| [1]李享德,吴钊英,邓玉虎,等.无机介孔钙硅基止血材料的制备及性能研究[J].化学世界,2012,67(S1):13-17.
[2]Henderson PW,Kadouch DJM,Singh SP,et al.A rapidly resorbable hemostatic biomaterial based on dihydroxyacetone.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;93(2): 776-782.
[3]Ellis-Behnke R.At the nanoscale: nanohemostat, a new class of hemostatic agent. Wiley interdisciplinary reviews: nanomedicine and nanobiotechnology.2011; 3(1):70-78.
[4]黄远铿,肖百全,欧慧瑜,等.新型止血材料纤维蛋白贴的止血作用研究[J].中国药理学通报,2013,29(8):1140-1145.
[5]Kheirabadi B.Evaluation of topical hemostatic agents for combat wound treatment. US Army Med Dep J. 2011;2(1):25-37.
[6]高金伟,刘万顺,韩宝琴.壳聚糖纤维止血效果研究[J].安徽农业科学,2012,40(11): 6458-6459.
[7]王建,葛宝丰,刘兴炎,等战伤止血方法及材料研究进展[J].人民军医,2008,51(1): 5-6.
[8]李东红,高华,李鹏熙,等.几种止血材料对兔实质脏器创伤止血性能的比较[J].创伤外科杂志,2012,14(5):435-438.
[9]尹刚,陈汇浩,郭兴锋,等.温敏性壳聚糖止血膜的止血作用及体内降解吸收[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014,18(34): 5461-5465.
[10]马茂,范代娣.壳聚糖-类人胶原蛋白对兔肝创面的止血效果及组织相容性观察[J].第四军医大学学报, 2007,28(1): 1122-1124.
[11]Ye X,Kennedy JF,Li B,et al.Condensed state structure and bio-compatibility of the konjac glucomannan /chitosan blend films.Carbohydr Polym. 2006;64(4): 532-538.
[12]姜毅,王风华,段蕴铀.多糖类止血材料的研究及应用进展[J].解放军医学杂志,2014, 39(12):1004-1007.
[13]李钒,田丰,刘长军等.急救止血材料的研究进展[J].材料导报A:综述篇,2013,27(2): 70-73.
[14]尹刚,魏长征,郭兴锋,等.温敏性壳聚糖止血膜止血作用的实验研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013,27(5): 624-627.
[15]高文彪,张岩睿,张军.胶原/壳聚糖止血敷料在外科伤口中的应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(29):5477-5480.
[16]Achneck HE,Slileshi B,Jamiolkowski RM,et al.A comprehensive review of topical hemostatic agents: efficacy and recommendations for use. Ann Surg.2010; 251(2):217-228.
[17]许盈.纱泰祺快速止血纱布止血效果、安全性及体外抗菌效果研究[D].南宁:广西医科大学,2010:11.
[18]张宜,喻晶,曹利利,等.基于止血药研究的兔止血模型[J].华南国防医学杂志,2015,29(7): 560-562.
[19]Scarano A,Carinci F,Cimorelli E,et al.Application of calcium sulfate in surgical-orthodontic treatment of impacted teeth: a new procedure to control hemostasis.J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2010;68(5): 964-968.
[20]Noval-Padillo JA,León-Justel A,Mellado-Miras P,et al.Introduction of fibrinogen in the treatment of hemostatic disorders during orthotopic liver transplantation: implications in the use of allogenic blood. Transplant Proc. 2010; 42(8): 2973-2974.
[21]叶世富,王士斌,吴文果,等.可吸收止血材料现状及效果评价的研究进展[J].材料导报A:综述篇,2014,28(4):67-71.
[22]James B,Russell M.A review of topical hemostatic agents for use in cardiac surgery .Ann Thorac Surg. 2009;88(4):1377.
[23]Ellis-behnke RG,Liang YX,Trayd KC,et al. Nanohemostat solution: immediate hemostasis at the nanoscale.nanomedicine: Nanotechnology.Biol Med. 2006;6(2):207-215.
[24]Huang W,Wang Y,Chen Y,et al.Strong and Rapidly Self-Healing Hydrogels: Potential Hemostatic Materials.Adv Healthc Mater.2016.doi: 10.1002/adhm.201600720.
[25]Menéndez-Nieto I,Cervera-Ballester J,Maestre-Ferrín L,et al.Hemostatic Agents in Periapical Surgery: A Randomized Study of Gauze Impregnated in Epinephrine versus Aluminum Chloride.J Endod. 2016.pii: S0099-2399(16)30493-9.doi: 10.1016/j.joen.2016.08.005. [Epub ahead of print]
[26]Lechner R,Helm M,Mueller M,et al.Efficacy of Hemostatic Agents in Humans With Rotational Thromboelastometry: An in-vitro Study.Mil Med. 2016;181(8):907-912.
[27]Zilinsky I,Barazani TB,Shenkman B,et al.Topical Hemostatic-Anesthetic Solution to Reduce Bleeding During Mohs Micrographic Surgery: A Case Control Study.J Drugs Dermatol.2016;15(7):851-855.
[28]Chen J,Lan G,Li K,et al.Preparation of a partially carboxymethylated cotton gauze and study of its hemostatic properties.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2016;62:407-416.
[29]Li H,Wang L,Alwaal A,et al.Comparison of Topical Hemostatic Agents in a Swine Model of Extremity Arterial Hemorrhage: BloodSTOP iX Battle Matrix vs. QuikClot Combat Gauze.Int J Mol Sci.2016;17(4):545.
[30]Wan G,Yan M.Puncture Point Hemostatic Effect Observation of Different Materials with Modified Seldinger Technique in PICC Catheter.Zhongguo Yi Liao Qi Xie Za Zhi.2015;39(5):388-390.
[31]Crofton A,Chrisler J,Hudson S,et al.Effect of Plasma Sterilization on the Hemostatic Efficacy of a Chitosan Hemostatic Agent in a Rat Model.Adv Ther.2016; 33(2):268-281.
[32]Te Grotenhuis R,van Grunsven PM,Heutz WM,et al. Prehospital use of hemostatic dressings in emergency medical services in the Netherlands: A prospective study of 66 cases.Injury. 2016;47(5):1007-1011.
[33]Hutchinson RW,Werrlein S,Johns DB,et al.An In Vivo Comparison of Hemostatic Gelatin Matrix Products in a Porcine Spleen Biopsy-punch Model.Surg Technol Int. 2015;27:53-57.
[34]Conley SP,Littlejohn LF,Henao J,et al.Control of Junctional Hemorrhage in a Consensus Swine Model With Hemostatic Gauze Products Following Minimal Training.Mil Med.2015;180(11):1189-1195.
[35]Shina A,Lipsky AM,Nadler R,et al.Prehospital use of hemostatic dressings by the Israel Defense Forces Medical Corps: A case series of 122 patients.J Trauma Acute Care Surg.2015;79(4 Suppl 2):S204-209.
[36]巴迪•D.拉特纳,艾伦•S.霍夫曼,弗雷德里克•J.舍恩,杰克•E.莱蒙斯.生物材料科学:医用材料导论(原著第2版)[M].顾忠伟,刘伟,俞耀庭,等译.北京:科学出版社, 2011: 393-403.
[37]丁婷婷,章平,孙皎.生物材料引起机体炎症反应的研究进展[J].国外医学生物医学工程分册,2005,28(1):23-26.
[38]郭清奎,吕志前,张祎,等.新型可完全降解材料聚外消旋乳酸-三亚甲基碳酸脂聚合物体内降解行为和组织相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(34): 6368-6374.
[39]杨青,马显杰,马静,等.皮肤创伤后无瘢痕愈合的研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2014,25(9):569-570.
[40]张朝阳,陈聚伍,孟宇.磺胺嘧啶银脂质水胶敷料在植皮手术供皮区应用效果观察[J].郑州大学学报(医学版), 2014, 49(3):411-413. |
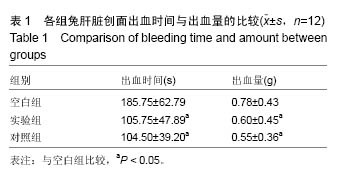
.jpg)
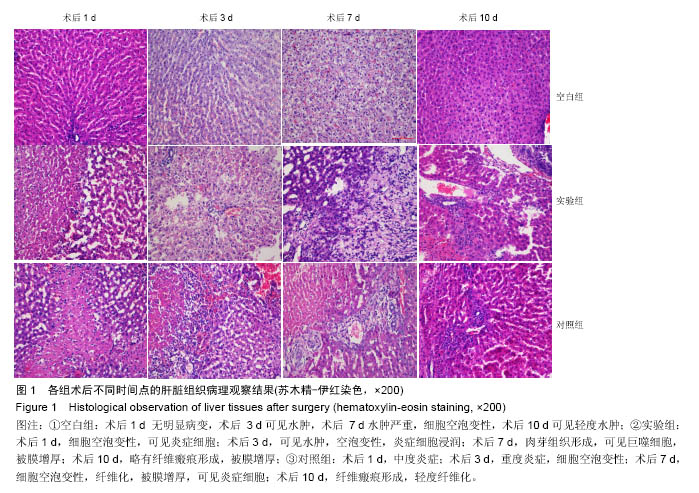
.jpg)