| [1] Oki S, Matsuda Y, Itoh T, et al. Scanning electron microscopic observations of the vascular structure of vertebral end-plates in rabbits. J Orthop Res. 1994; 12(3): 447-449. [2] 朱宗波,康建平,吴韬韬,等.A型胸腰段骨折椎体邻近椎间盘在磁共振T2加权像上的影像学特点[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2011,(11):900-904. [3] Oner FC, van der Rijt RR, Ramos LM, et al. Changes in the disc space after fractures of the thoracolumbar spine. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1998;80(5):833-839. [4] Sander AL, Laurer H, Lehnert T, et al. A clinically useful classification of traumatic intervertebral disk lesions. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2013;200(3):618-623. [5] 尚琦松,吴兵,盛文辉,等.椎间盘损伤程度对胸腰椎骨折术后疗效的影响[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(6):672-675. [6] Khan KM, Bhatti A, Khan MA. Posterior spinal fixation with pedicle screws and rods system in thoracolumbar spinal fractures. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2012;22 (12): 778-782. [7] 徐宝山,唐天驷,杨惠林.经后路短节段椎弓根内固定治疗胸腰椎爆裂型骨折的远期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2002, (11):4-10. [8] 杨子明,郭昭庆,党耕町,等.胸腰椎骨折诊断与治疗热点问题高峰论坛纪要[J].中华外科杂志,2006,44(8):505-508. [9] 初同伟,刘玉刚,钱奕铭,等.经后路椎间盘椎弓根间截骨矫正胸腰段脊柱后凸畸形[J].中华创伤杂志,2011,27(6): 513-516. [10] 王存平,韩思林,朱喆,等.改良经椎弓根椎间盘截骨术治疗胸腰椎后凸畸形[J].临床骨科杂志,2015,18(6):649-651. [11] Andress HJ, Braun H, Helmberger T, et al. Long-term results after posterior fixation of thoraco-lumbar burst fractures. Injury. 2002;33(4):357-365. [12] Hrabalek L, Houdek M, Vaverka M. Contribution of MRI to the thoracolumbar spine injuries diagnostics and therapy. Rozhl Chir. 2009;88(8):461-465. [13] Martiniani M, Vanacore F, Meco L, et al. Is posterior fixation alone effective to prevent the late kyphosis after T-L fracture?.Eur Spine J. 2013;22(6):S951-S956. [14] Jun DS, Shin WJ, An BK, et al. The Relationship between the Progression of Kyphosis in Stable Thoracolumbar Fractures and Magnetic Resonance Imaging Findings. Asian Spine J. 2015;9(2):170-177. [15] Leferink VJ, Zimmerman KW, Veldhuis EF, et al. Thoracolumbar spinal fractures: radiological results of transpedicular fixation combined with transpedicular cancellous bone graft and posterior fusion in 183 patients. Eur Spine J. 2001;10(6):517-523. [16] Jeanneret B, Ho PK, Magerl F. Burst-shear flexion-distraction injuries of the lumbar spine. J Spinal Disord. 1993;6(6):473-481. [17] Shi J, Mei X, Liu J, et al. The influence of correction loss in thoracolumbar fractures treated by posterior instrumentation: a minimum 7-year follow-up. J Clin Neurosci. 2011;18(4):500-503. [18] Osti OL, Vernon-Roberts B, Moore R, et al. Annular tears and disc degeneration in the lumbar spine. A post-mortem study of 135 discs. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1992;74(5):678-682. [19] Iatridis JC, Michalek AJ, Purmessur D, et al. Localized intervertebral disc injury leads to organ level changes in structure, cellularity, and biosynthesis. Cell Mol Bioeng. 2009;2(3):437-447. [20] Osti OL, Vernon-Roberts B, Fraser RD. 1990 Volvo Award in experimental studies. Anulus tears and intervertebral disc degeneration. An experimental study using an animal model. Spine. 1990;15(8):762-767. [21] 苏兵,付解辉,葛飞,等.经后路复位固定椎间融合治疗伴重度椎间盘损伤的胸腰椎骨折脱位[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2013,28(5):451-452. [22] 周成洪,龙亨国,沈万祥,等.经后外侧植骨与椎间孔椎体间植骨融合治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折伴椎间盘损伤的疗效比较[J].中医正骨,2013,25(2):43-45. [23] 官建,沈自力.两种方法治疗胸腰椎爆裂骨折伴椎间盘损伤的疗效比较分析[J].中国医药导刊,2014,(4):607-608. [24] Kuklo TR, Polly DW, Owens BD, et al. Measurement of thoracic and lumbar fracture kyphosis: evaluation of intraobserver, interobserver, and technique variability. Spine. 2001;26(1):61-66. [25] 孙天胜,张志成.胸腰椎损伤分类及损伤程度评分系统的评估及初步应用[J].脊柱外科杂志,2007,5(6):325-329. [26] 吕游,张大明,李瑞,等.胸腰椎损伤分类及损伤程度评分在胸腰段骨折治疗中的临床意义[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2011,19(8):620-623. [27] Pfirrmann CW, Metzdorf A, Zanetti M, et al. Magnetic resonance classification of lumbar intervertebral disc degeneration. Spine. 2001;26(17):1873-1878. [28] Vornanen M, Bostman O, Keto P, et al. The integrity of intervertebral disks after operative treatment of thoracolumbar fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993; (297):150-154. |
.jpg) 文题释义:
胸腰椎骨折:传统分类及手术方法常忽视了胸腰椎骨折伴随的椎间盘损伤,椎间盘是一个重要的维持活动节段高度的成分,在胸腰椎力学成分中占有重要地位,不同形式的损伤和愈合都会对脊柱的长期稳定性产生影响。
后路椎弓根螺钉内固定:为胸腰椎骨折的标准术式,单纯后路短节段内固定手术对骨折椎临近损伤的椎间盘未予处理,保留了其活动度,可以减少了临近节段的负荷,显著减少了邻椎病的发生。
文题释义:
胸腰椎骨折:传统分类及手术方法常忽视了胸腰椎骨折伴随的椎间盘损伤,椎间盘是一个重要的维持活动节段高度的成分,在胸腰椎力学成分中占有重要地位,不同形式的损伤和愈合都会对脊柱的长期稳定性产生影响。
后路椎弓根螺钉内固定:为胸腰椎骨折的标准术式,单纯后路短节段内固定手术对骨折椎临近损伤的椎间盘未予处理,保留了其活动度,可以减少了临近节段的负荷,显著减少了邻椎病的发生。
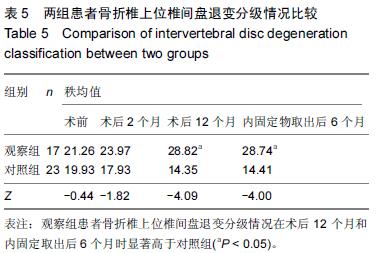
.jpg)
.jpg) 文题释义:
胸腰椎骨折:传统分类及手术方法常忽视了胸腰椎骨折伴随的椎间盘损伤,椎间盘是一个重要的维持活动节段高度的成分,在胸腰椎力学成分中占有重要地位,不同形式的损伤和愈合都会对脊柱的长期稳定性产生影响。
后路椎弓根螺钉内固定:为胸腰椎骨折的标准术式,单纯后路短节段内固定手术对骨折椎临近损伤的椎间盘未予处理,保留了其活动度,可以减少了临近节段的负荷,显著减少了邻椎病的发生。
文题释义:
胸腰椎骨折:传统分类及手术方法常忽视了胸腰椎骨折伴随的椎间盘损伤,椎间盘是一个重要的维持活动节段高度的成分,在胸腰椎力学成分中占有重要地位,不同形式的损伤和愈合都会对脊柱的长期稳定性产生影响。
后路椎弓根螺钉内固定:为胸腰椎骨折的标准术式,单纯后路短节段内固定手术对骨折椎临近损伤的椎间盘未予处理,保留了其活动度,可以减少了临近节段的负荷,显著减少了邻椎病的发生。