中国组织工程研究 ›› 2016, Vol. 20 ›› Issue (42): 6351-6356.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2016.42.018
• 精品专题 special topic • 上一篇 下一篇
拇外翻发病危险因素与足底压力特征
黄 萍,钱念东,齐 进,陈 博,邓廉夫
- 上海市伤骨科研究所,上海市中西医结合防治骨与关节病损重点实验室,上海交通大学医学院附属瑞金医院,上海市 200025
The risk factors and plantar pressure characteristics of hallux valgus
Huang Ping, Qian Nian-dong, Qi Jin, Chen Bo, Deng Lian-fu
- Shanghai Institute of Traumatology and Orthopaedics, Shanghai Key Laboratory for Prevention and Treatment of Bone and Joint Diseases with Integrated Chinese-Western Medicine, Shanghai Ruijin Hospital, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine, Shanghai 200025, China
摘要:
文章快速阅读:
.jpg) 文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
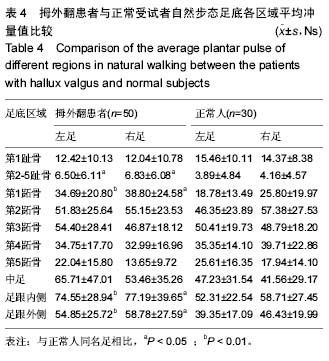
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。
文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。
.jpg) 文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。
文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。摘要
背景:拇外翻具有较复杂的足部解剖畸形,使足底区域的压力发生改变。
目的:分析拇外翻的发病危险因素,检测拇外翻患者平地自然行走下足底压力分布特征。
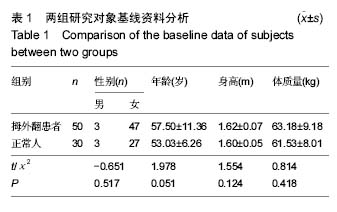
方法:采用比利时RSscan INTERNATIONAL公司生产的footscanUSB2平板式足底压力测试系统,检测50例拇外翻患者和年龄、身高、体质量匹配的30例正常人的动态足底压力。所有受试者测试时均脱鞋袜,以个人平常步态自然行走,每人测试3次以上,取得动态足底压力曲线及特征量参数,对曲线及各参数进行分析。
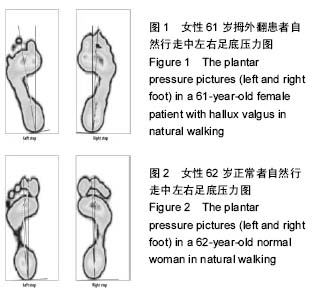
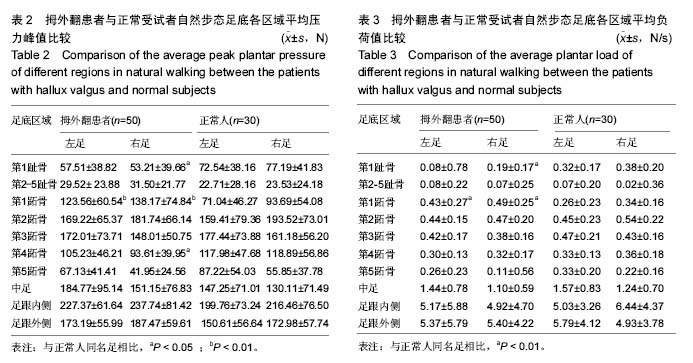
结果与结论:①测试的拇外翻患者中,女性占94%(均穿高跟尖头鞋),男性占6%(均不穿高跟尖头鞋),96%有遗传史;②在自然行走步态中,拇外翻患者双足第1跖骨区压力明显增高,与正常人足底压力图形明显不同;③拇外翻患者第1跖骨的平均压力峰值、平均负荷值、平均冲量与正常人相比,均明显增高(P < 0.05或P < 0.01)。④结果说明,除遗传因素外穿高跟尖头鞋是拇外翻发生的一个重要因素,拇外翻患者第1跖骨区压力、负荷、冲量明显增高,促使了拇外翻的发生发展。通过分析拇外翻的发病危险因素以及拇外翻患者动态足底压力情况,可以为拇外翻的预防、治疗、功能康复等提供重要参考。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:组织构建;骨细胞;软骨细胞;细胞培养;成纤维细胞;血管内皮细胞;骨质疏松;组织工程
ORCID:0000-0001-6780-3623(邓廉夫)
中图分类号:
.jpg) 文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。
文题释义:
拇外翻:是指拇趾在第1跖趾关节处向外侧过度偏斜移位。一般呈对称性发生。主要表现为拇趾的跖趾关节全/半脱位,内侧关节囊红肿、疼痛,伴或不伴胼胝体形成。
冲量:是指作用于物体的外力与外力作用时间的乘积,它表示了力在一定时间内对足底各区域连续作用所产生的积累效应。所以足底各区域冲量的大小受每个区域的压力值和接触时间两个因素的影响。冲量的大小是疲劳积累的直接原因,对足部易损伤部位的研究具有重要意义。