| [1] Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997; 276(5309): 71-74.
[2] Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[3] Scott MA, Nguyen VT, Levi B, et al. Current methods of adipogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2011;20(10):1793-1804.
[4] Saben J, Thakali KM, Lindsey FE, et al. Distinct adipogenic differentiation phenotypes of human umbilical cord mesenchymal cells dependent on adipogenic conditions. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2014; 239(10):1340-1351.
[5] Ninomiya Y, Sugahara-Yamashita Y, Nakachi Y, et al. Development of a rapid culture method to induce adipocyte differentiation of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010;394(2):303308.
[6] James AW. Review of Signaling Pathways Governing MSC Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation. Scientifica (Cairo). 2013;2013:684736.
[7] Pei L, Tontonoz P. Fat's loss is bone's gain. J Clin Invest. 2004;113(6):805-806.
[8] Amable PR, Teixeira MV, Carias RB, et al. Gene expression and protein secretion during human mesenchymal cell differentiation into adipogenic cells. BMC Cell Biol. 2014;15:46.
[9] Dragojevi? J, Logar DB, Komadina R,et al. Osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis are higher in osteoarthritic than in osteoporotic bone tissue. Arch Med Res. 2011;42(5):392-397.
[10] Hoshiba T, Kawazoe N, Chen G. The balance of osteogenic and adipogenic differentiation in human mesenchymal stem cells by matrices that mimic stepwise tissue development. Biomaterials. 2012; 33(7):2025-2031.
[11] Li J, Yang S, Lu S, et al. Differential gene expression profile associated with the abnormality of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in aplastic anemia. PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e47764.
[12] Janderová L, McNeil M, Murrell AN, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cells as an in vitro model for human adipogenesis. Obes Res. 2003;11(1):65-74.
[13] Knight DM, Chapman AB, Navre M, et al. Requirements for triggering of adipocyte differentiation by glucocorticoids and indomethacin. Mol Endocrinol. 1987;1(1):36-43.
[14] Styner M, Sen B, Xie Z, et al. Indomethacin promotes adipogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through a cyclooxygenase independent mechanism. J Cell Biochem. 2010;111(4):1042-1050.
[15] Park BH, Qiang L, Farmer SR. Phosphorylation of C/EBPbeta at a consensus extracellular signal-regulated kinase/glycogen synthase kinase 3 site is required for the induction of adiponectin gene expression during the differentiation of mouse fibroblasts into adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 2004; 24(19): 8671-8680.
[16] Tang QQ, Lane MD. Adipogenesis: from stem cell to adipocyte. Annu Rev Biochem. 2012;81:715-736.
[17] Cristancho AG, Lazar MA. Forming functional fat: a growing understanding of adipocyte differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2011;12(11):722-734.
[18] Chen Q, Shou P, Zheng C,Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts. Cell Death Differ. 2016 Feb 12. [Epub ahead of print]
[19] Lehmann JM, Moore LB, Smith-Oliver TA, et al. An antidiabetic thiazolidinedione is a high affinity ligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPAR gamma). J Biol Chem. 1995;270(22):12953- 12956.
[20] Wang L, Waltenberger B, Pferschy-Wenzig EM, et al. Natural product agonists of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ): a review. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014;92(1):73-89.
[21] Benvenuti S, Cellai I, Luciani P, et al. Rosiglitazone stimulates adipogenesis and decreases osteoblastogenesis in human mesenchymal stem cells. J Endocrinol Invest. 2007;30(9):RC26-30.
[22] Contador D, Ezquer F, Espinosa M, et al. Dexamethasone and rosiglitazone are sufficient and necessary for producing functional adipocytes from mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2015;240(9):1235-1246.
[23] Choi JH, Banks AS, Estall JL, et al. Anti-diabetic drugs inhibit obesity-linked phosphorylation of PPARgamma by Cdk5. Nature. 20102;466(7305):451-456.
[24] Spiegelman BM. PPAR-gamma: adipogenic regulator and thiazolidinedione receptor. Diabetes. 1998;47(4): 507-514.
[25] Chaldakov GN, Stankulov IS, Hristova M, et al. Adipobiology of disease: adipokines and adipokine-targeted pharmacology. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9(12):1023-1031.
[26] Ronti T, Lupattelli G, Mannarino E. The endocrine function of adipose tissue: an update. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf). 2006;64(4):355-365.
[27] Farmer SR. Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab. 2006;4(4):263-273.
[28] Gesta S, Blüher M, Yamamoto Y, et al. Evidence for a role of developmental genes in the origin of obesity and body fat distribution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(17):6676-6681.
[29] Takada I, Kouzmenko AP, Kato S. Wnt and PPARgamma signaling in osteoblastogenesis and adipogenesis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2009;5(8):442-447.
[30] Kawai M, Mushiake S, Bessho K, et al. Wnt/Lrp/beta-catenin signaling suppresses adipogenesis by inhibiting mutual activation of PPARgamma and C/EBPalpha. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2007;363(2):276-282. |
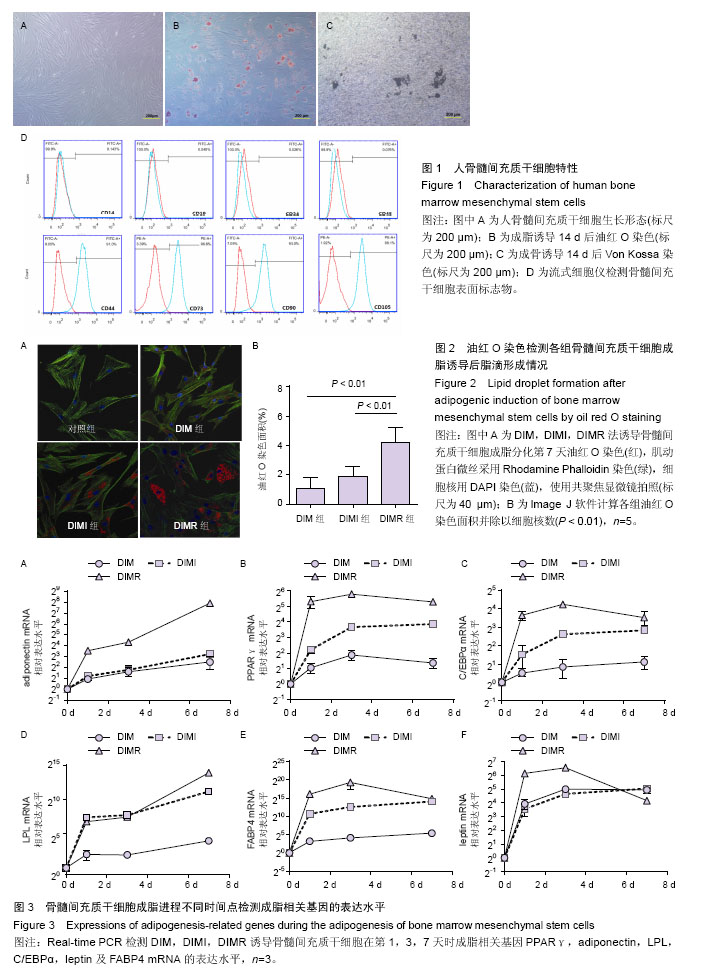
.jpg)
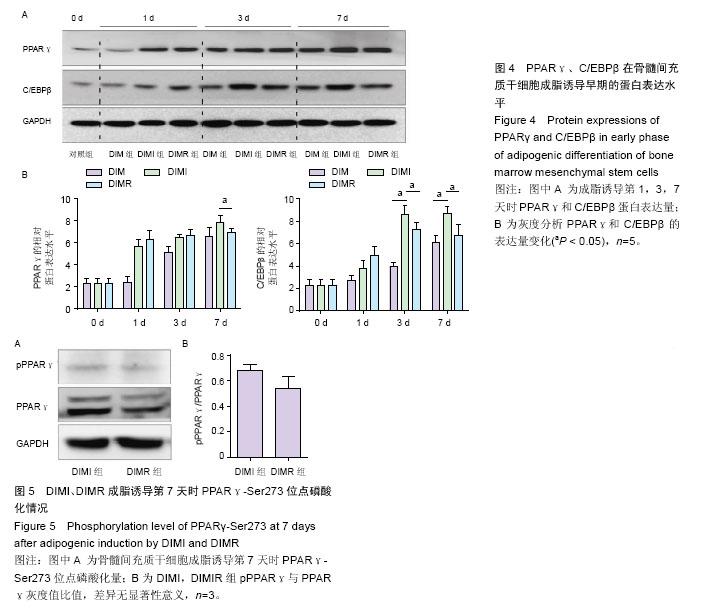
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)