesis of the optical isomers of a new anticholinergic drug, penehyclidine hydrochloride (8018). Bioorg Med Chem Lett.2005;15(8):1979-1982.
[140] WANG D, JIANG Q, DU X. Protective effects of scopolamine and penehyclidine hydrochloride on acute cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury after cardiopulmonary resuscitation and effects on cytokines. Exp Ther Med.2018;15(2):2027-2031.
[141] ZADEK F, SPINA S, HU J, et al. Nitric Oxide Treatment for Lungs and Beyond. Novel Insights from Recent Literature. Am J Respir Crit Care Med.2019;200(5):628-630.
[142] MARRAZZO F, SPINA S, ZADEK F, et al. Protocol of a randomised controlled trial in cardiac surgical patients with endothelial dysfunction aimed to prevent postoperative acute kidney injury by administering nitric oxide gas. BMJ Open. 2019;9(7):e026848.
[143] DEBSKA G, MAY R, KICIŃSKA A, et al. Potassium channel openers depolarize hippocampal mitochondria. Brain Res. 2001;892(1):42-50.
[144] FOSTER MN, COETZEE WA. KATP Channels in the Cardiovascular System. Physiol Rev. 2016;96(1):177-252.
[145] HAAPANEN HJ, ARVOLA O, HERAJÄRVI J, et al. Pharmacological Preconditioning with Diazoxide in the Experimental Hypothermic Circulatory Arrest Model. Heart Surg Forum. 2017;20(2): E069-069, E076.
[146] 中国心脏重症镇静镇痛专家委员会(2017). 中国心脏重症镇静镇痛专家共识[J].中华医学杂志, 97(10):726-734.
[147] DUNCAN D, SANKAR A, BEATTIE WS, et al. Alpha-2 adrenergic agonists for the prevention of cardiac complications among adults undergoing surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018;3:CD004126.
[148] SULEMANJI DS, DÖNMEZ A, ALDEMIR D, et al. Dexmedetomidine during coronary artery bypass grafting surgery:is it neuroprotective?--A preliminary study.Acta Anaesthesiol Scand.2007;51(8):1093-1098.
[149] 贾龙飞,陈群清.心脏手术脑保护药物及其机制研究进展[J].广东医学, 2016,37(2):300-302.
[150] 陈倩,顾健腾,鲁开智.右美托咪定的器官保护作用研究进展[J].中国药房, 2014,25(25):2385-2388.
[151] XIONG J, QUAN J, QIN C, et al. Dexmedetomidine Exerts Brain-Protective Effects Under Cardiopulmonary Bypass Through Inhibiting the Janus Kinase 2/Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription 3 Pathway. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2020;40(2):116-124.
[152] 张玉辉,高亚坤,肖连波, 等.右美托咪定对老年心脏瓣膜置换术患者心肌保护和脑保护的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2015,35(16):4606-4608. [153] 陈贤,黎必万,檀文好,等.盐酸右美托咪定对先天性心脏病快通道麻醉患儿的脑保护作用[J].重庆医学,2016,45(23):3252-3255. |
| [1] | 蒲 锐, 陈子扬, 袁凌燕. 不同细胞来源外泌体保护心脏的特点与效应[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | 陈进平, 李 奎, 陈 骞, 郭浩然, 张映波, 蔚 芃. 开放性脊柱手术应用氨甲环酸的疗效及安全性的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | 张雯雯, 金颂峰, 赵国梁, 宮丽鸿. 复方中药稳斑汤减少同型半胱氨酸诱导大鼠心肌微血管内皮细胞凋亡的作用机制[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 723-728. |
| [4] | 徐东紫, 张 婷, 欧阳昭连. 心脏组织工程领域全球专利竞争态势分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [5] | 宋凯凯, 张 锴, 贾 龙. 周围神经系统损伤的微环境与修复方式[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 651-656. |
| [6] | 潘 璇, 赵 萌, 张秀梅, 赵 杰, 翟运开. 生物3D打印技术在精准医学领域研究应用现状的中英文文献分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(21): 3382-3389. |
| [7] | 李尚志, 郑得志, 刘 军. 加速康复外科模式下鸡尾酒疗法对全膝关节置换后的早期镇痛[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(18): 2794-2798. |
| [8] | 陈天贵, 高 磊, 李天博, 王江宁. 脉络宁注射液干预挤压伤综合征模型猪线粒体自噬及PINK1/Parkin通路的变化[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(17): 2676-2680. |
| [9] | 王冬慧, 武 鑫, 孙宁宁, 张 晗, 高剑峰. 电针干预放射性脑损伤小鼠海马区突触可塑性相关蛋白的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(14): 2205-2210. |
| [10] | 来帅威, 张沙沙, 刘晓芸, Haniya Mazhar, Amber Naz, 贺 林, 朱洪新. 心脏细胞衰老与Uvrag基因的缺失[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(14): 2241-2246. |
| [11] | 毛 鑫, 余丽梅, 王 峰. 间充质干细胞在心脏移植免疫耐受诱导中的重要作用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(13): 2070-2078. |
| [12] | 李 行, 景 雅, 李云华, 李海荣, 杨艳萍. Cx43敲除小鼠胚胎心脏流出道内第二生心区和心脏神经嵴来源间充质细胞减少[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(13): 2018-2024. |
| [13] | 孙 凯, 陈 蕾, 麦 瑶, 胡 花, 陈 亮, 钟 俊, 胡 勇, 邱 波. 加速康复外科在前交叉韧带重建围术期的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(11): 1647-1651. |
| [14] | 荆宇澄, 王 乐, 王宪云, 魏 梅, 李 敏, 吉立双, 马芳芳, 刘 刚, 郑明奇 . 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗缺血性心脏病患者 3 年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(1): 6-12. |
| [15] | 王宏书, 韩 燊, 刘 卒, 李晓芳, 钟崇斌, 李立峰, 李亚雄, 蒋立虹. 转录因子NKX2-5分子结构与调控心血管前体细胞的生物学功能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(1): 108-115. |
近年来,随着心脏外科手术、体外循环技术和重症监护整体水平的提高,心脏手术并发症的发生率和死亡率等均明显下降。脑损伤作为成人心脏外科术后一种严重的并发症,发病率依然较高,是除心功能不全以外导致心脏外科手术患者预后不良的最主要因素之一[1]。脑损伤发生率与手术类型有一定的关系,非心脏、非神经和非大血管的手术脑损伤发生率<1%;而大血管和心脏外科手术与前者相比,其发生率可达1%-3%[2]。心脏手术后卒中患者,1年后死亡率升至33%,5年后升至53%,大约50%的脑卒中幸存者伴有严重的后遗症[3-4]。为减少心脏外科手术后脑卒中并发症,迫切需要制定相关方面诊治规范。
目前中国成人心外科术后脑损伤诊治还没有统一的共识。为此,中国研究型医院学会神经再生与修复专业委员会心脏重症脑保护学组联合神经重症护理与康复学组,组织国内心脏内外科、神经内外科、重症监护、体外循环、麻醉以及急诊等医学专家,参考国内外相关指南,结合中国的实际情况,从成人心脏外科术后脑损伤的表现形式、危险因素、非药物性保护策略、术中神经监测以及药物性保护策略等方面,经多次讨论最终成稿,制定本专家共识,以期指导临床工作。
1 脑损伤的表现形式和发病率 Manifestations and incidence of brain injury
心脏大血管外科术后脑损伤的表现形式多样,主要包括脑卒中、术后谵妄和神经认知功能障碍[1,5-6]。由于患者之间存在较大的异质性(如患者年龄、风险状况、手术类型等)、诊断定义不同以及监护措施的差异[1,4-11],不同类型脑损伤的发病率差异也较大(显性卒中发病率为1.2%-6%,隐性卒中发病率为25%-50%,术后谵妄发病率为14%- 50%,神经认知功能障碍发病率为30%-50%)。然而,许多脑损伤在临床常规处理中并没有被发现。心脏术后患者进行常规磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)和弥散加权成像(diffusion weighted imaging,DWI)检查,25%-50%的患者出现新发缺血性脑损伤,这可能与脑卒中或术后神经认知功能障碍密切相关[12-13]。脑损伤在接受多个心脏瓣膜手术的患者中发生率最高(9.7%),其次是单独二尖瓣手术(8.8%),冠状动脉旁路移植术(coronary artery bypass graft,CABG)合并瓣膜手术(7.4%),单纯主动脉瓣手术(4.8%),而单纯CABG的发生率最低(3.8%)[14]。脑损伤可能在苏醒后立即出现(早期卒中),也可能发生在术后几天甚至几个月,这就增加了心脏外科围术期预防和早期治疗的难度[13]。
2 心脏外科围术期脑损伤的危险因素及保护目的 Risk factors and protective purpose of brain injury during perioperative period of cardiac surgery
大多数脑损伤的危险因素(例如年龄、既往病史等)是不可改变的,而某些因素(例如栓塞、低血压、高血糖、高体温、手术方法等)是可优化、可改变的,见表1。围术期脑保护的目的是干预可改变的危险因素,进一步减少成人心脏外科术后的脑损伤的发生。脑保护措施可分为药物性和非药物性。非药物性策略最大限度地减少栓子的产生,通过血压、红细胞压积以及良好的温度管理来保护大脑;而药物性策略主要通过各种药物的炎症抑制作用,达到脑保护的目的。

此外,应重视气道、肺部疾患等原因所致的低氧血症引发脑缺氧对预后的影响。加强围术期气道护理、雾化排痰、俯卧位通气、注意黏稠痰液或痰栓阻塞气道加重低氧血症和脑乏氧,影响神经系统康复。个体化处理呼吸暂停睡眠综合征气管痉挛、哮喘等合并有特殊疾患的患者,警惕由于气道问题诱发心脏骤停或加重心脑损伤。
3 围术期脑损伤的非药物性保护策略 Non-drug protection strategies for perioperative brain injury
3.1 栓塞
3.1.1 气体栓塞 由于心脏手术的特殊性,在体外循环(cardiopulmonary bypass,CPB)过程中的各种动静脉插管、开放的左室以及操作不当等因素,可能形成气体栓塞[12]。体外循环开始前,使用CO2预充整个体外循环管路,减少预充液中微小气栓的形成[15]。一方面,CO2在血液和组织中的溶解度是空气的25倍,机体对CO2栓子的耐受性比空气栓子好得多[16];另一方面,相较于空气,CO2的气体密度要高的多(比空气高50%),从而更有利于与管路内的空气置换,降低导致气体栓塞的空气含量[17-21]。研究表明,使用CO2心包创口吹入,可显著降低脑部微气栓的发生 率[20]。尽管CO2吸收可减少超声心动图可检测到的心内和主动脉微气栓,但这项技术并没有被证明对认知结果有所改善[17,19-21]。另外,在体外循环术中建议使用CO2预充整个体外循环管后再开放升主动脉。如发生大量气体意外进入升主动脉,可采取以下措施:①立即停泵,取头低脚高位,剪断体外循环主动脉泵管,由根部排除部分气体;②将上腔静脉插管先与断开的主动脉管连接,进行暂时性逆行灌注,灌注流量1.0-2.0 L/min,灌注时间5-8 min,压力20-30 mm Hg;③全身降温,头部局部降温、使用激素、脱水降颅压等;④术中维持较高的灌注压,吸纯氧,利于气体的吸收和排出[22-23];⑤返回重症监护室(ICU)后采取冬眠疗法,视患者个体情况进行高压氧治疗。
3.1.2 固体栓塞 固体栓塞是由动脉粥样硬化斑块的碎片、脂肪或手术源性的颗粒物质等组成的栓子而导致的栓塞。动脉粥样硬化尤其是主动脉粥样硬化的病变程度与脑损伤呈正相关。涉及到主动脉手术的操作,比如主动脉的钳夹与开放可能会导致动脉壁内斑块的脱落。经食道超声心动图(transesophageal echocardiography,TEE)以及术中主动脉触诊可以帮助医生排查到术前漏诊的主动脉内大的非钙化斑块,主动脉外超声扫描是术中监测主动脉粥样硬化最敏感的方法,帮助医生在插主动脉管以及阻断主动脉时,避开动脉粥样硬化斑块[24-27]。升主动脉超声引导下主动脉手术操作可减少经颅多普勒超声可检测到的脑栓塞信号,改善神经系统的预后[28-29]。升主动脉弥漫性动脉粥样硬化患者的处理比较困难,因为术中很难确定有无动脉粥样硬化以及其所在的部位。对于以上情况,可采取以下措施:①对可以更改手术方式的患者,将体外循环手术转为非体外循环手术;②经腋动脉或其他替代部位的体外循环插管可有效避免从套管高速喷出的动脉血冲击动脉粥样硬化壁的“喷沙”作用,此外,在腋动脉灌注过程中,由于血流模式(逆向无名和竞争脑内从右到左的侧支血液)的作用,术中产生的任何动脉粥样硬化栓子都将被引导至远离大脑的血流中,从而发挥神经保护作用[30-31];③使用“单次交叉钳夹”技术避免近端旁路移植物吻合口出现部分闭塞;④使用纤颤停搏等方式避免主动脉交叉阻断;⑤行冠状动脉旁路移植术患者,使用全动脉旁路移植术,避免主动脉近端吻合;⑥先在深低温停循环(deep hypothermia circulatory arrest,DHCA)下行升主动脉置换术。
许多心脏术后死亡患者大脑中发现了导致小动脉毛细血管扩张的脂质负荷栓子(lipid microemboli,LME)[32],这些微小栓子主要来源于术野(心包、纵膈表等)。脂质负荷栓子在心包吸引血中形成,当这些滤过不完全的吸引血返回到体外循环回路时,脂质负荷栓子通过过滤材料返回到动脉套管,导致脑部细小毛细血管栓塞。体外循环过滤保护装置对这类栓子的清除作用是有限的,所以不建议单独使用此装置来减少脑血管栓塞事件[33]。使用细胞保护策略处理心包吸引血是预防神经认知功能障碍的重要手段。细胞保存器处理心包内抽吸血液可显著降低血脂含量,但也可导致使用更多的血液制品以及更严重的术后出血。近年来,新型心脏切开吸引过滤系统可以产生与细胞洗涤保护作用相似的临床效果,并且还能减少术后血液稀释。无论应用细胞保护策略还是心脏切开吸引过滤系统处理血液,心包吸引物中仍会残留一些脂质微栓[34]。使用细胞保护策略处理大量血液还可导致血小板减少或凝血因子稀释,导致出血和高输血率。更令人担忧的是,在接受心脏手术的患者中,围术期输血与不良临床结果密切相关[35-36]。故当心包吸引血量较低时,建议可以考虑丢弃心包吸引血。另外,既往心脑血管疾病史是心脏术后患者出现脑神经功能障碍的独立危险因素[37]。老年人与青年人相比,更易合并全身性的血管性疾病,其出现脑神经损伤的概率更高。而术前未诊断的脑血管疾病是导致老年人围术期脑卒中和认知功能障碍的重要危险因素[38]。“动脉-动脉”栓塞与围术期神经缺血性损伤有关,建议对于老年患者进行更加详细的术前颅内血管检查与评估,以及掌握更加严格的手术指征。
3.2 血糖控制 神经认知功能还受到血清葡萄糖水平的影响[39],即使轻微的血糖升高[>7.8 mmol/L(140 mg/dL)],也可通过多种机制途径影响脑卒中患者的预后[12]。许多心脏外科手术患者患有糖尿病,而外科手术应激反应可降低周围胰岛素敏感性,引起高血糖症,因此,作为减轻脑损伤的一种手段,血糖控制一直是心脏外科领域研究的重点。非糖尿病患者围术期目标血糖控制范围在4.4-6.1 mmol/L,可显著降低神经系统不良事件的发生率[40]。糖尿病患者暴露于高血糖症中,会引起生理性代偿性反应(例如脑毛细血管中葡萄糖转运蛋白的下调),从而减少过多的葡萄糖流入大脑。这种代偿性反应有助于解释为什么术中高血糖可能对非糖尿病患者的脑损伤更加严重[41]。
高血糖对神经系统会产生损害,其干预的措施各国学者进行了大量的研究。然而,目前仍没有确定的心脏手术围术期血糖控制标准[42]。根据美国临床内分泌学家协会和美国糖尿病协会(American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists and American Diabetes Association,AACE/ADA)的建议,大多数ICU患者(包括心脏术后患者)应静脉使用胰岛素来控制高血糖,起始阈值不高于 10.0 mmol/L(180 mg/dL)。一旦开始静脉使用胰岛素,应将血糖水平维持在7.8-10.0 mmol/L(140-180 mg/dL)。虽然较低的血糖指标可能更有利脑保护,为避免发生低血糖,不建议将目标血糖定为< 6.1 mmol/L(110 mg/dL)[43]。
3.3 血压管理 将血压保持与心脏术后脑损伤发生率较低的理想范围内是十分重要的,心脏外科手术体外循环期间的最佳血压目标一直是争论的焦点[7-8,44-46]。众所周知,杜绝意外高血压对预防出血性脑损伤十分重要,尤其是在麻醉诱导期及苏醒拔管时。而低血压可能会减少栓子的清除和脑灌注,特别是流向大脑分界区域的血液[46]。在体外循环期间,当平均动脉压< 64 mm Hg时,平均动脉压与脑卒中的发生密切相关[8]。心脏围术期使用去甲肾上腺素维持过高的血压,并不会降低脑损伤的发生率和严重程度[7]。在体外循环期间,若平均动脉压幅度和持续时间的乘积之和超过大脑自动调节的上限值时,可能导致更高的术后谵妄风险[47]。基于在长时间最佳平均动脉压下良好的脑血流(使用α-STAT pH管理)可确保足够的脑氧和营养供应的观点,体外循环期间平均动脉压通常维持在65-85 mm Hg,最佳平均动脉压为78 mm Hg[8,48-50]。另一个研究方向是基于脑血流自动调节的最佳脑灌注压力,这是大脑在面对波动的血压时保持稳定血流的机制。许多心脏外科手术患者患有高血压,高血压会改变正常的脑血流自动调节范围(60-160 mm Hg)。由于实际自动调节范围是未知的,体外循环期间自动调节的下限可能在45-80 mm Hg[51]。此外,术中脑自动调节功能可根据生理变化而动态变化。基于这种观点,可将平均动脉压目标保持在与患者年龄十年相同的数值内(例如:70岁以上患者> 70 mm Hg,80岁以上患者> 80 mm Hg)[52],但是平均动脉压的这一经验性目标尚未得到充分验证。
3.4 颈动脉狭窄 颈动脉粥样硬化是心脏外科术后脑卒中的独立性危险因素[51,53]。颈动脉狭窄或闭塞50%-99%患者围术期脑卒中风险为7.4%。排除有症状性狭窄和/或颈动脉闭塞的患者,即使狭窄50%-99%无症状患者也有 3.8%的脑卒中风险[53-54]。建议术前对高危患者进行颈动脉双向筛查,进行多学科评估并干预[55-56]。无论颈动脉粥样硬化狭窄在心脏术前治疗还是作为“联合”手术的一部分,均可降低术后脑卒中发生率。建议对单侧或双侧症状性颈动脉狭窄或闭塞患者进行同期或分期联合手术来重建颈动脉血运[54,56-59]。对于伴随无症状性颈动脉狭窄的心脏手术患者,干预指征目前仍存在一定争议。对于单纯性单侧无症状性颈动脉狭窄的心脏手术患者中预防性进行颈动脉手术干预并不会使患者获益[54,60]。对于无症状颈动脉狭窄患者,建议对于双侧重度狭窄(> 75%)或单侧狭窄伴随对侧闭塞的患者(有或无脑卒中病史),通过各种干预方式同时或分期进行颈动脉血运重建[60-62]。
3.5 血红蛋白/红细胞压积 体外循环期间血液稀释可降低低温期间血液的黏度,并减少异体输血的需要。大脑通过增加脑血流和组织氧摄取来补偿血液携氧能力的降低,但严重的贫血会影响脑氧输送,对大脑的调节功能产生影响[63]。过度血液稀释与术后脑卒中风险增加相关[64-65]。当体外循环期间红细胞压积22%以下时,红细胞压积每降低1%,围术期发生脑卒中的概率增加10%。但过多输注红细胞也会对患者的神经系统产生不良影响[66- 67]。红细胞输注超过2 U心脏外科术后脑卒中或短暂性脑缺血发作的风险会增加三四倍[68]。其潜在机制包括细胞水平的氧输送受损,继发于红细胞形态异常的血栓前事件以及红细胞释放有害物质[68-69]。建议体外循环期间血红蛋白< 60 g/L时或术后血红蛋白<70 g/L时输注红细胞;当存在末端器官缺血的风险时,体外循环期间将血红蛋白指标提高10-70 g/L;此外患者的临床情况(包括年龄、疾病严重程度、心功能、重要器官组织缺血的风险、大量或活动性出血、SVO2、心电图、心肌缺血的证据等)是决策输血过程中最重要的因素[70]。
3.6 温度管理 脑氧代谢率受到温度的密切调节,通过诱导低温降低脑氧代谢率减少氧供给(如体外循环期间)期间的脑缺氧和损伤。体外循环期间和术后避免脑温过高导致缺血性神经元损伤,从而产生保护作用,包括减少脑氧需氧量和降低兴奋性毒性[71]。建议在心脏骤停后诱导低温(外部头部冷却),改善神经预后和生存率[22-23]。为了避免体外循环复温阶段脑温过高,建议体外循环复温期间动脉管路出口温度限制在37 ℃以下,复温温度超过30 ℃时,复温速率应< 0.5 ℃/min[1,72-76]。心脏术后患者最高温度与术后长期认知功能障碍严重程度相关,建议对于高危患者心脏术后1周时轻度诱导低温,以期降低认知功能障碍发生率[77]。
3.7 心房颤动(atrial fibrillation,AF) 约50%成人心脏外科手术患者术后发生房颤,最常发生在术后两三天[78-79]。众所周知,术前房颤是术后患者早期和晚期卒中的危险因素,术后房颤也与术后晚期卒中相关。ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸可以降低术后心房颤动和脑卒中等不良结局事件的发生率[80-81],建议在高危患者中适当使用。β受体阻滞剂、胺碘酮、心房起搏和左心耳结扎均可降低围术期房颤的发生率[82-85]。
4 围术期神经监测措施 Perioperative neuromonitoring measures
除了常规血液动力学监测外,心脏外科手术患者还可以通过不同的监测设备进行神经监测。仅仅进行血流动力学监测不足以评价心脏手术对脑灌注和功能的影响,因此建议采用多模态方法结合系统,以期指导干预措施[86-87],最大化减少脑损伤的发生。
4.1 围术期脑灌注监测 经颅多普勒(transcranial doppler,TCD)和近红外光谱(near-infrared spectroscopy,NIRS)技术是目前具有代表性的无创性评价脑灌注的方式。有创方式包括颈静脉球血氧饱和度(SjvO2)监测,建议术中根据患者需求选择合适的方式。
4.1.1 经颅多普勒 在颧弓上方跨颞路放置2 MHz超声脉冲探头,测量颅底大脑前、中、后动脉的血流量,监测脑组织血流量半球对称性,并可检测和量化心脏手术中的栓塞现象[86-88]。它在接受体外循环手术的儿童患者中效果较好,因其可间接估计泵内和泵外手术期间的脑灌注[89]。TCD评估大脑中动脉平均血流速度与脑组织血流量的变化具有良好的相关性。由于TCD对操作者依赖性强,术中很难检测到血流信号[90]。TCD可以检测主动脉弓手术期间颈动脉血流中断。事实上,大脑中动脉平均血流速度与全主动脉弓置换术期间的局部血氧饱和度密切相关。在DHCA期间,如果顺行选择性脑灌注低于10 mL/(kg·min),TCD将无法检测到MCA信号[91]。微创主动脉瓣手术中,由于对钙化主动脉瓣的操作,大多数经导管主动脉瓣植入术患者可出现微栓塞。由于目前缺乏术中TCD显示数据,不能使其成为心脏手术中的一项独立的技术[92-93]。
4.1.2 脑近红外光谱 通过近红外光谱法测定脑氧饱和度,局部氧饱和度、动脉和静脉血的组合来检测组织缺氧[86-88,94-95]。局部氧饱和度低于55%意味着术后有神经系统并发症的可能,可以识别高危神经系统并发症的患者[94-95],与神经认知功能下降的风险增加和住院时间之间存在相关性。
4.1.3 颈静脉球血氧饱和度 连续或间歇性的SjvO2测量已用于评估心脏外科术中脑氧合状态[96-99]。目前普遍认为SjvO2的正常低值为55%-60%,高值为75%;SjvO2>75%提示脑氧供超出脑代谢所需,存在脑血流量增加,如脑充血或脑氧代谢降低、脑组织摄氧能力下降以及动静脉瘘;SjvO2<50%时脑氧供不足,存在局灶性缺血或全脑低灌注;SjvO2<40%时提示全脑缺血;SjvO2持续<50%或>70%均提示预后不良。术后及复温过程中非低温体外循环前40 min SjvO2<50%与术后认知功能受损有关[100-102]。但SjvO2监测存在不稳定性及有创性等缺点,反映的是全脑氧代谢的情况,不能反映局部脑氧代谢情况,目前尚未开展。
4.2 脑功能检测 脑电生理即脑电图、双频谱指数和体感诱发电位,可以方便、无创地评价脑功能,已被用于评估急性脑损伤患者的预后,建议在高危患者围术期使用。
4.2.1 脑电图(electroencephalograph,EEG) 多通道脑电图监测提供了与心脏手术期间脑组织血流量变化相关的临床信息。正常情况下脑组织血流量为50 mL/(100 g·min),若低于22 mL/(100 g·min)的低灌注可导致脑电图振幅降低和/或减慢[87]。目前单通道和/或多通道脑电图监测主要用于主动脉重建手术的DHCA停搏。术中脑电图监测确定DHCA时脑部降温的主要终点。局部残余活动的变化可能会导致术中治疗的改变。另外,脑电图监测可检测到术后非惊厥性癫痫发作,指导抗癫痫的治疗[103]。
4.2.2 双谱指数(bispectral index,BIS)监测 双谱指数是一种简化的脑电监测方法,通常用于评估手术期间患者的意识[104]。双谱指数包括:①从时域脑电测量的参数;②从频带计算的参数;③评估成分波形之间的同步程度[105]。其参数为介于0和100之间的无量纲数字,参数大小与患者的意识有关(100表完全清醒脑电图,0代表等电位脑电图)。双谱指数是一种无创的心脏手术期间大脑监测方式,主要是预防术中知晓[88,104-106],有助于优化平均动脉压的镇静和镇痛需求及其全身效应,平衡麻醉血管活性需求[61],避免过量麻醉剂量,因为麻醉药物可导致神经元损伤[88,104-106],但一些药物(例如氯胺酮和70%氧化亚氮)不改变双谱指数值[88]。
4.2.3 体感诱发电位(spinal somatosensory evoked potential,SSEP) 是通过刺激肢体末端粗大的感觉纤维,在躯体感觉上行通路不同部位记录的电位。腕关节正中神经、膝关节腓总神经和/或踝关节胫后神经是最常使用的神经。在主动脉手术期间体感诱发电位可以显示脑或脊髓缺血,指导药物和外科干预避免神经损伤。
5 脑损伤的药物性保护策略 Drug-protective strategies for brain injury
5.1 炎症反应与脑损伤 全身性炎症反应综合征(system inflammatory reaction syndrome,SIRS)和心脏手术创伤后随之而来的神经炎性反应在术后脑损伤中发挥着重要作用[1,107-110]。心脏手术中无菌组织损伤、缺血再灌注损伤、补体激活、肝素中和以及血液与体外循环管路材料的接触可导致损伤相关的分子模式(damage associated molecular patterns,DAMPs)、趋化因子和细胞因子的释放,这些可溶性介质通过激活模式识别受体导致SIRS,进而导致白细胞介素(白细胞介素1和白细胞介素6)、肿瘤坏死因子α和DAMP分子(如HMGB1和S100钙结合蛋白)的释放[111-113]。心脏术后50%以上患者会出现血脑屏障功能障 碍[113]。血脑屏障破坏后,全身炎症介质能够进入大脑[112]。此外,术后通过体液和神经途径的外周到中枢的信号传导,炎性细胞因子也可能在脑内产生,从而导致大脑损伤[114]。使用药物抑制炎症可能是一种有效的方法,但这种干预是否能改善神经预后,目前尚无定论。
5.2 抗炎药物 心脏手术患者中进行了许多具有抗炎作用药物在神经保护方面的试验,但对于心脏围术期预防性使用抗炎药物进行神经保护的有效性尚未达成一致意见[1,107-114]。
类皮质类固醇应用于全身炎症治疗,研究表明心脏手术围术期静脉使用地塞米松,可降低S100钙结合蛋白水平,减轻炎症反应造成的脑损伤[115-117]。但糖皮质激素对体外循环诱导的炎症的影响一直存在争议。一方面,由于炎症反应的复杂性,即使在高剂量下,并不是所有的炎症介质都能被糖皮质激素抑制;另一方面,尽管产生的炎症足够地被控制,也不会对临床结局产生明显影响[118-119]。因此,不建议心脏手术患者常规预防性使用糖皮质激素。
乌司他丁又称胰蛋白酶抑制剂,减轻心脏手术中炎症反应,并在低流量体外循环动物模型中表现出神经保护的特性[120],但其对术后神经功能无产生明显积极影响[121]。丙泊酚在体外循环期间使用具有抗炎作用[122],可降低体外循环后患者血浆S100β蛋白水平[123],有助于在CO2分压波动较大时保持脑血流的稳定,但并未发现其可有效减轻神经损伤,发挥积极的神经保护作用[124-125]。抑肽酶是一种抗纤维蛋白溶解剂,具有抗炎作用,围术期使用抑肽酶可降低脑卒中风险[126],但同样也可增加死亡的风险[127-129]。
氯胺酮作为一种非特异性N-甲基-D-天门冬氨酸(NMDA)受体阻滞剂,通过防止谷氨酸引起的兴奋性毒性损伤、调节凋亡蛋白和干扰炎症反应,减少缺血后神经细胞的丢失[130]。氯胺酮具有潜在的神经保护作用,显著减轻术后认知功能障碍[131-132],在麻醉期间可酌情使用。利多卡因是局部麻醉剂,属于IB类抗心律失常药物,可透过血脑屏障,通过缺血性跨膜离子移位减速,降低脑代谢率,减少缺血兴奋性毒素释放,调节炎症反应,保证脑部血流的供应[133]。利多卡因对神经元的缺血具有保护作用,但对术后认知功能的保护作用仍存在争议[134-136]。四环素衍生物米诺环素可显著减轻心脏骤停或体外循环引起的神经炎症[137-138],降低神经细胞肿瘤坏死因子α水平,抑制缺氧和凋亡细胞损伤,但临床尚未将其作为神经保护类药物使用的推荐。抗胆碱能药物盐酸戊乙奎醚(PHC)于2005年被首次合成,可拮抗乙酰胆碱的毒蕈碱能和烟碱能效应[139]。体外循环期间戊乙奎醚预处理后,神经元损伤、炎症和凋亡的标志物显著减少,线粒体受损的发生率明显降低[140]。但这些药物的有效性有待进一步探索研究,如有必要,需在多学科评估后,在专科医师的指导下进行应用。
5.3 非抗炎性神经保护药物 目前,还没有一种非抗炎性神经保护剂被证明是有效和安全的,尽管早期动物实验的结果看起来大有前途 ,但临床缺乏足够的循证医学的依据。虽然一氧化氮(Nitric oxide,NO)具有抗氧化、抗凋亡和心脏保护和预防术后肾损伤作用,但NO没有减少炎症标志物,也未被证实对大脑可能产生益处。由于NO供体或吸入NO用于治疗冠状动脉硬化和肺动脉高压,NO的血管舒张特性可能也有利于脑灌注[141-142],临床上肺动脉高压患者进行脑保护时可酌情使用。KATP通道已在许多细胞类型中发现,包括海马线粒体。近年发现KATP通道激动剂二氮嗪可减轻复苏后的脑损伤,保护线粒体功能,抑制脑细胞凋亡[143-145]。然而,体外循环期间KATP通道激动剂迄今为止尚未进行测试。α2受体激动剂右美托咪啶是目前唯一兼镇静与镇痛药物,具有镇静、镇痛、抑制交感神经活性、无呼吸抑制等药理性质,可减少其他镇静药物以及阿片类用量,产生可唤醒的/合作的镇静状态,减少受损脑组织坏死、减轻缺血/再灌注损伤、改善神经功能等方面具有保护作用[146-148]。对老年心脏瓣膜手术患者静脉泵注右美托咪定1.0 μg/(kg·h),于15 min内泵注完毕,随后以0.5 μg/(kg·h)的剂量进行维持直至手术结束,结果显示右美托咪定对心脏手术患者具有脑保护作 用[149-152]。对体外循环下行先天性心脏病快通道麻醉患儿在麻醉诱导前给予负荷剂量右美托咪定1 μg/kg缓慢静注(>10 min),随后以0.5 μg/(kg·h)剂量泵注至手术结束前30 min,结果显示右美托咪定通过改善脑组织代谢、减轻神经细胞损害,从而发挥脑保护作用[153]。
成人心脏手术后的脑损伤是患者预后不良的最主要因素之一。为了降低术后脑损伤的发生率,减少神经系统并发症发生需要采用个性化的、以患者为中心的方法来管理脑损伤危险因素,采用包括术中栓塞的预防,血压、血糖、体温的管理,以及针对术后神经炎性反应药物治疗等方法,达到改善手术效果、提高患者生活质量的目的。然而,目前仍需要进一步的研究,尤其是高质量的以结果为导向的随机对照试验,以提高脑损伤处理策略的证据支持。
双谱指数(bispectral index,BIS)是一种简化的脑电监测方法,通常用于评估手术期间患者的意识。双谱指数包括:①从时域脑电测量的参数;②从频带计算的参数;③评估成分波形之间的同步程度。其参数为介于0和100之间的无量纲数字,参数大小与患者的意识有关(100表完全清醒脑电图,0代表等电位脑电图)。双谱指数是一种无创的心脏手术期间大脑监测方式,主要是预防术中知晓,有助于优化平均动脉压的镇静和镇痛需求及其全身效应,平衡麻醉血管活性需求,避免过量麻醉剂量。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程#br#
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
