中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (49): 7307-7313.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.49.002
• 周围神经损伤动物模型 Animal models of peripheral nerve injury • 上一篇 下一篇
补肾益智方对D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35致老年痴呆模型 大鼠的作用及机制
王改凤
- 河南中医药大学第二附属医院脑病一区,河南省郑州市 450002
Effects of Bushen Yizhi Decoction on Alzheimer’s disease model rats induced by D-galactose combined with amyloid-beta 25-35 and the underlying mechanism
Wang Gai-feng
- First Encephalopathy Ward, the Second Affiliated Hospital of Henan University of Chinese Medicine, Zhengzhou 450002, Henan Province, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。
文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。
.jpg) 文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。
文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。摘要
背景:中药复方具有多靶点的作用特点,能通过多个环节对中枢胆碱能神经系统进行调节,有效改善患者的认知功能。研究证明,补肾益智方可以改善老年痴呆患者的症状,提高生活质量。
目的:探讨补肾益智方对D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35致老年痴呆模型大鼠的作用及其机制。
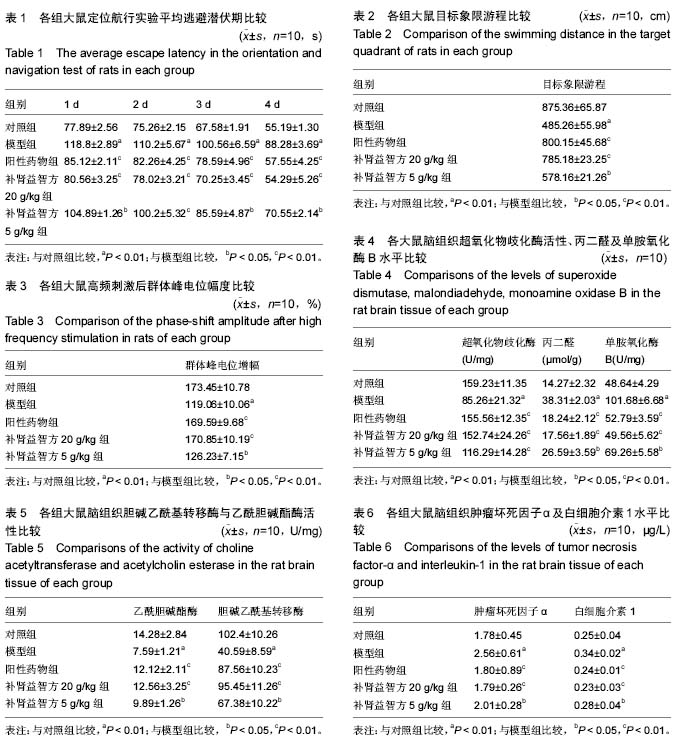
方法:选用健康成年SD大鼠,随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性药物组(多奈哌齐组0.3 g/kg)、补肾益智方20 g/kg组及补肾益智方5 g/kg组,每组10只,采用皮下注射D-半乳糖联合双侧海马注射β-淀粉样蛋白25-35构建痴呆大鼠模型。用补肾益智方药液灌胃治疗8周后,釆用Morris水迷宫测试检测大鼠的学习记忆能力;采用高频刺激Schaffer侧支,在同侧海马CA1区诱导长时程增强的方法检测大鼠海马神经元突触可塑性的变化;同时检测大鼠脑组织多种指标,包括超氧化物歧化酶活性、丙二醛、单胺氧化酶B、胆碱乙酰基转移酶、乙酰胆碱酯酶、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1等。
结果与结论:①水迷宫实验中补肾益智方组可显著改善大鼠的学习记忆能力,模型组与对照组相比海马CA1区长时程增强幅度显著降低(P < 0.05);②补肾益智方5 g/kg组与模型组比较,群体峰电位幅度差异无显著性意义;补肾益智方20 g/kg组群体峰电位幅度明显高于模型组和补肾益智方5 g/kg组,能减轻D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35对海马CA1区长时程增强的抑制作用,改善突触功能的可塑性;③补肾益智方组能显著降低肿瘤坏死因子α和白细胞介素1的水平(P < 0.05),明显提高胆碱乙酰基转移酶和超氧化物歧化酶活性(P < 0.05),降低乙酰胆碱酯酶活性及丙二醛水平(P < 0.05);④结果提示,
补肾益智方对阿尔茨海默病大鼠模型学习记忆的改善作用可能与抑制脑内炎症反应、调节胆碱能系统、抗氧化作用等有关。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:肾移植;肝移植;移植;心脏移植;组织移植;皮肤移植;皮瓣移植;血管移植;器官移植;组织工程
ORCID: 0000-0001-7427-3907(王改凤)
中图分类号:
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。
文题释义:
D-半乳糖制备衰老模型:D-半乳糖联合β-淀粉样蛋白25-35制备老年痴呆模型,能很好的模拟阿尔茨海默病复杂的病因病理和生化变化过程。大量研究证实,D-半乳糖制备的衰老模型是目前国内都认可的老年痴呆模型制备方法,可以有效的模拟与人类自然衰老相似的认知障碍、细胞退行性改变、生化改变及免疫功能低下等表现。
阿尔茨海默病:是一种以大脑神经退化为主的疾病,主要病理表现为中枢胆碱能神经元大量死亡及丢失,神经纤维缠结,神经炎斑,β-淀粉样蛋白沉积等,继而导致胆碱能神经损害、炎症反应,胆碱乙酰基转移酶水平下降和乙酰胆碱合成减少等。