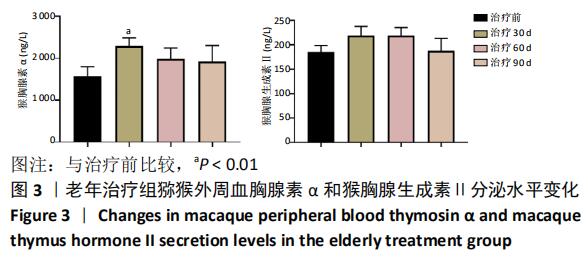
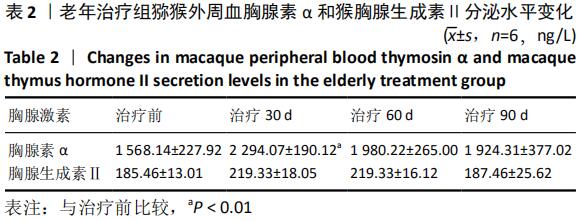
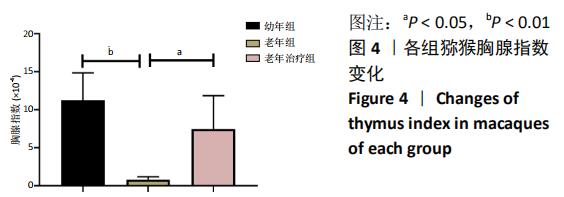
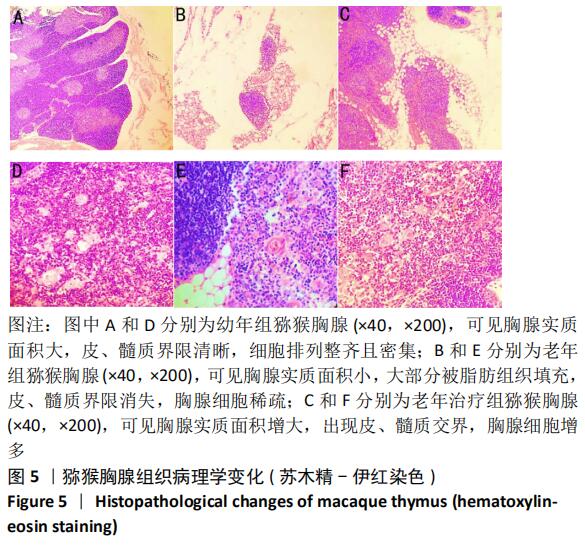
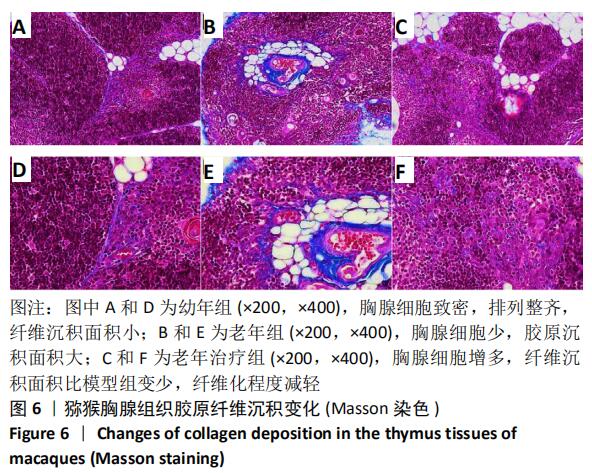
[1] 崔晓东,邹娇娇,王转花.细胞衰老与癌症治疗[J].中国生物化学与分子生物学报, 2020, 36(2): 119-126.
[2] CHINN IK, BLACKBURN CC, MANLEY NR, et al. Changes in primary lymphoid organs with aging. Semin Immunol. 2012;24(5):309-320.
[3] GUO L, CAO JH, WEI TT, et al. Gallic acid attenuates thymic involution in the d-galactose induced accelerated aging mice. Immunobiology. 2020;225(1):151870.
[4] AW D, TAYLOR-BROWN F, COOPER K, et al. Phenotypical and morphological changes in the thymic microenvironment from ageing mice. Biogerontology. 2009;10(3):311-322.
[5] HSIEH J, NG S, BOSINGER S, et al. A GMCSF and IL7 fusion cytokine leads to functional thymic-dependent T-cell regeneration in age-associated immune deficiency. Clin Transl Immunology. 2015;4(5):e37.
[6] JUNG WS, HAN SM, KIM SM, et al. Stimulatory effect of HGF-overexpressing adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells on thymus regeneration in a rat thymus involution model. Cell Biol Int. 2014;38(10):1106-1117.
[7] SONG Y, SU M, PANCHATSHARAM P, et al. c-Met signalling is required for efficient postnatal thymic regeneration and repair. Immunology. 2015;144(2):245-253.
[8] TAJIMA A, LIU W, PRADHAN I, et al. Promoting 3-D Aggregation of FACS Purified Thymic Epithelial Cells with EAK 16-II/EAKIIH6 Self-assembling Hydrogel. J Vis Exp. 2016;(112): 54062.
[9] LIM JH, CHO JH, JUNG HY, et al. Excellent outcome after desensitization in high immunologic risk kidney transplantation. PLoS One. 2019;14(9): e0222537.
[10] 陶果,信吉阁,肖晶,等.基因敲除技术最新研究进展及其应用[J].安徽农业科学, 2013, 41(29): 11605-11608,11644.
[11] HAIDER KH, ARAMINI B. Mircrining the injured heart with stem cell-derived exosomes: an emerging strategy of cell-free therapy. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):23.
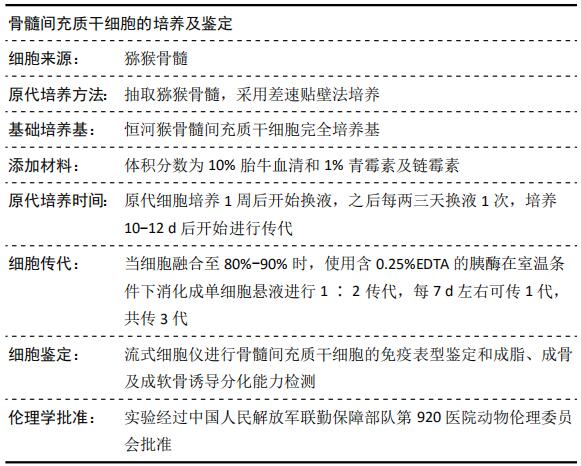
[12] 陈裕浩,朱向情,郭德镔,等.年龄对猕猴骨髓间充质干细胞体外分化和细胞因子水平的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2017, 21(25): 3971-3976.
[13] 阮光萍,姚翔,蔡学敏,等.同种异体脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗树鼩代谢综合征[J].中国组织工程研究, 2020, 24(1): 51-58.
[14] WŁODARSKI K, WŁODARSKI P. Regulation of the differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into osteoblastic and adipogenic lineage. Chir Narzadow Ruchu Ortop Pol. 2011;76(2):96-98.
[15] ZHANG L, GUO K, YIN S, et al. RNA-Seq Reveals Underlying Transcriptomic Mechanisms of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Regulation of Microglia-Mediated Neuroinflammation After Subarachnoid Hemorrhage. Stem Cells Dev. 2020 Feb 10. doi: 10.1089/scd.2019.0216. [Epub ahead of print]
[16] LIN M, LIU X, ZHENG H, et al. IGF-1 enhances BMSC viability, migration, and anti-apoptosis in myocardial infarction via secreted frizzled-related protein 2 pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2020;11(1):22.
[17] XU W, CHENG W, CUI X, et al. Therapeutic effect against retinal neovascularization in a mouse model of oxygen-induced retinopathy: bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells versus Conbercept. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020;20(1):7.
[18] PeNNISI E. Boom time for monkey research. Science. 2007;316(5822): 216-218.
[19] SONG Y, WANG B, SONG R, et al. T-cell Immunoglobulin and ITIM Domain Contributes to CD8+ T-cell Immunosenescence. Aging Cell. 2018; 17(2): e12716.
[20] 王黎明,王立华,李铭,等.脐带间充质干细胞对裸鼠胸腺发育的作用及机制[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(32): 5132-5139.
[21] FUJII S, MIURA Y, FUJISHIRO A, et al. Graft-Versus-Host Disease Amelioration by Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Is Associated with Peripheral Preservation of Naive T Cell Populations. Stem Cells. 2018;36(3): 434-445.
[22] SHEVACH EM, MCHUGH RS, PICCIRILLO CA, et al. Control of T-cell activation by CD4+ CD25+ suppressor T cells. Immunol Rev. 2001;182: 58-67.
[23] SALMINEN A. Activation of immunosuppressive network in the aging process. Ageing Res Rev. 2020;57:100998.
[24] 沈甜甜,方翼.间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].中国临床药理学杂志, 2019, 35(22): 2939-2942.
[25] DERGACHEVA TI, SHURLYGINA AV, MEL’NIKOVA EV, et al. Effects of Bone Marrow Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells and Their Secretion Products on the Cellular Composition of the Thymus and Spleen of Female Wistar Rats with Experimental Chronic Inflammation of the Internal Genitals. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2017;164(1):75-79.
[26] 左博靖,刘丽坤.中药多糖对调节性T细胞在肿瘤免疫调节的研究进展[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2018, 18(A2): 110-112.
[27] BLAZAR BR, MACDONALD KPA, HILL GR. Immune regulatory cell infusion for graft-versus-host disease prevention and therapy. Blood. 2018;131(24):2651-2660.
[28] MIYAGAWA I, NAKAYAMADA S, NAKANO K, et al. Induction of Regulatory T Cells and Its Regulation with Insulin-like Growth Factor/Insulin-like Growth Factor Binding Protein-4 by Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Immunol. 2017;199(5):1616-1625.
[29] WANG S, MUNDADA L, JOHNSON S, et al. Characterization and angiogenic potential of human neonatal and infant thymus mesenchymal stromal cells. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2015;4(4):339-350.
[30] 林喜娟,汪进平,肖磊.过表达FOXN1基因诱导人胚胎干细胞向胸腺上皮细胞定向分化的研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2015, 37(12): 1623-1631.
[31] 崔春红.雌激素与胸腺发育和退化的关系[J].科技信息, 2010(26): 356.
[32] ODINOKOV D, HAMBLIN MR. Aging of lymphoid organs: Can photobiomodulation reverse age-associated thymic involution via stimulation of extrapineal melatonin synthesis and bone marrow stem cells? J Biophotonics. 2018;11(8):e201700282.
[33] HUANG J, JIANG H, PAN M, et al. Immunopotentiator thymosin alpha-1 attenuates inflammatory pain by modulating the Wnt3a/β-catenin pathway in spinal cord. Neuroreport. 2020;31(1):69-75.
[34] 彭宗根.胸腺素在延缓衰老中的免疫调节作用[J].国外医学(老年医学分册), 2001, 22(6): 250-252.
[35] 王志红,林芸,陈为民,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植可增强衰老模型大鼠抗氧化能力和免疫活性[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2017, 33(2): 151-154.
[36] ZHAN Y, WANG L, LIU G, et al. The Reparative Effects of Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Chemotherapy-Damaged Thymus. Stem Cells Dev. 2019;28(3):186-195.
[37] WANG Z, LIN Y, CHEN W, et al. Transplantation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell improves antioxidant capacity and immune activity of aging model rats. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 2017; 33(2):151-154.
[38] ZHOU Y, YAMAMOTO Y, XIAO Z, et al. The Immunomodulatory Functions of Mesenchymal Stromal/Stem Cells Mediated via Paracrine Activity. J Clin Med. 2019;8(7): E1025.
[39] MARIGO I, DAZZI F. The immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells. Semin Immunopathol. 2011;33(6):593-602. |