| [1] Lortet-Tieulent J, Soerjomataram I, Ferlay J, et al. International trends in lung cancer incidence by histological subtype: adenocarcinoma stabilizing in men but still increasing in women. Lung Cancer. 2014; 84(1):13-22.
[2] Shaw AT, Kim DW, Mehra R, et al. Ceritinib in ALK-rearranged non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(13):1189-1197.
[3] Reya T, Morrison SJ, Clarke MF, et al. Stem cells, cancer, and cancer stem cells.Nature. 2001;414(6859): 105-111.
[4] Eramo A, Lotti F, Sette G, et al. Identification and expansion of the tumorigenic lung cancer stem cell population. Cell Death Differ. 2008;15(3):504-514.
[5] Kim HS, Lee KS, Bae HJ, et al. MicroRNA-31 functions as a tumor suppressor by regulating cell cycle and epithelial-mesenchymal transition regulatory proteins in liver cancer. Oncotarget. 2015;6(10):8089-8102.
[6] Christensen LL, Holm A, Rantala J, et al. Functional screening identifies miRNAs influencing apoptosis and proliferation in colorectal cancer. PLoS One. 2014; 9(6):e96767.
[7] Lei SL, Zhao H, Yao HL, et al. Regulatory roles of microRNA-708 and microRNA-31 in proliferation, apoptosis and invasion of colorectal cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 2014;8(4):1768-1774.
[8] Lin S, Gregory RI. MicroRNA biogenesis pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2015;15(6):321-333.
[9] Hermeking H. The miR-34 family in cancer and apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 2010;17(2):193-199.
[10] Rokavec M, Öner MG, Li H, et al. IL-6R/STAT3/ miR-34a feedback loop promotes EMT-mediated colorectal cancer invasion and metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124(4):1853-1867.
[11] Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, et al. The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med. 2011;17(2): 211-215.
[12] Bu P, Chen KY, Chen JH, et al. A microRNA miR-34a-regulated bimodal switch targets Notch in colon cancer stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12(5):602-615.
[13] Ji Q, Hao X, Zhang M, et al. MicroRNA miR-34 inhibits human pancreatic cancer tumor-initiating cells. PLoS One. 2009;4(8):e6816.
[14] Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, et al. MicroRNA-34a suppresses the breast cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1 pathway. Cancer Sci. 2015; 106(6): 700-708.
[15] Chen C, Bai LP, Cao FQ, et al. Lin28B mediated IKK-β sustains the stemness of breast cancer stem cell via regulating Wnt/TCF4 and miR-34a/LEF1 signaling pathway. Cancer Res. 2014;74: 3046.
[16] 赵欣.载microRNA-34a脂质体靶向治疗肺癌干细胞靶的研究[J].中国生化药物杂志,2014,35(1):68-71.
[17] Bjornson CR, Cheung TH, Liu L, et al. Notch signaling is necessary to maintain quiescence in adult muscle stem cells. Stem Cells. 2012;30(2):232-242.
[18] Tatarek J, Cullion K, Ashworth T, et al. Notch1 inhibition targets the leukemia-initiating cells in a Tal1/Lmo2 mouse model of T-ALL Blood. 2011;118(6): 1579-1590.
[19] Suman S, Das TP, Damodaran C. Silencing NOTCH signaling causes growth arrest in both breast cancer stem cells and breast cancer cells. Br J Cancer. 2013; 109(10):2587-2596.
[20] Liu C, Li Z, Bi L, et al. NOTCH1 signaling promotes chemoresistance via regulating ABCC1 expression in prostate cancer stem cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 2014; 393(1-2):265-270.
[21] Sullivan JP, Spinola M, Dodge M, et al. Aldehyde dehydrogenase activity selects for lung adenocarcinoma stem cells dependent on notch signaling. Cancer Res. 2010;70(23):9937-9948.
[22] Hassan KA, Wang L, Korkaya H, et al. Notch pathway activity identifies cells with cancer stem cell-like properties and correlates with worse survival in lung adenocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(8): 1972-1980.
[23] Kashat M, Azzouz L, Sarkar SH, et al. Inactivation of AR and Notch-1 signaling by miR-34a attenuates prostate cancer aggressiveness. Am J Transl Res. 2012;4(4):432-442.
[24] Schwitalla S, Fingerle AA, Cammareri P, et al. Intestinal tumorigenesis initiated by dedifferentiation and acquisition of stem-cell-like properties. Cell. 2013;152(1-2):25-38.
[25] Wang P, Gao Q, Suo Z, et al. Identification and characterization of cells with cancer stem cell properties in human primary lung cancer cell lines. PLoS One. 2013;8(3):e57020.
[26] Ponti D, Zaffaroni N, Capelli C, et al. Breast cancer stem cells: an overview. Eur J Cancer. 2006;42(9):1219-1224.
[27] Tirino V, Camerlingo R, Franco R, et al. The role of CD133 in the identification and characterisation of tumour-initiating cells in non-small-cell lung cancer. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2009;36(3):446-453.
[28] Mizugaki H, Sakakibara-Konishi J, Kikuchi J, et al. CD133 expression: a potential prognostic marker for non-small cell lung cancers. Int J Clin Oncol. 2014; 19(2):254-259.
[29] Ha M, Kim VN. Regulation of microRNA biogenesis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15(8):509-524.
[30] Spies N, Burge CB, Bartel DP. 3' UTR-isoform choice has limited influence on the stability and translational efficiency of most mRNAs in mouse fibroblasts. Genome Res. 2013;23(12):2078-2090.
[31] Calin GA, Dumitru CD, Shimizu M, et al. Frequent deletions and down-regulation of micro- RNA genes miR15 and miR16 at 13q14 in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99(24): 15524-15529.
[32] Cuk K, Zucknick M, Heil J, et al. Circulating microRNAs in plasma as early detection markers for breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 2013;132(7):1602-1612.
[33] Rane JK, Scaravilli M, Ylipää A, et al. MicroRNA expression profile of primary prostate cancer stem cells as a source of biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Eur Urol. 2015;67(1):7-10.
[34] Xua D, Lia S, Zhanga M, et al. microRNAs act as potential regulators in apoptosis and senescence against carcinogenicity induced by environmental pollutants. Critical Reviews in Environmental Science and Technology. 2015; 45(4): 319-335.
[35] Li N, Fu H, Tie Y, et al. miR-34a inhibits migration and invasion by down-regulation of c-Met expression in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Lett. 2009;275(1):44-53.
[36] Yamakuchi M, Ferlito M, Lowenstein CJ. miR-34a repression of SIRT1 regulates apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105(36):13421-13426.
[37] Nalls D, Tang SN, Rodova M, et al. Targeting epigenetic regulation of miR-34a for treatment of pancreatic cancer by inhibition of pancreatic cancer stem cells. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e24099.
[38] Guessous F, Zhang Y, Kofman A, et al. microRNA-34a is tumor suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2010;9(6):1031-1036.
[39] Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, et al. Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer cells. Cancer Res. 2001;61(7):3200-3205.
[40] Kang J, Kim E, Kim W, et al. Rhamnetin and cirsiliol induce radiosensitization and inhibition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) by miR-34a-mediated suppression of Notch-1 expression in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines. J Biol Chem. 2013;288(38):27343-27357. |
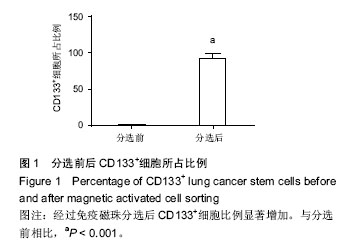
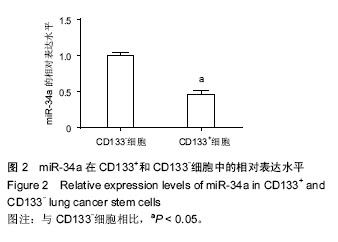
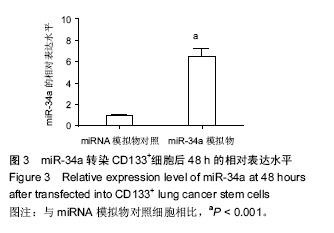
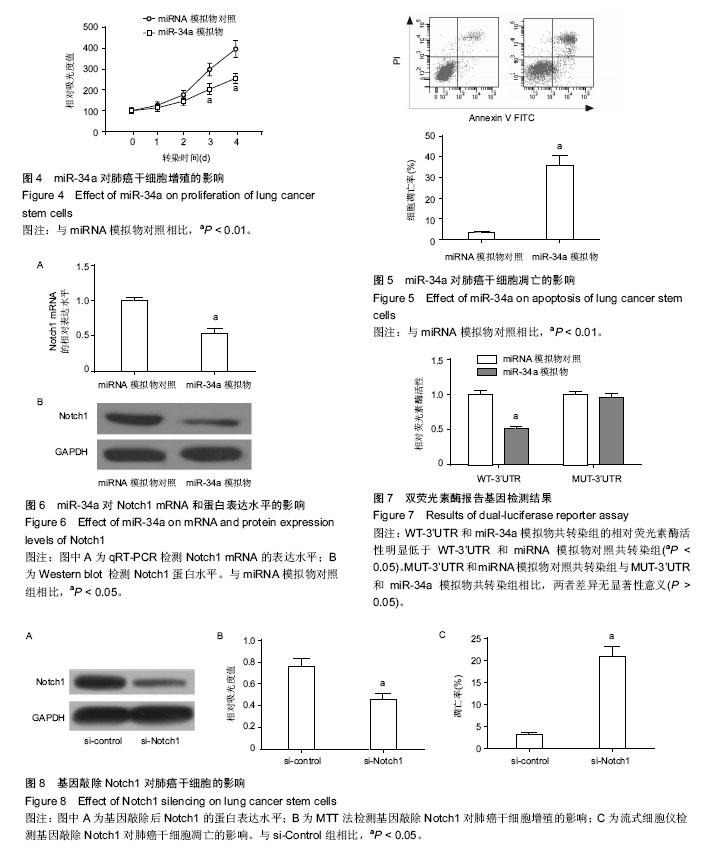
.jpg)
.jpg)