| [1] 王军强,赵春鹏,龚晓峰,等.锁定加压接骨板内固定结合自体髂骨植骨治疗肱骨干骨折术后骨不连[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2012,14(2):127-131.[2] 张万标,于建伟,张濛.粗通道髓芯减压髂骨颗粒植骨联合自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头坏死50例[J].风湿病与关节炎, 2014,3(10):39-41.[3] 李凯,叶招明,张中伟,等.自体骨移植治疗四肢骨折术后骨不连失败因素分析[J].中国骨伤, 2013,26(4): 272-276.[4] 郑金文,刘显东,王小兵,等.下肢骨干骨折术后骨不连的原因分析及手术治疗[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志, 2014, 29(12): 1236-1238.[5] Wakitani S, Okabe T, Horibe S, et al. Safety of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation for cartilage repair in 41 patients with 45 joints followed for up to 11 years and 5 months. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2011;5(2):146-150.[6] Fernandez-Bances I, Perez-Basterrechea M, Perez-Lopez S, et al. Repair of long-bone pseudoarthrosis with autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells combined with allogenic bone graft. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(5):571-577.[7] 陆继梅.自拟接骨方治疗四肢长骨骨折内固定术后延迟愈合32例[J].中国药业,2015,24(2):77-79.[8] 付新生,蒋攀峰.髂骨瓣联合自体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头坏死[J].中国骨与关节外科, 2012, 5(2): 169-172.[9] 杨辉,巴黎,陈国强.自体髂骨植骨在 SchatzkerⅢ~Ⅴ型胫骨平台骨折治疗中的应用[J].重庆医学,2013, 42(18): 2143-2144.[10] 熊浩,黄东,林伟文,等.胫骨骨膜瓣联合自体植骨治疗胫骨创伤性骨缺损18例[J].中华显微外科杂志, 2014, 37(3): 289-291.[11] 邵晓冬,郭晓钟,王迪,等. CD133+细胞含量对自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗肝硬化疗效的影响[J]. 现代消化及介入诊疗, 2013, 18(1):8-10.[12] 郑越.头颈开窗髂骨植骨联合干细胞移植治疗早期股骨头坏死的研究[D]. 石家庄:河北医科大学, 2013.[13] Spahr L, Chalandon Y, Terraz S, et al. Autologous bone marrow mononuclear cell transplantation in patients with decompensated alcoholic liver disease: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e53719.[14] 薛汉中,孙亮,李忠,等.自体髂骨改良结构植骨治疗四肢骨不连[J].中华创伤骨科杂志, 2013, 15(8):671-675.[15] 王新昌,郝连升.自体髂骨移植联合解剖锁定加压钢板内固定术治疗锁骨骨折不愈合13例[J].山东医药, 2014, 54(39):107-108.[16] 贾文杰. 颈椎前路减压钛网植骨与自体髂骨植骨融合内固定术治疗脊髓型颈椎病的对比研究[D].济南:山东中医药大学,2013.[17] 王希宁,丛玉杰.内固定结合自体髂骨植骨治疗老年肱骨外科颈骨折的临床疗效观察[J].宁夏医学杂志, 2014, 36(12):1163-1164[18] Xu T, Wang X, Chen G, et al. Autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation attenuates hepatocyte apoptosis in a rat model of ex vivo liver resection and liver autotransplantation.J Surg Res. 2013;184(2): 1102-1108.[19] 孟光强,耿德虎.切开复位内固定加自体髂骨植骨治疗跟骨骨折32例疗效分析[J]. 贵州医药, 2015,39(9): 823-824.[20] 吴俊,张俊,刘锦波. 锁定钢板及自体髂骨植骨治疗股骨髓内钉固定术后骨不连[J].浙江临床医学, 2015,17(2):295-296.[21] Liu Y, Liu Y, Wang P, et al. Autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation for the treatment of postoperative hand infection with a skin defect in diabetes mellitus: A case report. Oncol Lett. 2014; 7(6):1857-1862.[22] 钟俊,杨淮河,张军,等.自体髂骨移植加锁定钢板内固定治疗短管状骨内生软骨瘤21例[J]. 海南医学, 2015,26(14): 2129-2131.[23] 周国林,陈同磊,朱建平,等.跟骨锁定钢板内固定加自体髂骨植骨治疗跟骨粉碎性骨折的临床疗效观察[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2015, 23(4):377-379.[24] Li T, Zhu J, Ma K, et al. Autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation promotes liver regeneration after portal vein embolization in cirrhotic rats. J Surg Res. 2013;184(2):1161-1173.[25] Zafarghandi RM. The effect of autologous bone marrow stem cell transplantation on graft function in cadaver kidney recipients. Inter J Urology. 2014; 21: A291.[26] 张健,王红伟,郭建欣.自体髂骨植骨用于胫骨 SchatzkerⅢ-Ⅴ型平台骨折的研究[J].现代中西医结合杂志, 2015,24(10):1073-1075.[27] 徐林,向柄彦,柏小金,等.锁定钢板内固定联合自体髂骨植骨治疗肱骨干骨不连21例分析[J].重庆医学, 2014,43 (15):1933-1935.[28] Woolthuis CM, Mariani N, Verkaik-Schakel RN, et al. Aging impairs long-term hematopoietic regeneration after autologous stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2014;20(6):865-871.[29] 张华俊,王树金,王遥伟,等. 锁定钢板联合自体髂骨植骨治疗肱骨干骨折术后骨不连[J]. 临床骨科杂志, 2013, 16(1):101-102.[30] Dispenzieri A, Seenithamby K, Lacy MQ, et al. Patients with immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation have superior outcomes compared with patients with multiple myeloma: a retrospective review from a tertiary referral center. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013; 48(10):1302-1307.[31] 屈宗斌,靳嘉昌,唐刚健,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗陈旧性胫骨中下1/3骨折临床研究[J].华夏医学, 2015, 28(2): 66-68.[32] 胡长付.自体骨髓干细胞移植疗法治疗106例下肢严重缺血患者的临床疗效分析[J]. 海南医学院学报, 2013, 19(3):365-366.[33] Bhansali A, Asokumar P, Walia R, et al. Efficacy and safety of autologous bone marrow-derived stem cell transplantation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: a randomized placebo-controlled study. Cell Transplant. 2014;23(9):1075-1085.[34] 王玉龙,王明贵,贺小兵,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗胫骨骨折骨不连[J].局解手术学杂志, 2014,23(2):131-134.[35] 张宏军,刘又文,范克杰,等.微创减压植骨联合自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗股骨头坏死[J].中医正骨, 2013, 25(3):56-58.[36] 罗实.富集自体骨髓干细胞移植联合手术治疗骨折30例效果分析[J].广西医学, 2013,35(12):1623-1625.[37] 李涛,翁习生,彭慧明,等.髓心减压并自体骨髓干细胞移植术治疗早期股骨头坏死疗效与安全性的系统评价[J]. 中国矫形外科杂志, 2013, 21(22):2241-2248. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。
文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。.jpg) 文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。
文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。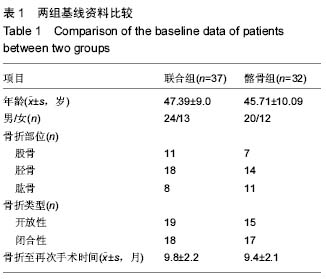
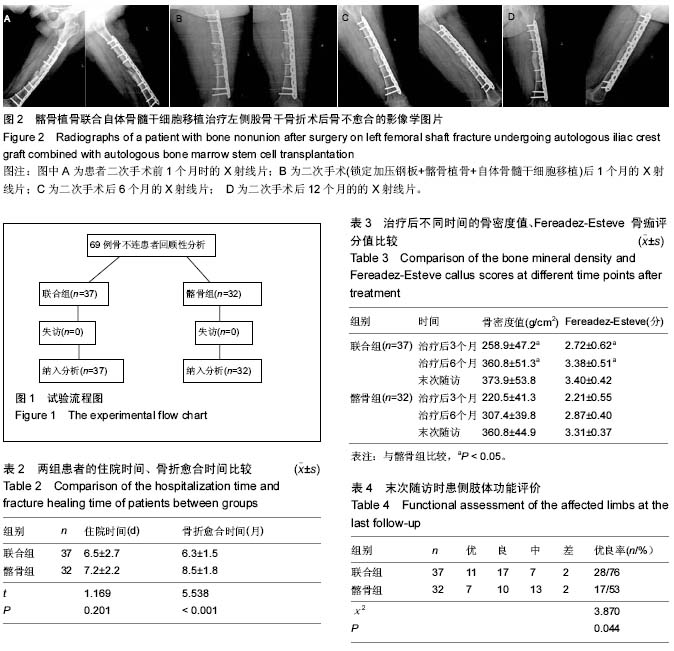
.jpg) 文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。
文题释义:
自体骨髓干细胞移植:自体骨髓干细胞移植分为自体干细胞采集与干细胞移植2个步骤。自体骨髓来源较为丰富,植入后无排斥反应,易于患者接受,减轻患者二次手术造成的机体疼痛,符合骨修复的生理需求,利于骨组织愈合。
骨不连:骨组织具有强大的自身修复能力,骨折治疗后,大部分患者骨组织能够愈合,但仍有小部分患者骨折因感染、局部血液供应不足、骨折不稳定等因素所致愈合速度比较缓慢,称为延迟愈合。当骨折不能愈合,则称为骨不连。