[1] POLAK D, SHAPIRA L. An update on the evidence for pathogenic mechanisms that may link periodontitis and diabetes. J Clin Periodontol. 2018;45(2):150‐166.
[2] PRESHAW PM, ALBA AL, HERRERA D, et al. Periodontitis and diabetes: a two-way relationship. Diabetologia. 2012;55(1):21-31.
[3] BARMAN PK, URAO N, KOH TJ. Diabetes induces myeloid bias in bone marrow progenitors associated with enhanced wound macrophage accumulation and impaired healing. J Pathol. 2019; 249(4):435‐446.
[4] PHIMPHILAI M, POTHACHAROEN P, KONGTAWELERT P, et al. Impaired osteogenic differentiation and enhanced cellular receptor of advanced glycation end products sensitivity in patients with type 2 diabetes. J Bone Miner Metab. 2017 ;35(6):631-641.
[5] ASADIPOOYA K, UY EM. Advanced Glycation End Products (AGEs), Receptor for AGEs, Diabetes, and Bone: Review of the Literature. J Endocr Soc. 2019;3(10):1799‐1818.
[6] XIONG Y, ZHANG Y, GUO Y, et al. 1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3 increases implant osseointegration in diabetic mice partly through FoxO1 inactivation in osteoblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2017; 494(3-4):626‐633.
[7] YANG Y, ZHAO C, LIANG J, et al. Effect of Dipeptidyl Peptidase-4 Inhibitors on Bone Metabolism and the Possible Underlying Mechanisms. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:487.
[8] FARDEL O. Cytokines as molecular targets for aryl hydrocarbon receptor ligands: implications for toxicity and xenobiotic detoxification. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2013;9(2):141-152.
[9] WEIDENBUSCH M, RODLER S, SONG S, et al. Gene expression profiling of the Notch-AhR-IL22 axis at homeostasis and in response to tissue injury. Biosci Rep. 2017;37(6):BSR20170099.
[10] 黄璟.芳香烃受体(AhR)通路激活剂FICZ治疗牙周炎的实验研究[C]. 中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会.第十一次全国口腔修复学学术会议论文汇编.中华口腔医学会口腔修复学专业委员会:中华口腔医学会,2017:199.
[11] LAMBERTUCCI AC, LAMBERTUCCI RH, HIRABARA SM, et al. Glutamine supplementation stimulates protein-synthetic and inhibits protein-degradative signaling pathways in skeletal muscle of diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2012;7(12):e50390.
[12] KIM HR, KANG SY, KIM HO, et al. Role of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Activation and Autophagy in Psoriasis-Related Inflammation. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(6):2195.
[13] FUELDNER C, KOHLSCHMIDT J, RIEMSCHNEIDER S, et al. Benzo(a)pyrene attenuates the pattern-recognition-receptor induced proinflammatory phenotype of murine macrophages by inducing IL-10 expression in an aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent manner.Toxicology. 2018;409:80‐90.
[14] MASUDA K, KIMURA A, HANIEH H, et al. Aryl hydrocarbon receptor negatively regulates LPS-induced IL-6 production through suppression of histamine production in macrophages. Int Immunol. 2011;23(10):637-645.
[15] 梅素音,许宗仁,侯胜平.芳香烃受体(AhR)激活剂的虚拟筛选及治疗葡萄膜炎的实验研究[J].免疫学杂志,2019,35(12):1067-1073.
[16] KWAN TAT S, PADRINES M, THÉOLEYRE S, et al. IL-6, RANKL, TNF-alpha/IL-1: interrelations in bone resorption pathophysiology. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15(1):49‐60.
[17] KIMAK A, STRYCHARZ-DUDZIAK M, BACHANEK T, et al. Lipids and lipoproteins and inflammatory markers in patients with chronic apical periodontitis.Lipids Health Dis. 2015;14:162.
[18] LIU C, FENG X, LI Q, et al. Adiponectin, TNF-α and inflammatory cytokines and risk of type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Cytokine. 2016;86:100‐109.
[19] RODRIGUES KF, PIETRANI NT, BOSCO AA, et al. IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-10 levels/polymorphisms and their association with type 2 diabetes mellitus and obesity in Brazilian individuals.Arch Endocrinol Metab. 2017;61(5):438‐446.
[20] TANG X, HAN J, MENG H, et al. Downregulation of RANKL and RANKL/osteoprotegerin ratio in human periodontal ligament cells during their osteogenic differentiation. J Periodontal Res. 2016;51(1):125‐132.
[21] HERRICK DB, LIN B, Peterson J, et al. Notch1 maintains dormancy of olfactory horizontal basal cells, a reserve neural stem cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2017;114(28):E5589-E5598.
[22] PRASASYA RD, MAYO KE. Notch Signaling Regulates Differentiation and Steroidogenesis in Female Mouse Ovarian Granulosa Cells. Endocrinology. 2018;159(1):184‐198.
[23] YIN J, HU H, LI X, et al. Inhibition of Notch signaling pathway attenuates sympathetic hyperinnervation together with the augmentation of M2 macrophages in rats post-myocardial infarction.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2016;310(1):C41‐C53.
[24] ORTIZ-MASIÁ D, COSÍN-ROGER J, CALATAYUD S, et al. M1 Macrophages Activate Notch Signalling in Epithelial Cells:Relevance in Crohn’s Disease. J Crohns Colitis. 2016;10(5):582‐592.
[25] 赵洪伟,车楠,黄超,等.Notch1信号激活核因子κB(NF-κB)参与小鼠RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎症介质释放[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2017,33(10):1310-1315.
[26] 陆艳,杨义,张彦兵,等.在猪肺泡巨噬细胞上Notch信号通路调控LPS诱导的炎性反应研究[J/OL].中国动物传染病学报, 2020,1-7. [2020-11-06].http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/31.2031.S.20200212.0746.006.html.
[27] DEREGOWSKI V, GAZZERRO E, PRIEST L, et al. Notch 1 overexpression inhibits osteoblastogenesis by suppressing Wnt/beta-catenin but not bone morphogenetic protein signaling. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(10): 6203‐6210.
[28] CANALIS E, PARKER K, FENG JQ, et al. Osteoblast lineage-specific effects of notch activation in the skeleton. Endocrinology. 2013;154(2): 623‐634.
[29] LUO Z, SHANG X, ZHANG H, et al. Notch Signaling in Osteogenesis, Osteoclastogenesis, and Angiogenesis. Am J Pathol. 2019;189(8): 1495‐1500.
[30] HILTON MJ, TU X, WU X, et al. Notch signaling maintains bone marrow mesenchymal progenitors by suppressing osteoblast differentiation. Nat Med. 2008;14(3):306‐314.
[31] HUANG KC, CHUANG PY, YANG TY, et al. Hyperglycemia inhibits osteoblastogenesis of rat bone marrow stromal cells via activation of the Notch2 signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2019;16(5):696‐703. |
 文题释义:
文题释义:
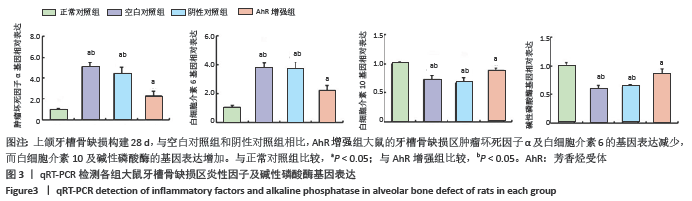

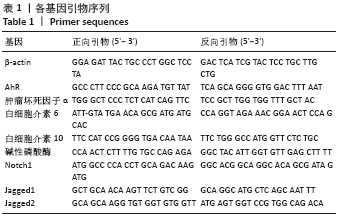
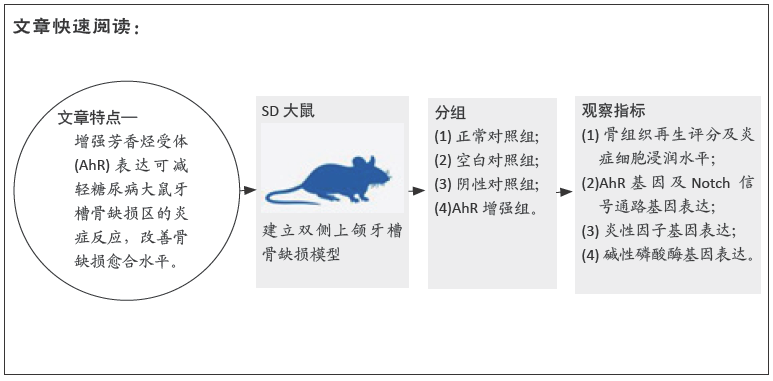 文题释义:
文题释义: