[2] 顾晓峰,王琼,夏仁云,等. 转化生长因子β1诱导永生化人前软骨干细胞向髓核样细胞分化的实验研究[J].中华骨科杂志,2012,32(3):271-276.
[3] 丁然,王庆,蔡贤华.转化生长因子-β不同亚型对前软骨干细胞增殖分化的影响[J].华中科技大学:医学版,2013, 42(6):659-664.
[4] 黄国平.转人端粒酶基因骨髓间充质干细胞的构建及其细胞特征分析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2007.
[5] Varras M, Polonifi K, Mantzourani M, et al. Expression of antiapoptosis gene survivin in luteinized ovarian granulosa cells of women undergoing IVF or ICSI and embryo transfer: clinical correlations. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2012;10:74.
[6] Lee MS, Liu CH, Lee TH, et al. Association of creatin kinase B and peroxiredoxin 2 expression with age and embryo quality in cumulus cells. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2010;27(11):629-639.
[7] Ouandaogo ZG, Haouzi D, Assou S, et al. Human cumulus cells molecular signature in relation to oocyte nuclear maturity stage. PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27179.
[8] 叶田.TERT在人卵巢颗粒细胞中的表达及与体外受精-胚胎移植结局关系的研究[J].郑州:郑州大学,2013.
[9] Ding D, Zhou J, Wang M, et al. Implications of telomere-independent activities of telomerase reverse transcriptase in human cancer. FEBS J. 2013; 280(14): 3205-3211.
[10] Zhou JZ,Xi P,Zhou Q, et al. The putative tumor suppressor C53 interacts with the human telomerase reverse transcriptase hTERT and regulates telomerase activity.Chin Sci Bull. 2014;59(19):2324-2330.
[11] Chen FH, Rousche KT, Tuan RS. Technology Insight: adult stem cells in cartilage regeneration and tissue engineering. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2006;2(7): 373-382.
[12] Masotti A, Mossa G, Cametti C, et al. Comparison of different commercially available cationic liposome-DNA lipoplexes: Parameters influencing toxicity and transfection efficiency. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2009;68(2):136-144.
[13] Horton WA, Hall JG, Hecht JT. Achondroplasia.Lancet. 2007;370(9582):162-172.
[14] 李昆朋,许涛,杜宇,等.波长620 nm红光促进前软骨干细胞向软骨细胞分化的实验研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志, 2012,34(3):172-176.
[15] 孙晓宇.前软骨干细胞对于周围神经再生的功能与作用[J].内蒙古民族大学学报2010,25(1):105-107.
[16] 杨宝林,刘德明. 异种雪旺细胞移植在中枢神经系统损伤修复中的作用[J].江西医学院学报,2005,45(5):185-187.
[17] Schagemann JC, Kurz H, Casper ME, et al. The effect of scaffold composition on the early structural characteristics of chondrocytes and expression of adhesion molecules. Biomaterials. 2010;31(10): 2798-1805.
[18] 滕勇,胡蕴玉,王臻,等.成人骨髓基质干细胞体外定向诱导分化为软骨细胞的实验研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005, 22(2):144-146.
[19] Khan IM, Redman SN, Williams R, et al. The development of synovial joints. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2007;79:1-36.
[20] Abdallah BM, Haack-Sørensen M, Burns JS, et al. Maintenance of differentiation potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells immortalized by human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene despite [corrected] extensive proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(3):527-538.
[21] 邢莹,秦洁,曹孟德,等. 细胞因子诱导人脐血间充质干细胞分化过程中细胞巢蛋白、神经丝亚单位和端粒酶逆转录酶mRNA的表达[J].郑州大学学报:医学版,2005,40(2): 250-253.
[22] Autexier C, Lue NF. The structure and function of telomerase reverse transcriptase. Annu Rev Biochem. 2006;75:493-517.
[23] 唐峰,顾栋桦,王虹,等.端粒酶hTERT mRNA表达在乳腺癌进展中的意义及其与p53的相关性[J].中华肿瘤杂志, 2006,28(3):192-195.
[24] 张洁,廖亚平,吴灵芝,等.hTERT基因转染对人胚胎皮层神经元生长的影响[J].解剖学研究,2008,30(4):251-256.
[25] Xu L, Li S, Stohr BA. The role of telomere biology in cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 2013;8:49-78.
[26] 吴灵芝,李水彬,程刚卫,等. hTERT基因转染对人神经元活力的影响[J].赣南医学院学报,2014,34(2):170-173.
[27] Harley CB.Telomerase and cancer therapeutics.Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8(3):167-179.
[28] 靳斌,王伟,刘泽阳,等.外源hTERT基因转染对老年大鼠供肝缺血再灌注损伤的防护作用[J].山东大学学报:医学版,2013,51(8):13-16.
[29] Park YJ, Kim EK, Moon S, et al. Human telomerase reverse transcriptase is a promising target for cancer inhibition in squamous cell carcinomas.Anticancer Res. 2014;34(11):6389-6395.
[30] 刘云燕,裘秀春,张殿忠,等. hTERT反义寡核苷酸对脊索瘤细胞周期及增殖的影响[J].现代肿瘤医学,2011, 19(10):1922-1924.
[31] 张晓辉,张建宁,康春生,等.hTERT正、反义表达载体转染大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞的实验 研究[J].中华神经医学杂志,2006,5(3):217-221.
[32] 张志宏,曾永秋,税青林,等. hTERT-siRNA表达载体的构建及对MCF-7细胞生长、端粒酶活性的抑制作用[J].解放军医学杂志,2007,32(6):561-564.
[33] 李宏良,曾荣香,陈鹏,等. 清毒片和hTERT反义核酸对HL-60细胞增殖及凋亡的协同作用[J].辽宁中医杂志, 2010,37(3):395-398.
[34] Abdallah BM, Haack-Sørensen M, Burns JS, et al. Maintenance of differentiation potential of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells immortalized by human telomerase reverse transcriptase gene despite [corrected] extensive proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2005;326(3):527-538.
[35] 王开利,迟淑萍,孙杰,等.外源hTERT基因对人肝细胞增殖及CYP45019A1表达的影响[J].军医进修学院学报, 2011,32(11):1137-1138.
.jpg)
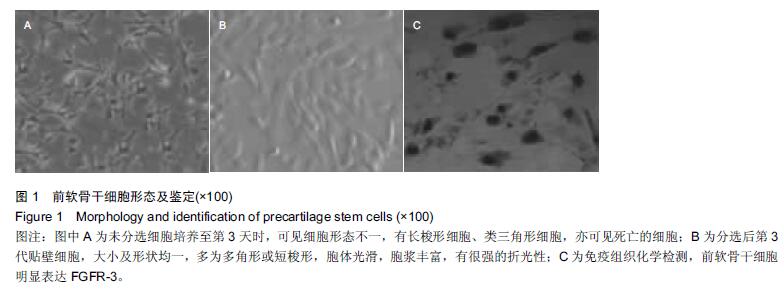

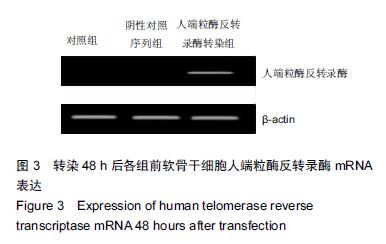

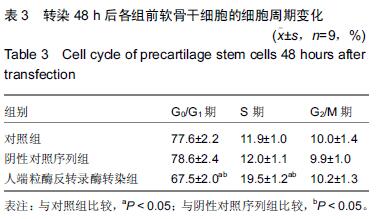
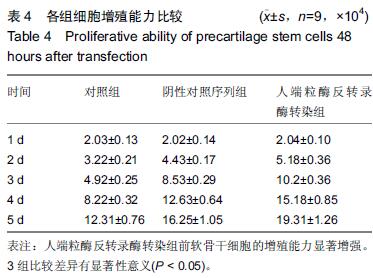
.jpg)
.jpg)