| [1]Shao H,Shen J,Wang M,et al.Icariin protects against titanium particle-induced osteolysis and inflammatory response in a mouse calvarial model.Biomaterials. 2015;60:92-99.[2]Johanson PE,Digas G,Herberts P,et al.Highly crosslinked polyethylene does not reduce aseptic loosening in cemented THA 10-year findings of a randomized study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2012;470: 3083-3093.[3]Dorr LD,Wan Z,Shahrdar C,et al.Clinical performance of a Durasul highly cross-linked polyethylene acetabular liner for total hip arthroplasty at five years.J Bone Joint Surg Am.2005;87:1816-1821.[4]Kurtz S,Ong K,Lau E,et al.Projections of primary and revision hip and knee arthroplasty in the United States from 2005 to 2030.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2007;89: 780-785.[5]Lee YE,Park KS,Park EK,et al.Polycan suppresses osteoclast differentiation and titanium particle-induced osteolysis in mice.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2015;104(6):1170-1175. [6]Jin S,Park JY,Hong JM,et al.Inhibitory effect of (-) -epigallocatechin gallate on titanium particle-induced TNF-alpha release and in vivo osteolysis.Exp Mol Med. 2011;43(7):411-418.[7]Wang W, Wu C, Tian B, et al. The inhibition of RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis through the suppression of p38 signaling pathway by naringenin and attenuation of titanium-particle-induced osteolysis. International journal of molecular sciences. 2014;15: 21913-34.[8]Bi F,Shi Z,Zhou C,et al.Intermittent Administration of Parathyroid Hormone [1-34] Prevents Particle-Induced Periprosthetic Osteolysis in a Rat Model.PloS One. 2015;10:e0139793.[9]Park SY,Seetharaman R,Ko MJ,et al.Ethyl linoleate from garlic attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced pro-inflammatory cytokine production by inducing heme oxygenase-1 in RAW264.7 cells.Int Immunopharmacol.2014;19:253-261.[10]Baeuerle PA.IkappaB-NF-kappaB structures: at the interface of inflammation control.Cell. 1998;95:729-731.[11]Lawrence T,Willoughby DA,Gilroy DW. Anti-inflammatory lipid mediators and insights into the resolution of inflammation.Nat Rev Immunol. 2002; 2(10):787-795.[12]Lv H,Ren W,Zheng Y,et al.Tenuigenin exhibits anti-inflammatory activity via inhibiting MAPK and NF-kappaB and inducing Nrf2/HO-1 signaling in macrophages. Food & function. 2015.[13]Becker S,Mundandhara S,Devlin RB,et al.Regulation of cytokine production in human alveolar macrophages and airway epithelial cells in response to ambient air pollution particles: further mechanistic studies.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.2005;207:269-275.[14]Hungund BL,Zheng Z,Barkai AI.Turnover of ethyl-linoleate in rat plasma and its distribution in various organs.Alcohol Clin Exp Res. 1995;19(2): 374-377.[15]Fujii J,Niida S,Yasunaga Y,et al.Wear debris stimulates bone-resorbing factor expression in the fibroblasts and osteoblasts. Hip Int.2011;21:231-237.[16]Geng D,Wu J,Shao H,et al.Pharmaceutical inhibition of glycogen synthetase kinase 3 beta suppresses wear debris-induced osteolysis.Biomaterials.2015;69:12-21.[17]Liu X,Qu X,Wu C,et al.The effect of enoxacin on osteoclastogenesis and reduction of titanium particle-induced osteolysis via suppression of JNK signaling pathway. Biomaterials.2014;35:5721-5730.[18]Dobzyniak M,Fehring TK,Odum S.Early failure in total hip arthroplasty.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2006;447: 76-78.[19]Mabilleau G,Pandit H,Jinnah RH,et al.Biological response to common surface bearings used in orthopaedics.J Surg Orthop Adv.2008;17(1):34-39.[20]Ingham E,Fisher J.Biological reactions to wear debris in total joint replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H.2000; 214(1):21-37.[21]Antonios JK,Yao Z,Li C,et al. Macrophage polarization in response to wear particles in vitro.Cell Mol Immunol. 2013;10(6):471-482.[22]Nich C,Takakubo Y,Pajarinen J,et al.Macrophages-Key cells in the response to wear debris from joint replacements.J Biomed Mater Res A.2013;101(10): 3033-3045.[23]Eteraf-Oskouei T,Allahyari S,Akbarzadeh- Atashkhosrow A, et al.Methanolic Extract of Ficus carica Linn. Leaves Exerts Antiangiogenesis Effects Based on the Rat Air Pouch Model of Inflammation. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med.2015;2015: 760405.[24]Colville-Nash PR,Scott DL.Angiogenesis and rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic and therapeutic implications.Ann Rheum Dis.1992;51(7):919-925.[25]Lappas M,Permezel M,Georgiou HM,et al.Nuclear factor kappa B regulation of proinflammatory cytokines in human gestational tissues in vitro.Biol Reprod.2002; 67(2):668-673.[26]Murakami A,Ohigashi H.Targeting NOX,INOS and COX-2 in inflammatory cells: chemoprevention using food phytochemicals.Int J Cancer. 2007;121(11): 2357-2363.[27]Sturm A,Schulte C,Schatton R,et al.Transforming growth factor-beta and hepatocyte growth factor plasma levels in patients with inflammatory bowel disease.Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol.2000;12(4): 445-450.[28]Surh YJ,Chun KS,Cha HH,et al.Molecular mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS through suppression of NF-kappa B activation.Mutat Res.2001;480-481:243-268.[29]Goodman SB,Ma T,Spanogle J,et al.Effects of a p38 MAP kinase inhibitor on bone ingrowth and tissue differentiation in rabbit chambers.J Biomed Mater Res A.2007;8(2)1:310-316.[30]Goodman SB,Gibon E,Pajarinen J,et al.Novel biological strategies for treatment of wear particle-induced periprosthetic osteolysis of orthopaedic implants for joint replacement.J R Soc Interface.2014;11(93):20130962.[31]Deny A,Loiez C,Deken V,et al.Epidemiology of patients with MSSA versus MRSA infections of orthopedic implants: Retrospective study of 115 patients.Orthop Traumatol Surg Res.2016;102(7):919-923.[32]Zaborowska M,Tillander J,Brånemark R,et al.Biofilm formation and antimicrobial susceptibility of staphylococci and enterococci from osteomyelitis associated with percutaneous orthopaedic implants.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater.2016.doi: 10.1002/jbm.b.33803.[Epub ahead of print][33]Hallock K,Vaughn NH,Juliano P,et al.Metal Hypersensitivity and Orthopedic Implants: A Survey of Orthopedic Surgeons.Dermatitis.2016.[Epub ahead of print][34]Veronesi F,Giavaresi G,Fini M,et al.Osseointegration is improved by coating titanium implants with a nanostructured thin film with titanium carbide and titanium oxides clustered around graphitic carbon. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl.2017;70(Pt 1): 264-271. [35]Zhao D,Witte F,Lu F,et al.Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based orthopaedic implants: A review from clinical translational perspective. Biomaterials.2016;112:287-302. |
.jpg)
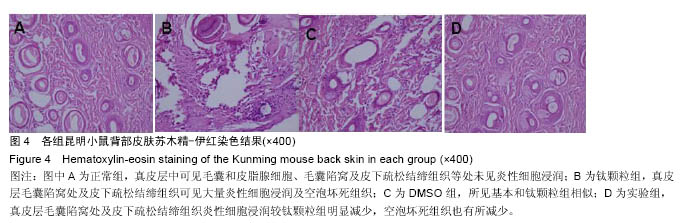
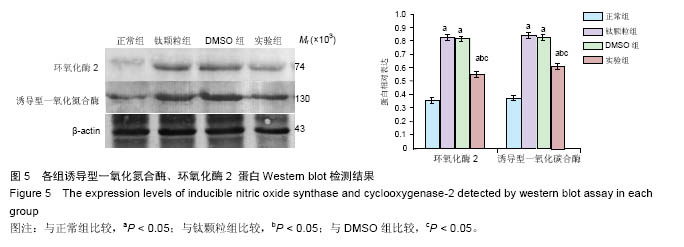
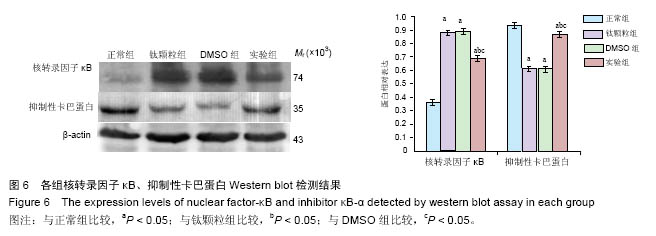
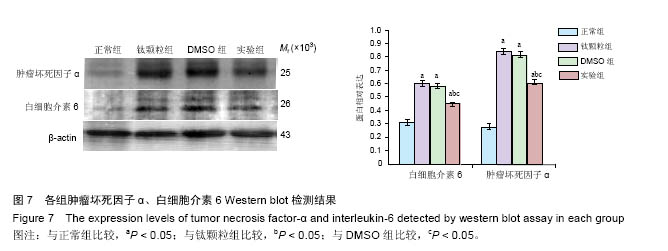
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)