| [1] Shore EM, Xu M, Feldman GJ, et al.A recurrent mutation in theBMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited andsporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat Genet .2006; 38: 525-527.[2] Weinreb JH, Sheth C, Apostolakos J,et al.Tendonstructure, disease, and imaging. Muscles LigamentsTendons J.2014;4: 66-73.[3] O’Brien EJ, Frank CB, Shrive NG,et al.Heterotopic mineralization (ossificationor calcification) in tendinopathy or following surgicaltendon trauma. Int J Exp Pathol.2012; 93:319-331.[4] Oliva F, Via AG,Maffulli N.Physiopathologyof intratendinous calcific deposition. BMC Med.2012; 10:95.[5] Ateschrang A, Gratzer C,Weise K.Incidenceand effect of calcifications after open-augmentedAchilles tendon repair. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg.2008;128:1087-1092.[6] Richards PJ, Braid JC, Carmont MR,et al.Achilles tendon ossification: pathology, imagingand aetiology. Disabil Rehabil. 2008; 30:1651-1665.[7] Johansson KJ, Sarimo JJ, Lempainen LL,et al. Calcific spurs at theinsertion of the Achilles tendon: a clinical andhistological study. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J.2012;2:273-277.[8] Kan L, Liu Y, McGuire TL,et al.Dysregulation oflocal stem/progenitor cells as a common cellularmechanism for heterotopic ossification. Stem Cells.2009;27:150-156.[9] Kaplan FS,Glaser DL,Shore EM,et al.Hematopoietic stem-cell contribution to ectopicskeletogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007; 89:347-357.[10] Kan L , Kessler JA.Evaluation of the cellularorigins of heterotopic ossification. Orthopedics.2014; 37:329-340.[11] Lin F, Wang N,Zhang TC.The role ofendothelial-mesenchymal transition in development andpathological process. IUBMB Life.2012; 64:717-723.[12] Arciniegas E, Sutton AB, Allen TD,et al.Transforming growth factor beta 1 promotes thedifferentiation of endothelial cells into smoothmuscle-like cells in vitro. J Cell Sci.1992;103 (Pt 2),521-529.[13] Piera-Velazquez S, Li Z,Jimenez SA. Role ofendothelial- mesenchymal transition (EndoMT) in thepathogenesis of fibrotic disorders. Am J Pathol.2011; 179:074-1080.[14] Medici D, Shore EM, Lounev VY,et al.Conversion of vascularendothelial cells into multipotent stem-like cells. NatMed.2010;16:1400-1406.[15] Lounev VY, Ramachandran R, Wosczyna MN,et al.Identification ofprogenitor cells that contribute to heterotopicskeletogenesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2009; 91:652-663.[16] Fang Z, Zhu T, Shen WL,et al.Transplantation of fetal instead of adult fibroblastsreduces the probability of ectopic ossification duringtendon repair. Tissue Eng Part A.2014; 20:1815-1826.[17] Mazonakis M, Berris T, Lyraraki E,et al.Cancer risk estimates from radiation therapy forheterotopic ossification prophylaxis after total hiparthroplasty. Med Phys.2013; 40:101702.[18] Hoff P, Rakow A, Gaber T,et al.Preoperative irradiation for theprevention of heterotopic ossification induces localinflammation in humans. Bone.2013; 55:93-101.[19] Beckmann JT, Wylie JD, Kapron AL,et al.The effect of NSAIDprophylaxis and operative variables on heterotopicossification after hip arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med.2014;42:1359-1364.[20] Lin L, Chen L, Wang H,et al. Adenovirus-mediatedtransfer of siRNA against Runx2/Cbfa1 inhibits theformation of heterotopic ossification in animal model.Biochem Biophys Res Commun.2006; 349:564-572.[21] Glaser DL, Economides AN, Wang L,et al.In vivo somatic cell gene transfer ofan engineered Noggin mutein prevents BMP4-inducedheterotopic ossification. J Bone Joint Surg Am.2003; 85-a:2332-2342.[22] Freedman BR, Gordon JA,Soslowsky LJ.TheAchilles tendon: fundamental properties andmechanisms governing healing. Muscles LigamentsTendons J.2014; 4:245-255.[23] Yoshimatsu Y,Watabe T.Roles of TGF-betasignals in endothelial-mesenchymal transition duringcardiac fibrosis. Int J Inflam.2011:724080.[24] Lamouille S, Xu J,Derynck R.Molecularmechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. NatRev Mol Cell Biol. 2014; 15:178-196.[25] Zhong B, Ma Y, Fu D,et al.Induction ofapoptosis in osteosarcoma s180 cells by polysaccharidefrom dictyophora indusiata. Cell Biochem Funct.2013;31:719-723.[26] Sobral LM, Montan PF, Zecchin KG, et al. SMAD7blocks transforming growth factor-beta1-inducedgingival fibroblast-myofibroblast transition viainhibitory regulation of Smad2 and connective tissuegrowth factor. J Periodontol. 2011; 82:642-651.[27] Chung AC, Dong Y, Yang W, et al.SMAD7 suppresses renal fibrosis via alteringexpression of TGF-beta/Smad3-regulated microRNAs.Mol Ther.2013;21:388-398.[28] Peterson JR, Agarwal S, Brownley RC,et al.Direct mouse trauma/burn modelof heterotopic ossification. J Vis Exp.2015; e52880.[29] Hast MW,Zuskov A,Soslowsky LJ.The roleof animal models in tendon research. Bone Joint Res.2014; 3:193-202.[30] Oliva F,Barisani D,Grasso A,et al.Gene expression analysis in calcific tendinopathy of therotator cuff. Eur Cell Mater.2011; 21:548-557.[31] Zhang C, Zhang Y, Zhong B,et al. SMAD7 prevents heterotopic ossification in a rat Achilles tendon injury model via regulation of endothelial-mesenchymal transition. FEBS J. 2016;283(7):1275-1285. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。
文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。.jpg) 文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。
文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。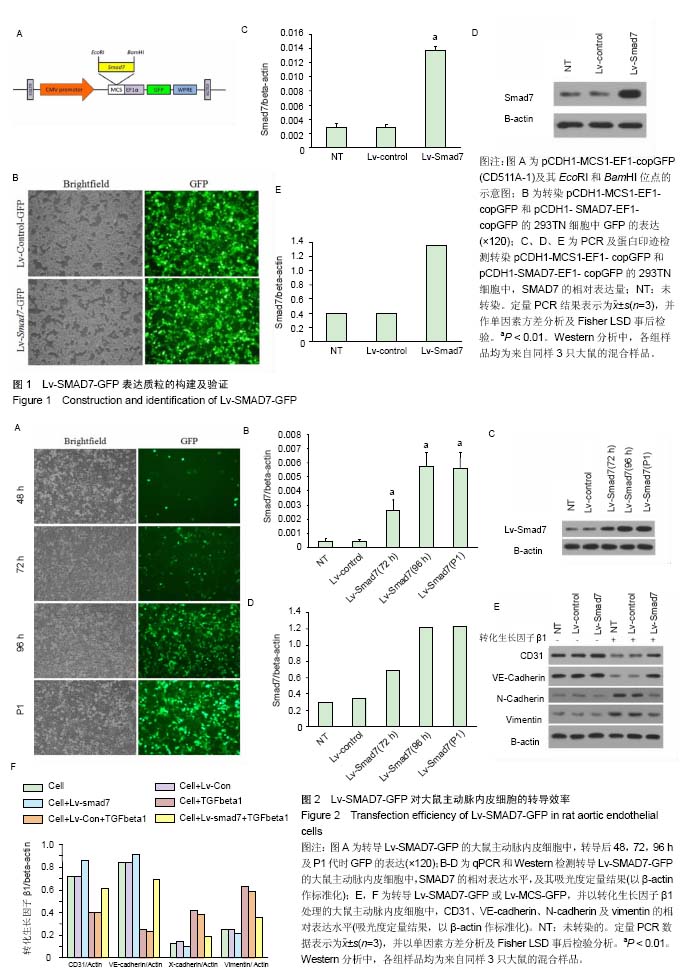
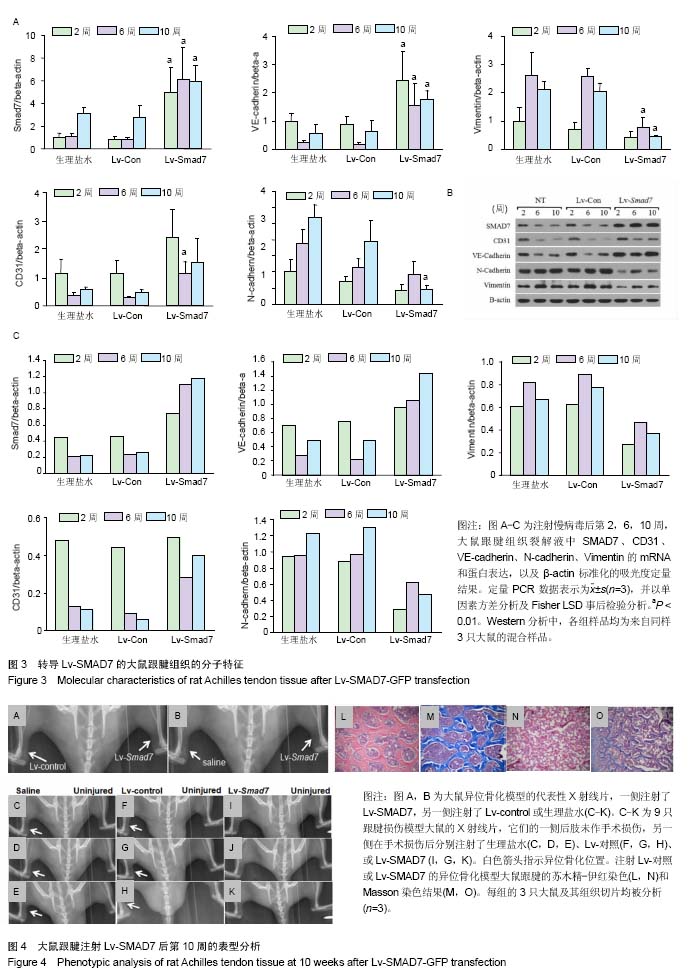
.jpg) 文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。
文题释义:
异位骨化:是指在软组织出现成骨细胞,并形成骨组织。多半发生在大关节周围,例如髋关节、肘关节等,常见于神经瘫痪的患者。其发病机制不清楚,诱发因素可能是神经和生物电因素。早期局部有明显肿痛,关节活动受限;晚期由于骨组织形成,导致关节活动限制。其基本病理改变是在纤维结缔组织中,原始细胞增殖活跃伴有丰富的毛细血管网,钙盐沉积,形成骨。