| [1]Niu X, Chen G. Clinical biomarkers and pathogenic-related cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. 2014;2014:698192.[2]肖瑶,方宁,陈代雄,等.人羊膜间充质干细胞对大鼠胶原性关节炎的疗效及免疫调节作用[J].免疫学杂志,2013,29(6):461-466. [3]Fiehn C, Holle J, Iking-Konert C,et al.S2e guideline:treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with disease-modifying drugs.Z Rheumatol. 2018; 77(Suppl 2):35-53.[4]McInnes IB, Schett G. The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med. 2011;365(23):2205-2219.[5]McInnes IB, Buckley CD, Isaacs JD. Cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis - shaping the immunological landscape. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2016; 12(1):63-68.[6]Chastek B, Becker LK, Chen CI, et al. Outcomes of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor cycling versus switching to a disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug with a new mechanism of action among patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Med Econ. 2017;20(5):464-473.[7]Bongartz T, Sutton AJ, Sweeting MJ, et al. Anti-TNF antibody therapy in rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of serious infections and malignancies: systematic review and meta-analysis of rare harmful effects in randomized controlled trials.JAMA. 2006;295(19):2275-2285.[8]Salliot C, Gossec L, Ruyssen-Witrand A, et al. Infections during tumour necrosis factor-alpha blocker therapy for rheumatic diseases in daily practice: a systematic retrospective study of 709 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007;46(2):327-334.[9]Castro-Manrreza ME, Montesinos JJ. Immunoregulation by mesenchymal stem cells: biological aspects and clinical applications. J Immunol Res. 2015;2015:394917.[10]刘荣霞,杨炳,余丽梅,等.不同来源间充质干细胞治疗卵巢早衰的作用及机制研究进展[J].山东医药,2018,58(40):106-110. [11]罗欣,余丽梅.外泌体在间充质干细胞治疗骨性关节炎中的作用:新策略与新思路[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(1):140-145. [12]Munir H, McGettrick HM. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Autoimmune Disease: Risks and Rewards. Stem Cells Dev. 2015; 24(18):2091-2100.[13]Baharlou R, Ahmadi-Vasmehjani A, Faraji F, et al. Human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells in rheumatoid arthritis: Regulatory effects on peripheral blood mononuclear cells activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 2017;47:59-69.[14]Vasilev G, Ivanova M, Ivanova-Todorova E, et al. Secretory factors produced by adipose mesenchymal stem cells downregulate Th17 and increase Treg cells in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatol Int. 2019;39(5):819-826.[15]Park KH, Mun CH, Kang MI, et al. Treatment of Collagen-Induced Arthritis Using Immune Modulatory Properties of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Transplant. 2016;25(6):1057-1072.[16]Greish S, Abogresha N, Abdel-Hady Z, et al. Human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells as treatment of adjuvant rheumatoid arthritis in a rat model. World J Stem Cells. 2012;4(10):101-109.[17]Álvaro-Gracia JM, Jover JA, García-Vicuña R, et al. Intravenous administration of expanded allogeneic adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells in refractory rheumatoid arthritis (Cx611): results of a multicentre, dose escalation, randomised, single-blind, placebo- controlled phase Ib/IIa clinical trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76(1): 196-202.[18]Ghoryani M, Shariati-Sarabi Z, Tavakkol-Afshari J, et al. Amelioration of clinical symptoms of patients with refractory rheumatoid arthritis following treatment with autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells: A successful clinical trial in Iran. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;109:1834-1840.[19]Park EH, Lim HS, Lee S, et al. Intravenous Infusion of Umbilical Cord Blood-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Phase Ia Clinical Trial. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2018;7(9):636-642.[20]Shadmanfar S, Labibzadeh N, Emadedin M, et al. Intra-articular knee implantation of autologous bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients with knee involvement: Results of a randomized, triple-blind, placebo-controlled phase 1/2 clinical trial. Cytotherapy. 2018;20(4):499-506.[21]Uccelli A, de Rosbo NK. The immunomodulatory function of mesenchymal stem cells: mode of action and pathways. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2015;1351:114-126.[22]Yan X, Cen Y, Wang Q. Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate experimental rheumatoid arthritis through microRNA-regulated IκB expression. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28915.[23]MacDonald GI, Augello A, De Bari C. Role of mesenchymal stem cells in reestablishing immunologic tolerance in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(9):2547-2557.[24]Toupet K, Maumus M, Luz-Crawford P, et al. Survival and biodistribution of xenogenic adipose mesenchymal stem cells is not affected by the degree of inflammation in arthritis. PLoS One. 2015;10(1):e0114962.[25]Nam Y, Jung SM, Rim YA, et al. Intraperitoneal infusion of mesenchymal stem cell attenuates severity of collagen antibody induced arthritis. PLoS One. 2018;13(6):e0198740.[26]Zhang L, Wang XY, Zhou PJ, et al. Use of immune modulation by human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells to treat experimental arthritis in mice. Am J Transl Res. 2017;9(5):2595-2607.[27]Baharlou R, Rashidi N, Ahmadi-Vasmehjani A, et al. Immunomodulatory Effects of Human Adipose Tissue-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on T Cell Subsets in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019;18(1):114-119.[28]Usha Shalini P, Vidyasagar JV, Kona LK, et al. In vitro allogeneic immune cell response to mesenchymal stromal cells derived from human adipose in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol. 2017;314:18-25.[29]Liu R, Li X, Zhang Z, et al. Allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells inhibited T follicular helper cell generation in rheumatoid arthritis. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12777.[30]Rosado MM, Bernardo ME, Scarsella M, et al. Inhibition of B-cell proliferation and antibody production by mesenchymal stromal cells is mediated by T cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2015;24(1):93-103.[31]Liu Y, Yin Z, Zhang R, et al. MSCs inhibit bone marrow-derived DC maturation and function through the release of TSG-6. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2014;450(4):1409-1415.[32]Spaggiari GM, Moretta L. Cellular and molecular interactions of mesenchymal stem cells in innate immunity. Immunol Cell Biol. 2013; 91(1):27-31.[33]Shin TH, Kim HS, Kang TW, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-stem cells direct macrophage polarization and block inflammasome activation to alleviate rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Death Dis. 2016;7(12): e2524.[34]Zhang S, Chu WC, Lai RC, et al. Exosomes derived from human embryonic mesenchymal stem cells promote osteochondral regeneration. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2016;24(12):2135-2140.[35]Feng Z, Zhai Y, Zheng Z, et al. Loss of A20 in BM-MSCs regulates the Th17/Treg balance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Sci Rep. 2018;8(1):427. [36]Horai R, Saijo S, Tanioka H, et al. Development of chronic inflammatory arthropathy resembling rheumatoid arthritis in interleukin 1 receptor antagonist-deficient mice. J Exp Med. 2000;191(2):313-320.[37]Lee K, Park N, Jung H, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells ameliorate experimental arthritis via expression of interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. PLoS One. 2018;13(2):e0193086.[38]Headland SE, Jones HR, Norling LV, et al. Neutrophil-derived microvesicles enter cartilage and protect the joint in inflammatory arthritis. Sci Transl Med. 2015;7(315):315ra190. [39]Chen Z, Wang H, Xia Y, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Mesenchymal Cell-Derived miRNA-150-5p-Expressing Exosomes in Rheumatoid Arthritis Mediated by the Modulation of MMP14 and VEGF. J Immunol. 2018;201(8):2472-2482.[40]Cosenza S, Toupet K, Maumus M, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells- derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis. Theranostics.2018;8(5):1399-1410.[41]张中原,余丽梅,王信. 膝骨关节炎再生修复治疗新方法研究进展[J]. 实用医学杂志,2018,34(9):1561-1564. [42]Zaiss MM, Frey B, Hess A, et al. Regulatory T cells protect from local and systemic bone destruction in arthritis.J Immunol. 2010;184(12): 7238-7246.[43]Oshita K, Yamaoka K, Udagawa N, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells inhibit osteoclastogenesis through osteoprotegerin production. Arthritis Rheum. 2011;63(6):1658-1667.[44]Varin A, Pontikoglou C, Labat E, et al. CD200R/CD200 inhibits osteoclastogenesis: new mechanism of osteoclast control by mesenchymal stem cells in human. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e72831.[45]Garimella MG, Kour S, Piprode V, et al. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Prevent Systemic Bone Loss in Collagen-Induced Arthritis. J Immunol. 2015;195(11):5136-5148.[46]Chemel M, Brion R, Segaliny AI, et al. Bone Morphogenetic Protein 2 and Transforming Growth Factor β1 Inhibit the Expression of the Proinflammatory Cytokine IL-34 in Rheumatoid Arthritis Synovial Fibroblasts. Am J Pathol. 2017;187(1):156-162.[47]Le Blanc K, Tammik C, Rosendahl K, et al. HLA expression and immunologic properties of differentiated and undifferentiated mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Hematol. 2003;31(10):890-896.[48]Sakaguchi Y, Sekiya I, Yagishita K, et al. Comparison of human stem cells derived from various mesenchymal tissues: superiority of synovium as a cell source. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(8):2521-2529.[49]De Bari C, Dell'Accio F, Karystinou A, et al. A biomarker-based mathematical model to predict bone-forming potency of human synovial and periosteal mesenchymal stem cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2008;58(1):240-250.[50]Melief SM, Zwaginga JJ, Fibbe WE, et al. Adipose tissue-derived multipotent stromal cells have a higher immunomodulatory capacity than their bone marrow-derived counterparts. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(6):455-463.[51]Abdelmawgoud H, Saleh A. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of mesenchymal and hematopoietic stem cells in a rheumatoid arthritis rat model. Adv Clin Exp Med. 2018;27(7):873-880.[52]Abd Elhalem SS, Haggag NZ, El-Shinnawy NA. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells suppress IL-9 in adjuvant-induced arthritis. Autoimmunity. 2018;51(1):25-34.[53]Yu Y, Yoon KA, Kang TW, et al. Therapeutic effect of long-interval repeated intravenous administration of human umbilical cord blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells in DBA/1 mice with collagen-induced arthritis. Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2019 Apr 8. doi: 10.1002/term.2861. [Epub ahead of print][54]Kim KW, Kim HJ, Kim BM, et al. Epigenetic modification of mesenchymal stromal cells enhances their suppressive effects on the Th17 responses of cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;9(1):208.[55]Yang Y, He X, Zhao R, et al. Serum IFN-γ levels predict the therapeutic effect of mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in active rheumatoid arthritis. J Transl Med. 2018;16(1):165. |
.jpg)
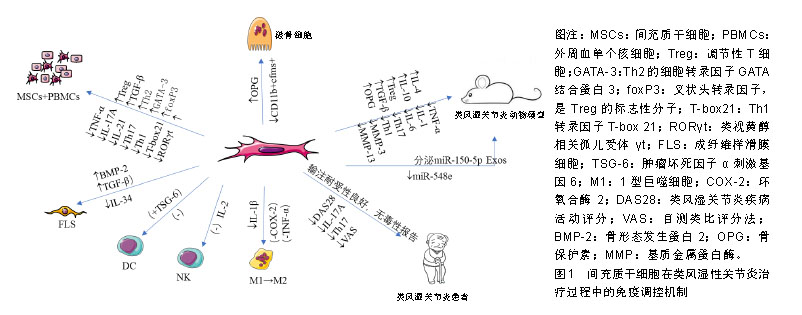
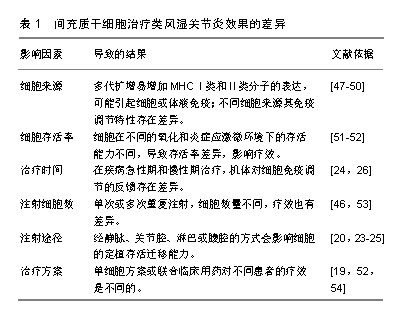
.jpg)