2.1 髓内钉固定概述 组织工程在医学领域已有较多应用,近年来随着生物医学、材料学和生物力学等在临床骨科中不断发展,已取得突破性进展,新的内固定器材已广泛应用于骨科手术中。在管状骨的治疗中,髓内钉固定已成为主流,但髓内钉亦有其医源性术后疼痛、适应证局限等劣势。文章就解剖型髓内钉避免传统髓内钉的不足,以及其历史发展、在管状骨的应用特点、操作方法和未来发展的趋势等进行详细综述。为组织工程更全面应用于医学骨科提供重要的理论依据和数据支撑。
解剖型髓内钉可应用于四肢管状骨骨折,因其科学的主钉设计可完美匹配各管状骨髓腔,多维度的近、远端锁钉可提供更有效、更全面的生物力学优势,因此是今后四肢管状骨骨折的主流治疗方式。目前国内外解剖型髓内钉的主要合成材料为经阳极氧化处理的钛合金,以及符合人体生物环境的1型聚乙烯。国内外鲜有生物不相容性报道,部分不良反应为:因髓内固定及扩髓腔操作可增加感染及血栓风险;无法提供特定的偏心性固定而有一定程度的旋转及翻修风险;以及部分少见的断钉、主钉或螺钉切出等。
2.2 解剖型髓内钉的历史由来 Kuntscher教授于1939年自主设计并首次引入了治疗股骨干骨折的不锈钢二叶草髓内钉,这也是近现代以来第一次有临床意义的髓内钉应用,被认为是第1代髓内钉[1],此髓内钉系统无锁钉装置,因此骨折断端旋转移位较明显。带有锁钉系统的第2代髓内钉虽克服了第1代非抗旋转的缺陷,但学者通过大量临床病例验证,认为其术后骨折畸形愈合率以及断钉率较高。第3代R-T髓内钉通过对螺钉材料和结构的改变,弥补了上述缺点,并扩大了适应证范围[2],但因主钉无法与骨髓腔完美匹配、远近端内置物或螺钉不稳、其接触骨质等造成患者术后疼痛的问题依旧时有报道。因此,第3代髓内钉的改进版——解剖型髓内钉应运而生,它通过独特的解剖型设计,使得主钉契合管状骨的髓腔,进针和扩髓都更易操作,减少了术后的疼痛;同时,主钉近端的钉帽与远端的多角度锁钉,更加强了手术操作的安全性和术后满意率。
2.3 解剖型髓内钉在下肢管状骨的应用与进展
2.3.1 股骨 临床中多见低能量所致的老年人股骨转子间、股骨转子下骨折及高能量所致的年轻人股骨干骨折。手术中有微创、力学优势的髓内固定为主要治疗方法。目前对于髋部骨折(如股骨转子间和转子下)及股骨干骨折的手术方式通常包括髓外固定和髓内固定术式,髓外固定有动力髋、髁螺钉,髓内固定有Gamma Ⅲ、股骨近端防旋髓内钉(proximal femoral nail antirotation,PFNA)及Intertan髓内钉;髓内固定具有良好的力学抗旋性能,结合微创原理,显著提升了骨折愈合率。
髓内钉插入或穿出股骨是由二者生理性前弓不匹配造成[3-4],且股骨曲率半径与其长度成正比。由于股骨具有生理性前弓,而老年患者尤其是老年女性患者股骨长度较短, 所以有时候使用髓内钉会出现置入主钉困难。强行置入易造成医源性损伤,如继发骨折。针对股骨解剖特点, 捷迈公司设计出了贴合其髓腔解剖弧度的内置物,即ZNN(Zimmer Natural Nail)髓内钉,见图2。主钉根据股骨生理弧度, 使得在置入的时候阻力较低,更容易插入,无需扩髓。

ZNN髓内钉中亚洲型短钉有2种颈干角型号,分别为125°、130°。有符合亚洲人群股骨髓腔解剖结构的1 275 mm弧度的主钉[5]。其上部直径15.5 mm,全长180 mm。特殊的15°前倾角更符合人体解剖模型。ZNN髓内钉长钉及其沟槽均设计为螺旋形,适合合并有骨质疏松患者入钉。该解剖型装置含有精确调节股骨颈前倾角的导向器,符合精准医疗的手术概念。手术操作时,选取130°颈干角的内置物,组合套管的同时穿瞄准器,旋转其把手并固定,将导针钻入达股骨头8 mm,测深并打入拉力螺钉。垂直加压后在近端、远端分别固定螺钉,尾端可用瞄准器锁钉。
陈健等[6]对59例老年股骨转子间骨折进行PFNA与ZNN髓内钉回顾性比较研究,在随访(10.8±4.0)个月后,ZNN的术后内固定并发症发生率低于PFNA,术后尖顶距较后者更符合生物力学。梁伟等[7]对114例老年股骨转子间骨折的病例进行Intertan髓内钉与解剖型ZNN髓内钉回顾性研究,认为解剖型髓内钉有利于耐受能力较差的患者。
强生公司所生产的PFNA Ⅱ亚洲型股骨近端抗逆旋髓内钉是一款较早的解剖型髓内钉,其独特的设计避免了普通髓内钉因股骨内侧皮质与主钉近端的接触风险,近端6°的外偏角更适合亚洲人的股骨生理弧度[8-9],但其矢状面与髓腔无法完全贴合,会造成主钉置入困难[8]。研究发现主钉远近端端、外翻角等设计会引起术后股骨部分区域的疼痛[10]。而捷迈公司设计的解剖型髓内钉ZNN,正是在以上方面进行了科学、规范的设计,进而增加了髓内钉的安全性与稳定性[11]。
2.3.2 胫骨 胫骨中下段骨折在创伤骨科中常见。其中下1/3处为四边形,胫骨髓腔在中段为三棱形[12]。其前部、侧方均以皮肤覆盖,骨折后骨折断面容易戳破患处皮肤,造成开放性创伤。手术时多使用钢板及髓内钉治疗简单或多段、粉碎性的胫骨骨折。发生于中下1/3的胫骨骨折若钢板固定会使原本血供不足的部位更加缺血,造成骨不愈合。普通髓内钉无多方向螺钉有效固定、无尾端多根螺钉置入,使得旋转及成角较大的骨折不易恢复,同时也对合并干骺端的骨折无有效作用,易致畸形。
专家型胫骨解剖髓内钉Expert ETN(Expert Tibial Nail)因近端、远端(距主钉尾 5 mm)多维度螺钉有效提升接触骨面积,也使得远端把持力可锁定近踝部位[13]。除普通髓内钉的优点外,还具有干骺端三维锁定,维持骨长度;主钉贴合髓腔内侧面,配合螺纹的锁钉加强固定、减少应力遮挡;近端特殊松质骨螺钉及自内而外的锁定钉,利于动力或加压模式切换;间隔5 mm的尾帽可抓紧上端螺钉;可见其固定效果优于普通髓内固定装置[14],为胫骨骨折的治疗提供了更优的解决方案。
其他普通型髓内钉如Schanz钉有延迟愈合的并发症,ProTek胫骨髓内钉、以及Piccolc,Trigen Meta和Centronail胫骨髓内钉均不及解剖型髓内钉Expert(ETN专家级胫骨髓内钉)符合人体胫骨解剖学设计,便于髓内插入和拔出,并且可以较传统髓内钉达到有效坚强固定旋转移位过大的胫骨骨折。此部位解剖型髓内钉还包括ZNN。
其置钉方式为:膝关节屈曲90°于支架上,由髌韧带入路, 髌腱正中偏内0.5 cm纵行劈开髌腱,在胫骨平台前沿开口,牵引复位后,导针正中位穿患侧踝上1 cm,扩髓后插主钉至胫距关节0.5 cm上,先远后近进行螺钉锁钉。
王红星等[14]对22例胫骨下端开放性骨折病例进行解剖型髓内钉(Expert ETN)的治疗,平均手术时间75 min、出血量65 mL,平均随访16.4个月,愈合时间4.8个月,Johner-Wruhs评分优良率为86.4%。其对Gustilo Ⅰ,Ⅱ型胫骨骨折疗效可靠,预后满意。
除辛迪斯公司生产的Expert胫骨钉,另一款解剖型胫骨髓内钉在国外被广泛使用,即捷迈(Zimmer)公司的ZNN胫骨钉。其特点是:主钉设计为24-44 cm,适合几乎所有身材矮小或高大的患者;交锁钉使用Stabilize锁钉技术,与主钉绑定,减少退钉风险;内置物近端多平面交锁和超远端锁定等。基于以上优势,ZNN的解剖型胫骨髓内钉将会在国内有进一步的临床应用。
2.3.3 腓骨 作为下肢非负重骨的腓骨,对小腿肌力及远端踝部的稳定性有重要作用。若腓骨严重受损(如粉碎性骨折),导致胫骨不紊、踝部受力不均、小腿力线不良及下肢长度缺失等需要手术干预。
加压或重建钢板切开复位内固定常见于腓骨合并踝部骨折,但因软组织损伤严重、无法耐受等原因,克氏针、腓骨髓内钉也多见于临床。钢板内固定可能导致受伤创伤大、粉碎性骨折不能实行解剖复位,对腓骨的软组织和血供破坏较多导致骨折不愈合、术后局部感染等。与克氏针相比,髓内钉的稳定性更好,具有抗折弯、轴向和横向的稳定性,有效预防骨折的成角和再移位。弹性髓内钉防止骨折旋转与移位的性能不及髓内钉系统,且易因较长的尾端与远端组织发生激惹炎症现象。
普通髓内钉系统中,Rush棒及Knowles钉无法分担较大载荷负担;Inyo钉、圆柱型髓内钉、锥形空心髓内钉及Fibulock钉内置物材料硬度和宽度与髓腔有较多不匹配报道;而解剖型髓内钉的设计可解决上述问题[15]。对腓骨骨折皮肤张力性水疱、肿胀等处可使用髓内钉治疗来减少相关并发症。Acumed解剖型腓骨髓内钉的瞄准器可有25°外旋,使可能打入的下胫腓螺钉按骨质的解剖学原理由后向前置入;2枚内/外螺钉孔使得腓骨固定更更牢靠;3.0 mm和3.6 mm的近端设计与腓骨解剖结构愈加科学的贴合[16];手术时,1.6 mm导针由腓骨尖端进针,6.1 mm钻由远端 4 cm处扩髓至刻度线后置钉。钻头或3.5 mm套筒入A/P孔,标记后抵达远端,至2层皮肤后测深。选取的一两枚锁钉不穿骨皮质后部。
肖进飞等[16]应用解剖型髓内钉Acumed腓骨髓内钉治疗25例腓骨远端骨折,平均随访11个月,末次随访Baird-Jackson踝关节评分评定为(95.63±3.31)分,优良率高达96%。认为Acumed解剖型腓骨髓内钉治疗腓骨远端骨折,能很好地维持腓骨长度以及腓骨外翻角,且减少手术时间,临床疗效满意。
同样具有解剖型腓骨髓内钉特性的是Arthrex公司生产的Fibulock Nail[15]。该髓内钉系统近端设计为“撑开爪”的形式来达到抗旋的作用,远端的下胫腓处使用可以横跨对侧皮质骨的TightRope,使得腓骨远端具有更强的稳定性,但较宽的主钉设计依然会有医源性骨折的风险。因此,Acumed解剖型腓骨髓内钉较高的骨愈合率使其广泛应用于腓骨骨折的治疗[17]。
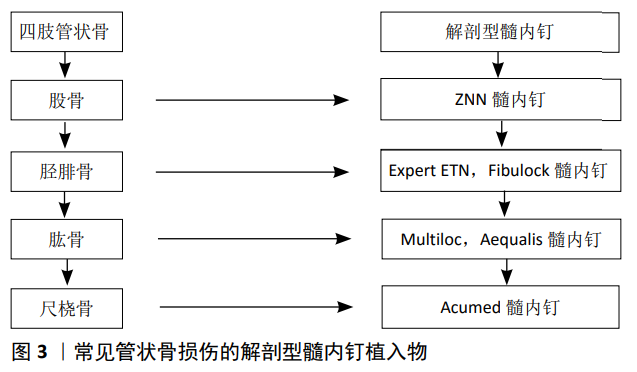
2.4 解剖型髓内钉在上肢管状骨的应用与进展 目前常见管状骨损伤的解剖型髓内钉植入物见图3。
2.4.1 肱骨 肱骨干骨折约占全身骨折的3%[18]。常见于骨质疏松的老年人,发病率与年龄增长成正相关。肱骨干骨折常见的致伤原因包括交通事故伤、跌伤或其他暴力损伤等。对于Neer分型一部分肱骨近端骨折,保守治疗可获得骨折愈合和良好关节功能。对于Neer分型二-四部分肱骨近端骨折,保守治疗效果欠佳,多以PHILOS钢板为主导。随着其应用增多,相关并发症逐渐凸现出来,对于骨质疏松性症患者,多有螺钉失效、内翻型畸形愈合、肱骨头坏死等并发症。近年来随着微创技术开展的日趋增多,髓内钉作为治疗肱骨近端骨折的一种新型方法,具有中心性固定、生物力学优越性及微创置入创伤小等特点。
第1代肱骨髓内钉以Rush棒为代表,易滑出且不能提供足够的固定来中和骨折变形力,并常导致急性愈合或不愈合;第2代肱骨髓内钉,如Polarus,Telegraph,Targon和Austofix髓内钉等,常常丢失螺钉的固定,螺钉后退现象很常见,需要二次手术才能取出;第3代解剖型肱骨髓内钉有Struyker T2,Tornier Aequalis和Synths Multiloc肱骨近端骨钉。上述3种髓内钉系统对于延伸到肱骨干的骨折,大多数都有较长的钉子可供选择,较短髓内钉的锁钉配置可以允许静态或动态锁钉模式。其设计的许多特点巧妙地解决了插入和固定问题,更符合人体解剖学[19]。Struyker T2包括小直径、左右两种版本;Tornier Aequalis更以较小的核心直径和较短的长度,以避免与肱骨近端的峡部啮合;Synths Multiloc近端锁钉螺钉以骨密度强的后内侧区域为目标,潜在地降低了内翻塌陷的风险,近端上升螺钉可附着更多骨质,从而为内侧支持提供了额外的坚强固定。Multiloc肱骨交锁髓内钉更是由于以下优点而被称为解剖型髓内钉:①肱骨头最高点直行进钉,该部位骨质好,可增加软骨下骨的把持力,增强固定稳定性,降低肩袖损伤风险;②肱骨距螺钉重建肱骨近端内侧柱,增加其稳定性,避免术后内翻畸形;③增多了的肱骨头内的螺钉,增强对骨折近端的把持力,提高其抗剪切力和轴向稳定性;④髓内钉远近端螺钉多角度设计,减少螺钉松动和退出,增加髓内钉的稳定性[20]。其置入方式为:取肩峰前外侧长3.0-4.0 cm切口。选择三角肌前、中肌间隙劈开三角肌,显露冈上肌,沿肌纤维纵形切开,显露肱骨头。选择肱骨头最高点作为入钉点,正中心位进导针,扩髓后置入顶端入软骨下2 mm的主钉,近端与远端通过定向器打入3枚和2枚锁定钉,主钉尾帽置顶部。
罗仲伟等[20]对16例肱骨近端骨折患者进行Multiloc肱骨解剖型交锁髓内钉治疗,平均随访(12.35±2.36)个月,Constant-Murley得分(82.56±16.62)分,优良率达87.5%。研究者认为Multiloc髓内钉用于肱骨近端骨折创伤及术中时间均少,固定可靠,早期功能锻炼后关节功能恢复良好,是治疗肱骨近端骨折的有效手段[21-23]。
目前,国内外多使用Synths MultiLoc肱骨解剖髓内钉系统治疗肱骨近端骨折。中国江苏艾迪尔医疗公司生产的肱骨解剖型交锁髓内钉也已进入市场,其与MultiLoc肱骨钉相近的设计理念与较低的价格,会在今后的临床治疗中有更多的应用。
2.4.2 尺、桡骨 尺骨和桡骨骨干骨折占全身骨折的11.2%。尺、桡骨共同组成前臂,骨折可导致成角、移位和旋转等畸形[24-25]。前臂(尺、桡骨)骨折,可能会影响前臂及上肢功能,被视为关节内骨折,切开复位内固定是治疗成人前臂骨折的主流术式,然而该技术存在一定弊端,如广泛的软组织及骨膜损伤增加了骨不连及伤口感染的风险;应力遮挡导致钢板取出时发生二次骨折;桡骨上1/3骨折切开复位钢板固定存在桡神经损伤的潜在风险。对于前臂双骨折而言进行切开复位钢板内固定意味着更高的手术风险和并发症。尺桡骨骨折后发生深部感染率高达4%,骨不连发生率5%-12%[26],而且内固定物拆除后易发生二次骨折,据报道发生率高达4%-22%[27]。对于桡骨中上1/3骨折采用钢板螺钉技术有发生桡神经损伤的风险。对于前臂双骨折而言,特别是粉碎性骨折及多节段骨折、骨折合并软组织损伤较重的患者,如果采取切开复位内固定,手术风险将进一步加大。
随着前臂髓内钉的不断改进,应用髓内钉治疗前臂骨折的方法在临床逐渐开展,骨折愈合率不逊于传统的钢板固定。在前臂髓内钉的历史发展中,由可屈行的银棒插入髓腔,到Rush,Kirschner,Steinmann,Kuntscher V及LoRes钉等得到应用,以上均无法匹配前臂骨的生理解剖弧度,强行置钉易发生尺桡骨不愈合,发生骨折不愈合率为21%[28]。随着对前臂髓内钉的不断改进,特别是Acumed解剖型髓内钉的出现,髓内钉治疗前臂骨折的治疗效果明显提高并逐步被临床认可。相比于普通髓内钉,Acumed髓内钉透视次数少、术中耗时少。同时,由于Acumed桡骨髓内钉为棱形,进钉点子在Lister结节尺侧距离关节面5 mm的桡侧腕伸肌腱下方,其钉尾锁钉而近端不锁钉的设计避免了桡神经浅支和深支的损伤[29]。
置钉流程为:桡骨、尺骨相继复位,桡骨Lister结节做2 cm纵向切口, 在桡侧腕短伸肌腱和拇长伸肌腱之间显露Lister结节, 注意保护桡神经浅支及拇长伸肌腱。在Lister结节尺侧(拇长伸肌腱下方) 开骨槽进钉,桡骨髓内钉根据其弓形结构设计,与桡骨的自然曲度相对应兼具一定弹性,加之进针点在桡骨远侧中央对应髓腔无成角,故插入髓。尺骨鹰嘴尖1.5 cm进钉,其中尺骨髓内钉具有10°外翻设计提供三点固定,近端有交锁螺钉,远端无锁定。
何红英等[30]观察了解剖型髓内钉Acumed前臂髓内钉修复86例成人前臂双骨折的临床疗效,平均随访86.8周,Grace-Eversmenp评价结果,优良率为93%。认为该解剖型髓内钉治疗前臂双骨折具有微创、手术时间短及并发症少等优点,围术期效果满意,值得临床推广。同时,何红英等[30]对Galaezzi骨折与Monteggia骨折患者使用Acumed解剖型髓内钉,取得良好效果。Lee等[31]认为前臂干部骨折使用解剖型Acumed髓内钉可取得良好手术效果,骨折愈合时间平均为14周,愈合率为97%,优良率为92.6%,是一种有效的治疗方式。
目前,尚未见到改进后解剖型髓内钉Acumed髓内钉临床结果逊于钢板治疗的报告,尽管如此,该方法尚未在更大范围内应用,其优势与不足仍需更大宗病例的验证。前臂尺桡骨发生骨折以钢板内固定治疗为主,其次是弹性髓内针,儿童前臂骨折主要使用弹性髓内针内固定[32-34]。前臂Acumed解剖型髓内钉主要适用于成人尺桡骨骨折,合并有软组织严重损伤。该针对性的适应证使得Acumed尺桡骨钉为前臂髓内钉系统中主要的解剖型内置物。
2.5 解剖型髓内钉的缺陷与展望 尽管解剖型髓内钉在国内外均取得了较优的临床疗效,正逐渐成为治疗管状骨髓内钉的首选材料。但内置物是人体外源性物质,仍无法避免与其接触的组织感染和免疫排斥反应,而且术后成功置钉后便需患者自身的愈合与锻炼,解剖型髓内钉的主要作用仅是维持生物力学功能。因此,解剖型髓内钉的发展仍有较大空间。在不久的将来,新髓内钉系统即第4代髓内钉将会由3代的解剖型髓内钉进化而来,其优势为钉道系统的表面覆盖生物制剂,会极大降低与人体的各种排异反应;解剖型髓内钉系统附着微型传感器,可检测骨折断端术后的生长环境,评估骨愈合的进展,协助医师更科学的制定康复和训练计划等。当前,手术机器人和计算辅助导航运用于髓内钉系统正是第3代向第4代髓内钉过渡的重要标志。
解剖型髓内钉已将髓内钉系统的物理力学设计达到了较高水平。未来治疗人体管状骨的髓内钉会在此基础上通过生化制剂、生物和感应工程等方面的研究,全面实现精准化、个性化和数字化医疗。