| [1] 列才华,陈香美,谢院生,等. IgA肾病肾病综合征临床病理特点及肾脏病理危险因素[J].中国中西医结合肾病杂志, 2008,9(4):321-324.
[2] 张茵.肾病综合征的治疗进展[J].医学综述,2014,20(2): 260-262.
[3] 何文兵,刘光陵.原发性肾病综合征的免疫致病机制探讨[J].中国全科医学,2010,13(30):3461-3463.
[4] 河内裕,万毅刚.肾病综合征的发病机理——蛋白尿发病机制的最新认识[J].日本医学介绍,2005,26(9):385-387.
[5] Tryggvason K, Wartiovaara J. Molecular basis of glomerular permselectivity. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2001;10(4):543-549.
[6] Tryggvason K. Unraveling the mechanisms of glomerular ultrafiltration: nephrin, a key component of the slit diaphragm. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1999;10(11): 2440-2445.
[7] Jalanko H, Patrakka J, Tryggvason K, et al. Genetic kidney diseases disclose the pathogenesis of proteinuria. Ann Med. 2001;33(8):526-533.
[8] 冯影,卢士红,王昕,等.人骨髓来源间充质干细胞分泌外泌体特性研究[J].中国实验血液学杂志,2014,22(3): 595-599.
[9] 程庆,陈香美,师锁柱,等.中药淫羊藿对慢性肾衰大鼠免疫病理及细胞外基质的影响[J].中华内科杂志,1994(2):83- 86.
[10] 杨维娜,于琳华,郭尚温,等.改良阿霉素肾病大鼠模型的建立[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2009,30(4):445-448.
[11] Gorriz JL, Martinez-Castelao A. Proteinuria: detection and role in native renal disease progression. Transplant Rev (Orlando). 2012;26(1):3-13.
[12] 何正宏,陈西北,白云凯.原发性肾病综合征患者脂代谢紊乱及炎症反应与蛋白尿的关系[J].中国民康医学,2008, 20(20):2349.
[13] Lahdenkari AT, Lounatmaa K, Patrakka J, et al. Podocytes are firmly attached to glomerular basement membrane in kidneys with heavy proteinuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2004;15(10):2611-2618.
[14] Cunard R, Kelly CJ. T cells and minimal change disease. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13(5):1409-1411.
[15] Grimbert P, Audard V, Remy P, et al. Recent approaches to the pathogenesis of minimal-change nephrotic syndrome. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2003; 18(2):245-248.
[16] Audard V, Lang P, Sahali D. Minimal change nephrotic syndrome : new insights into disease pathogenesis. Med Sci (Paris). 2008;24(10):853-858.
[17] Oh J, Kemper MJ. Minimal change (steroid sensitive) nephrotic syndrome in children: new aspects on pathogenesis and treatment. Minerva Pediatr. 2012; 64(2):197-204.
[18] 陈继红,孙伟,高坤,等.高脂饲料加速阿霉素肾小球硬化模型的建立[J].南京中医药大学学报,2007,23(3):162-163.
[19] Pedrycz A, Wieczorski M, Czerny K. Histological and histochemical assessment of the effects of a single dose adriamycin on fetal rat kidney. Acta Histochem. 2005;107(3):215-220.
[20] Fukudome K, Fujimoto S, Sato Y, et al. Comparison of the effects of intravenous methylprednisolone pulse versus oral prednisolone therapies on the first attack of minimal-change nephrotic syndrome in adults. Nephrology (Carlton). 2012;17(3):263-268.
[21] Fujinaga S, Hirano D, Murakami H, et al. Nephrotoxicity of once-daily cyclosporine A in minimal change nephrotic syndrome. Pediatr Nephrol. 2012; 27(4):671-674.
[22] Park SJ, Shin JI. Complications of nephrotic syndrome. Korean J Pediatr. 2011;54(8):322-328.
[23] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[24] Poulsom R, Forbes SJ, Hodivala-Dilke K, et al. Bone marrow contributes to renal parenchymal turnover and regeneration. J Pathol. 2001;195(2):229-235.
[25] 周乐,崔燎,吴铁.淫羊藿对肾阳虚雄性大鼠肾脏和股骨BMP-7表达的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2008,14(2): 90-94.
[26] Kronsteiner B, Peterbauer-Scherb A, Grillari-Voglauer R, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells and renal tubular epithelial cells differentially influence monocyte-derived dendritic cell differentiation and maturation. Cell Immunol. 2011;267(1):30-38.
[27] 张逸凡,于庆海.淫羊藿总黄酮的抗炎作用[J].沈阳药科大学学报,1999,16(2):47.
[28] 杨维娜,任淑婷,成少利,等.Nephrin?TGF-β1和WT1在阿霉素肾病模型肾小球中的表达及意义[J].西安交通大学学报:医学版,2010,31(2):172-176.
[29] 田琳,李才,赵岩,等.尾加压素Ⅱ和转化生长因子β 1 在糖尿病大鼠肾脏的表达及其意义[J] .吉林大学学报:医学版, 2007,33(4):607-611. |
.jpg)
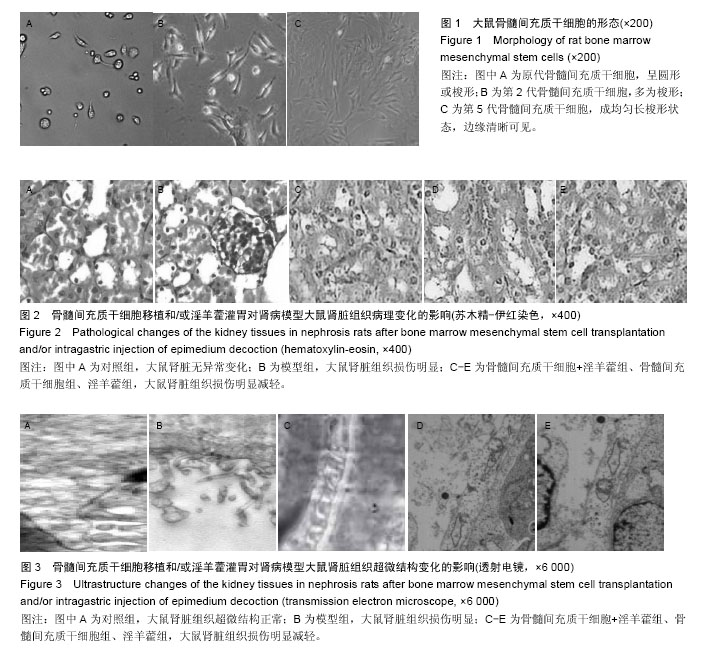
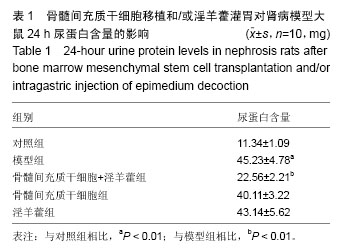
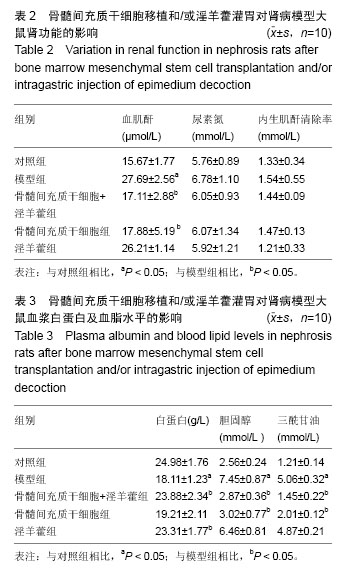
.jpg)
.jpg)