| [1] Heppner FL,Ransohoff RM,Becher B.Immune attack: the role of inflammation in Alzheimer disease.Nat Rev Neurosci.2015;16(6):358-372.[2] Kim JA,Ha S,Shin KY,et al.Neural stem cell transplantation at critical period improves learning and memory through restoring synaptic impairment in Alzheimer's disease mouse model.Cell Death Dis. 2015;6:e1789.[3] Li XY,Bao XJ,Wang RZ. Potential of neural stem cell-based therapies for Alzheimer's disease.J Neurosci Res. 2015;93(9):1313-1324.[4] Weninger SC,Yankner BA.Inflammation and Alzheimer disease: the good, the bad, and the ugly.Nat Med.2001; 7(5):527-528.[5] Wyss-Coray T,Mucke L.Ibuprofen, inflammation and Alzheimer disease. Nat Med.2000; 6(9):973-934.[6] Shepherd CE,Thiel E,McCann H,et al.Cortical inflammation in Alzheimer disease but not dementia with Lewy bodies. Arch Neurol.2000;57(6):817-822.[7] Roses AD.Causes or consequences of inflammation and pathological signs of Alzheimer disease.Neurobiol Aging.2000;21(3):423-425.[8] 赵保胜,徐暾海.老年性痴呆疾病模型的建立[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(6):274-276.[9] Zhang W,Wang PJ,Sha HY,et al.Neural stem cell transplants improve cognitive function without altering amyloid pathology in an APP/PS1 double transgenic model of Alzheimer's disease.Mol Neurobiol.2014; 50(2):423-437.[10] Zhang W,Gu GJ,Shen X,et al.Neural stem cell transplantation enhances mitochondrial biogenesis in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease-like pathology.Neurobiol Aging.2015;36(3):1282-1292.[11] 李胜修,舒斯云,包新民 等.海人藻酸损毁纹状体边缘区后对大鼠学习和记忆功能影响的研究[J].神经解剖学杂志,1996,12(1):37-41.[12] Kolarik BS,Shahlaie K,Hassan A,et al.Impairments in precision, rather than spatial strategy, characterize performance on the virtual Morris Water Maze: A case study. Neuropsychologia.2015;80:90-101.[13] Hernández-Pérez JJ,Gutiérrez-Guzmán BE,López-Vázquez MÁ,et al.Supramammillary serotonin reduction alters place learning and concomitant hippocampal, septal, and supramammillar theta activity in a Morris water maze.Front Pharmacol. 2015;6: 250.[14] Singh S,Kaur H,Sandhir R.Fractal dimensions: A new paradigm to assess spatial memory and learning using Morris water maze.Behav Brain Res.2016;299:141- 146.[15] Blurton-Jones M,Spencer B,Michael S,et al.Neural stem cells genetically-modified to express neprilysin reduce pathology in Alzheimer transgenic models. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(2):46.[16] 谷海刚,龙大宏,李晓滨,等.神经干细胞移植对老年痴呆模型鼠基底前脑小白蛋白阳性神经元和学习记忆能力的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12): 2235-2239.[17] 谷海刚.神经干细胞移植治疗老年性痴呆的实验研究[D].广州医学院,2004.[18] Tang JX, Baranov D, Hammond M, et al. Human Alzheimer and inflammation biomarkers after anesthesia and surgery. Anesthesiology. 2011; 115(4):727-732.[19] Candore G,Bulati M,Caruso C,et al.Inflammation, cytokines,immune response, apolipoprotein E, cholesterol, and oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: therapeutic implications.Rejuvenation Res.2010; 13(2-3):301-313.[20] McGeer PL,Rogers J,McGeer EG.Inflammation, anti-inflammatory agents and Alzheimer disease: the last 12 years.J Alzheimers Dis.2006;9(3 Suppl): 271-276.[21] Ager RR,Davis JL,Agazaryan A,et al.Human neural stem cells improve cognition and promote synaptic growth in two complementary transgenic models of Alzheimer's disease and neuronal loss.Hippocampus. 2015;25(7):813-826.[22] Dawkins E,Small DH.Insights into the physiological function of the beta-amyloid precursor protein: beyond Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem.2014;129(5): 756-769.[23] Samanta MK,Wilson B,Santhi K,et al.Alzheimer disease and its management: a review. Am J Ther. 2006;13(6):516-526.[24] 高平,孙占胜,王伯珉,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导成神经元样细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤[J].中国组织工程研究,2013, 17(23):4256-4263.[25] 禤璇,戎志斌,刘纯,等.柴胡疏肝散对肝郁型老年性痴呆大鼠模型行为学及海马单胺神经递质的影响[J].深圳中西医结合杂志,2013,23(3):129-134.[26] 戴立彬,吴金娟,刘涛.炎症反应参与老年痴呆病的研究近况[J].中医学报,2013,28(3):425-427.[27] Gallagher M,Burwell R,Burchinal M.Severity of spatial learning impairment in aging: Development of a learning index for performance in the Morris water maze. Behav Neurosci. 2015;129(4):540-548.[28] Gehring TV,Luksys G,Sandi C,et al.Detailed classification of swimming paths in the Morris Water Maze: multiple strategies within one trial.Sci Rep. 2015;5:14562.[29] 王闯.磷酸二酯酶-4及其亚型对β-淀粉样蛋白诱导的认知障碍及神经炎症的调节作用[D]. 南方医科大学,2011: 230.[30] McGeer PL,McGeer EG.Inflammation, autotoxicity and Alzheimer disease.Neurobiol Aging.2001;22(6): 799-809.[31] Rockenstein E,Desplats P,Ubhi K,et al.Neuro-peptide treatment with Cerebrolysin improves the survival of neural stem cell grafts in an APP transgenic model of Alzheimer disease.Stem Cell Res.2015;15(1):54-67.[32] Zhang Q,Wu HH,Wang Y,et al.Neural stem cell transplantation decreases neuroinflammation in a transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.J Neurochem.2015. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13413. [Epub ahead of print][33] Lilja AM,Malmsten L,Röjdner J,et al.Neural Stem Cell Transplant-Induced Effect on Neurogenesis and Cognition in Alzheimer Tg2576 Mice Is Inhibited by Concomitant Treatment with Amyloid-Lowering or Cholinergic alpha7 Nicotinic Receptor Drugs. Neural Plast.2015; 2015:370432. |
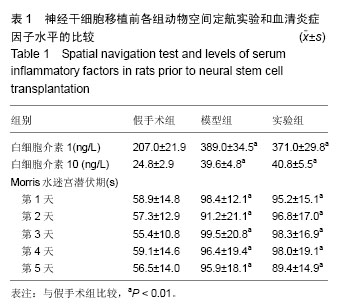
.jpg)
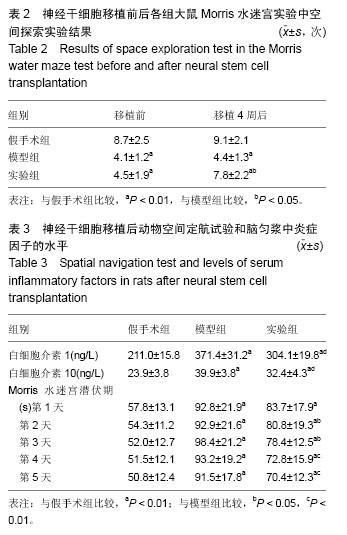
.jpg)
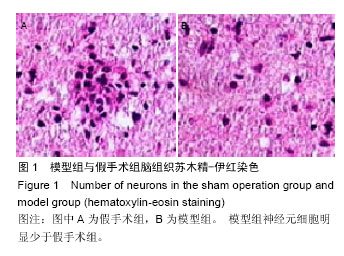
.jpg)