| [1] Go AS, Mozaffarian D, Roger VL, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics--2013 update: a report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2013;127(1): e6-e245.
[2] Rohde LE, Bertoldi EG, Goldraich L, et al. Cost-effectiveness of heart failure therapies. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2013;10(6):338-354.
[3] Heidenreich PA, Trogdon JG, Khavjou OA, et al. Forecasting the future of cardiovascular disease in the United States: a policy statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2011;123(8):933-944.
[4] Braunschweig F, Cowie MR, Auricchio A. What are the costs of heart failure. Europace. 2011;13 Suppl 2:ii13-17.
[5] Clifford DM, Fisher SA, Brunskill SJ, et al. Stem cell treatment for acute myocardial infarction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2012;2:CD006536.
[6] Wollert KC, Drexler H. Cell therapy for the treatment of coronary heart disease: a critical appraisal. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2010;7(4):204-215.
[7] Rehman J. Bone marrow tinctures for cardiovascular disease: lost in translation. Circulation. 2013;127(19): 1935-1937.
[8] Strauer BE, Steinhoff G. 10 years of intracoronary and intramyocardial bone marrow stem cell therapy of the heart: from the methodological origin to clinical practice. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2011;58(11):1095-1104.
[9] Traverse JH, Henry TD, Pepine CJ, et al. Effect of the use and timing of bone marrow mononuclear cell delivery on left ventricular function after acute myocardial infarction: the TIME randomized trial. JAMA. 2012;308(22):2380-2389.
[10] Perin EC, Willerson JT, Pepine CJ, et al. Effect of transendocardial delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells on functional capacity, left ventricular function, and perfusion in chronic heart failure: the FOCUS-CCTRN trial. JAMA. 2012;307(16): 1717-1726.
[11] Traverse JH, Henry TD, Ellis SG, et al. Effect of intracoronary delivery of autologous bone marrow mononuclear cells 2 to 3 weeks following acute myocardial infarction on left ventricular function: the LateTIME randomized trial. JAMA. 2011;306(19): 2110-2119.
[12] 郝牧,漆佩静,李刚,等.人脐带间充质干细胞对脐血CD34+细胞在NOD/SCID小鼠体内造血重建的影响[J].中国医学科学院学报,2010,32(1):71-75.
[13] 车京津,张承宗,陈元禄,等.缬沙坦、苯那普利及合用时对心肌梗死后心室重构影响的比较[J].中国心血管杂志, 2002,7(6):381-384.
[14] 张军霞,李瑞,赵鹏,等.CD133免疫磁珠分选肪血内皮祖细胞的培养及鉴定[J].中国肿瘤生物治疗杂志,2008, 15(2):159-162.
[15] 中华医学会心血管病学分会,中华心血管病杂志编辑委员会.中国心力衰竭诊断和治疗指南2014 [J].中华心血管病杂志,2014,42(2):98-122.
[16] Ferrario CM, Schiffrin EL. Role of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in cardiovascular disease. Circ Res. 2015;116(1):206-213.
[17] Kim HY, Bae EH, Ma SK, et al. Effects of spironolactone in combination with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors or Angiotensin receptor blockers in patients with proteinuria. Kidney Blood Press Res. 2014;39(6): 573-580.
[18] Zannad F, McMurray JJ, Krum H, et al. Eplerenone in patients with systolic heart failure and mild symptoms. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(1):11-21.
[19] Bisping E, Wakula P, Poteser M, et al. Targeting cardiac hypertrophy: toward a causal heart failure therapy. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2014;64(4):293-305.
[20] Tendera M, Talajic M, Robertson M, et al. Safety of ivabradine in patients with coronary artery disease and left ventricular systolic dysfunction (from the BEAUTIFUL Holter Substudy). Am J Cardiol. 2011; 107(6):805-811.
[21] Swedberg K, Komajda M, Böhm M, et al. Effects on outcomes of heart rate reduction by ivabradine in patients with congestive heart failure: is there an influence of beta-blocker dose?: findings from the SHIFT (Systolic Heart failure treatment with the I(f) inhibitor ivabradine Trial) study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2012;59(22):1938-1945.
[22] 崔炜.2012欧洲心脏病学会心力衰竭指南更新要点[J].中国心血管杂志,2012,17(5): 324-326.
[23] Shaffer JA, Thompson JL, Cheng B, et al. Association of quality of life with anticoagulant control in patients with heart failure: the Warfarin and Aspirin in Reduced Cardiac Ejection Fraction (WARCEF) trial. Int J Cardiol. 2014;177(2):715-717.
[24] McMurray J, Packer M, Desai A, et al. A putative placebo analysis of the effects of LCZ696 on clinical outcomes in heart failure. Eur Heart J. 2015;36(7): 434-439.
[25] 张艳,杨辉,冯志强.益气活血中药对慢性心力衰竭临床疗效及预后分析研究[J].辽宁中医杂志,2014,41(2):193-195.
[26] 张治祥,马宏秀,张康.芪黄颗粒治疗慢性心力衰竭60例[J].陕西中医,2014,35(10):1377-1379.
[27] 赵瑞刚,蔡俊彦,王军力.N端脑钠肽在心力衰竭诊治中的应用进展[J].河北医药,2013,35(2):268-270.
[28] 魏艳静.血浆NT-proBNP 水平对慢性心力衰竭患者的临床诊断意义[J].中国医药指南,2013,11(1):559-560.
[29] 黄佩花.难治性心力衰竭临床治疗进展研究[J].中国美容医学,2012,21(8):387-388.
[30] 魏瑾.干细胞移植有望治疗扩张型心肌病[J].临床心血管病杂志,2013,29(2):81-82.
[31] Zimmet H, Porapakkham P, Porapakkham P, et al. Short- and long-term outcomes of intracoronary and endogenously mobilized bone marrow stem cells in the treatment of ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a meta-analysis of randomized control trials. Eur J Heart Fail. 2012;14(1):91-105.
[32] Moccetti T, Sürder D, Klersy C, et al. Sustained improvement in left ventricular function after bone marrow derived cell therapy in patients with acute ST elevation myocardial infarction. A 5-year follow-up from the Stem Cell Transplantation in Ischaemic Myocardium Study. Swiss Med Wkly. 2012;142: w13632.
[33] 任晓庆,浦介麟,张澍,等.自体骨髓间叶干细胞诱导分化移植重建窦房结起搏功能的实验研究[J].中国循环杂志, 2004,19(6):462-465.
[34] Huang XP, Sun Z, Miyagi Y, et al. Differentiation of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells induces immunogenicity and limits their long-term benefits for myocardial repair. Circulation. 2010;122(23): 2419-2429.
[35] Hirsch A, Nijveldt R, van der Vleuten PA, et al. Intracoronary infusion of mononuclear cells from bone marrow or peripheral blood compared with standard therapy in patients after acute myocardial infarction treated by primary percutaneous coronary intervention: results of the randomized controlled HEBE trial. Eur Heart J. 2011;32(14):1736-1747.
[36] 邱小华,戴育成,胡葵葵.脐带间充质干细胞的研究进展[J].中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2012, 6(6):1494-1497.
[37] Ye L, Zhang S, Greder L, et al. Effective cardiac myocyte differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cells requires VEGF. PLoS One. 2013;8(1): e53764.
[38] Perin EC, Willerson JT. CD34+ autologous human stem cells in treating refractory angina. Circ Res. 2011;109(4):351-352.
[39] Losordo DW, Henry TD, Davidson C, et al. Intramyocardial, autologous CD34+ cell therapy for refractory angina. Circ Res. 2011;109(4):428-436.
[40] Irollo E, Pirozzi G. CD133: to be or not to be, is this the real question. Am J Transl Res. 2013;5(6):563-581.
[41] Donovan LK, Pilkington GJ. CD133: holy of grail of neuro-oncology or promiscuous red-herring. Cell Prolif. 2012;45(6):527-537.
[42] Ma N, Ladilov Y, Moebius JM, et al. Intramyocardial delivery of human CD133+ cells in a SCID mouse cryoinjury model: Bone marrow vs. cord blood-derived cells. Cardiovasc Res. 2006;71(1):158-169. |
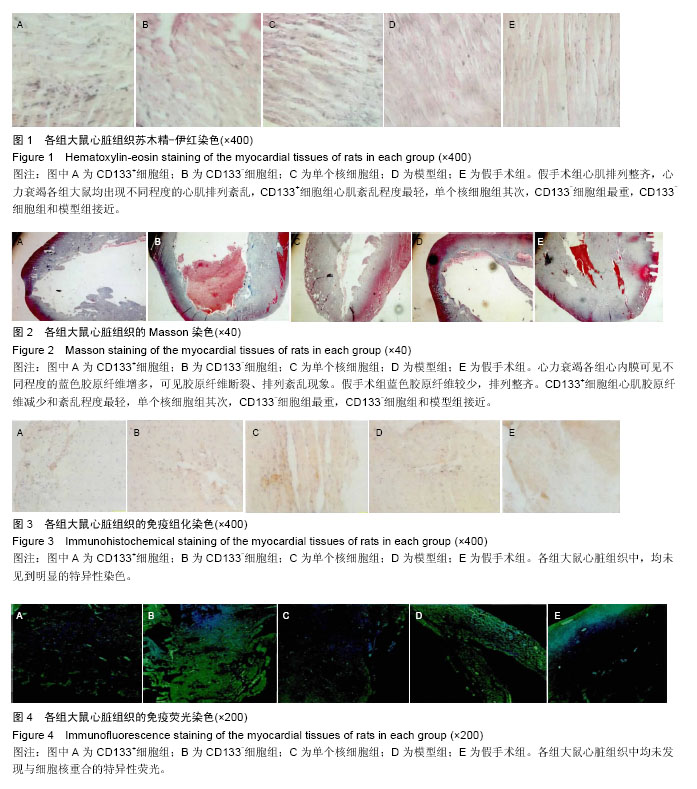
.jpg)
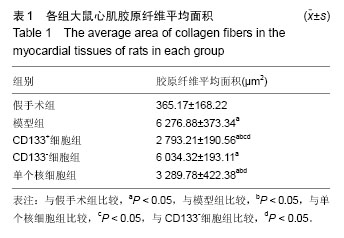
.jpg)