| [1] 仇长敬,金超,刘焕宝,等.腺病毒介导的基因治疗在胃癌中的研究进展[J].中国现代医药杂志, 2014,16(12): 106-109.
[2] Kwee RM, Kwee TC. Role of imaging in predicting response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(7):1650- 1656.
[3] Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;358(1):36-46.
[4] Hamburger AW, Salmon SE. Primary bioassay of human tumor stem cells. Science. 1977;197(4302): 461-463.
[5] Kreso A, Dick JE. Evolution of the cancer stem cell model. Cell Stem Cell. 2014;14(3):275-291.
[6] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Wang TC. Gastric cancer stem cells. J Clin Oncol. 2008;26(17):2876-2882.
[7] Zieker D, Bühler S, Ustündag Z, et al. Induction of tumor stem cell differentiation--novel strategy to overcome therapy resistance in gastric cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2013;398(4):603-608.
[8] Boyanapalli SS, Tony Kong AN. "Curcumin, the King of Spices": Epigenetic Regulatory Mechanisms in the Prevention of Cancer, Neurological, and Inflammatory Diseases. Curr Pharmacol Rep. 2015; 1(2):129-139.
[9] Prasad S, Gupta SC, Tyagi AK, et al. Curcumin, a component of golden spice: from bedside to bench and back. Biotechnol Adv. 2014;32(6):1053-1064.
[10] Kuttan R, Bhanumathy P, Nirmala K, et al. Potential anticancer activity of turmeric (Curcuma longa). Cancer Lett. 1985;29(2):197-202.
[11] Limtrakul P, Lipigorngoson S, Namwong O, et al. Inhibitory effect of dietary curcumin on skin carcinogenesis in mice. Cancer Lett. 1997;116(2): 197-203.
[12] Li Y, Zhang T. Targeting cancer stem cells by curcumin and clinical applications. Cancer Lett. 2014;346(2): 197-205.
[13] Ramasamy TS, Ayob AZ, Myint HH, et al. Targeting colorectal cancer stem cells using curcumin and curcumin analogues: insights into the mechanism of the therapeutic efficacy. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15:96.
[14] Mukherjee S, Mazumdar M, Chakraborty S, et al. Curcumin inhibits breast cancer stem cell migration by amplifying the E-cadherin/β-catenin negative feedback loop. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(5):116.
[15] Polivka J Jr, Janku F. Molecular targets for cancer therapy in the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Pharmacol Ther. 2014;142(2):164-175.
[16] Guo Y, Du J, Kwiatkowski DJ. Molecular dissection of AKT activation in lung cancer cell lines. Mol Cancer Res. 2013;11(3):282-293.
[17] Bergamaschi A,Madakerdogan Z,Lu H,et al. FOXM1-dependent gene expression program controls cancer stem cell and metastasis properties of breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2014; 73(3 Supplement): C85.
[18] Ning YX, Li QX, Ren KQ, et al. 7-difluoromethoxyl- 5,4'-di-n-octyl genistein inhibits ovarian cancer stem cell characteristics through the downregulation of FOXM1. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(1):295-300.
[19] Joshi K, Kim S, Lee J, et al. The MELK/FOXM1 axis is a master regulator of proneural to mesenchymal transition (PMT) in glioma stem cells by controlling EZH2 transcriptional activity. Cancer Res. 2014; 74(19 Supplement):3039.
[20] Yung MM, Chan DW, Liu VW, et al. Activation of AMPK inhibits cervical cancer cell growth through AKT/FOXO3a/FOXM1 signaling cascade. BMC Cancer. 2013;13:327.
[21] Ho C, Wang C, Mattu S, et al. AKT (v-akt murine thymoma viral oncogene homolog 1) and N-Ras (neuroblastoma ras viral oncogene homolog) coactivation in the mouse liver promotes rapid carcinogenesis by way of mTOR (mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1), FOXM1 (forkhead box M1)/SKP2, and c-Myc pathways. Hepatology. 2012; 55(3):833-845.
[22] Wang Z, Li Y, Ahmad A, et al. Down-regulation of Notch-1 is associated with Akt and FoxM1 in inducing cell growth inhibition and apoptosis in prostate cancer cells. J Cell Biochem. 2011;112(1):78-88.
[23] Lee AS, Tang C, Rao MS, et al. Tumorigenicity as a clinical hurdle for pluripotent stem cell therapies. Nat Med. 2013;19(8):998-1004.
[24] Serakinci N, Fahrioglu U, Christensen R. Mesenchymal stem cells, cancer challenges and new directions. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(8):1522-1530.
[25] Tirino V, Desiderio V, Paino F, et al. Cancer stem cells in solid tumors: an overview and new approaches for their isolation and characterization. FASEB J. 2013;27(1):13-24.
[26] Takaishi S, Okumura T, Tu S, et al. Identification of gastric cancer stem cells using the cell surface marker CD44. Stem Cells. 2009;27(5):1006-1020.
[27] Xue Z, Yan H, Li J, et al. Identification of cancer stem cells in vincristine preconditioned SGC7901 gastric cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem. 2012;113(1):302-312.
[28] Gupta SC, Patchva S, Aggarwal BB. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J. 2013;15(1):195-218.
[29] Park W, Amin AR, Chen ZG, et al. New perspectives of curcumin in cancer prevention. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2013;6(5):387-400.
[30] Cai XZ, Wang J, Li XD, et al. Curcumin suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells by downregulation of PAK1 activity and cyclin D1 expression. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009;8(14):1360-1368.
[31] Yu LL, Wu JG, Dai N, et al. Curcumin reverses chemoresistance of human gastric cancer cells by downregulating the NF-κB transcription factor. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(5):1197-1203.
[32] Norris L, Karmokar A, Howells L, et al. The role of cancer stem cells in the anti-carcinogenicity of curcumin. Mol Nutr Food Res. 2013;57(9):1630-1637.
[33] 刘尧,刘月平,王小玲,等.PI3K/AKT 通路与肿瘤的研究进展[J].食管外科电子杂志, 2014,2(3): 109-113.
[34] Madden J, Chien J. Evidence for modulation of FoxM1 by p21 in ovarian cancer. Cancer Research. 2015; 75 (15 Supplement): 1992.
[35] Tan X, Fu Y, Chen L, et al.miR-671-5p promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition by downregulating FOXM1 expression in breast cancer. Cancer Research. 2015; 75(15 Supplement): 3062.
[36] Li Z, Jia Z, Gao Y, et al. Activation of vitamin D receptor signaling downregulates the expression of nuclear FOXM1 protein and suppresses pancreatic cancer cell stemness. Clin Cancer Res. 2015;21(4):844-853. |
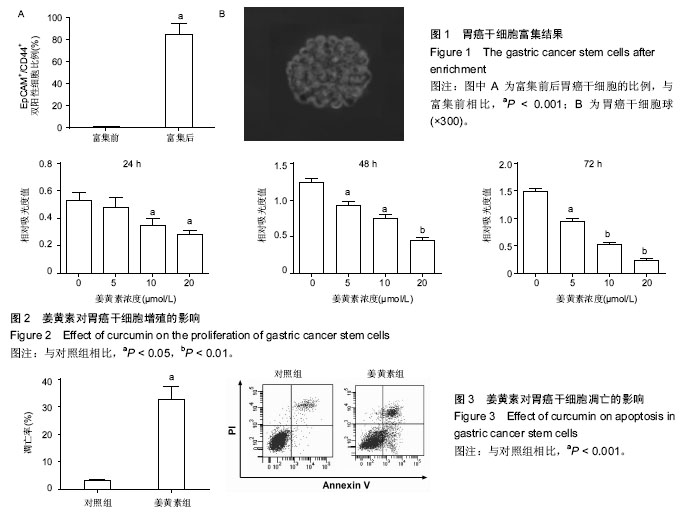
.jpg)
.jpg)
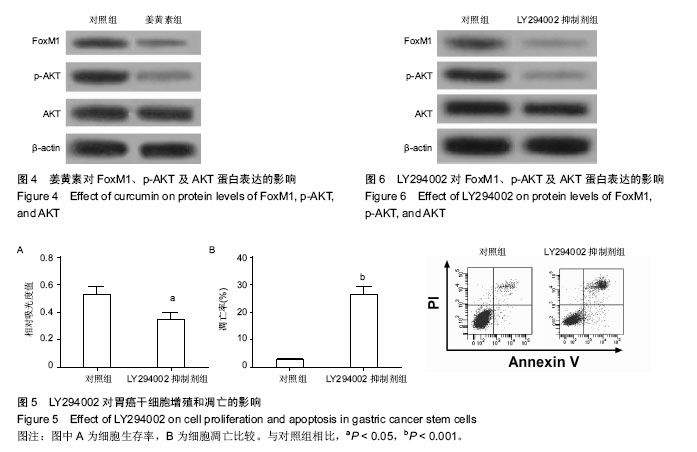
.jpg)