| [1] Wang DA,Ji J,Sun YH,et al.Blends of stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer in chitosan as coating materials for polyurethane intravascular catheters.J Biomed Mater Res. 2001;58:372-383.[2] Wang DA,Ji J,Gao CY,et al.Surface coating of stearyl poly(ethylene oxide) coupling-polymer on polyurethane guiding catheters with poly(ether urethane) film-building additive for biomedical applications. Biomaterials. 2001;22: 1549-1562. [3] Santerre JP,Woodhouse K,Laroche G,et al.Understanding the biodegradation of polyurethanes: from classical implants to tissue engineering materials. Biomaterials. 2005;26:7457- 7470.[4] Miyamoto K,Sugimoto T,Okada M,et al.Usefulness of polyurethane for small-caliber vascular prostheses in comparison with antologous vein graft.J Artif Organs.2002; 5(2):113-116.[5] Anderson JM,Hiltner RA,Wiggins MJ,et al.Recent advance in biomedical-polyurethane biostability and biodegradation.Polymer International.1998;46(3):163-171.[6] Dragganova PM.Biocompatible and biodegrable polyurethane polymers. Biomaterials.1993;4(1):1024-1029.[7] Michael S. Polyurethanes in vascular grafts. Rubber World. 1998, 218(1): 44-46. [8] Lin HB,Sun W,Mosher DF,et al.Synthesis, surface, and cell-adhesion properties of polyurethanes containing covalently grafted RGD-peptides.J Biomed Mater Res. 1994;28:329-342. [9] Utracki LA.Clay-containing Polymeric Nanocompositions. Shawbury shrewsbury Shropshire UK: Rapra Technology Limited,2004:66.[10] Li LH,Tu M,Mou SS,et al. Preparation and Blood Compatibility of Polysiloxane/Liquid-crystal Composite Membranes. Biomaterials.2001;22(16):2595-2599.[11] Kuo SW,Chang FC.POSS related polymer nanocomposites. Progress in Polymer Science. 2011;36(12):1649-1696.[12] Jovanovic J,Adnadjevic B,Kicanovic M,et al.The influence of hydroxyapatite modification on the cross-linking of polydimethylsiloxane/HAp composites.Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces.2004;39(1):181-186.[13] Tanaka K,Chujo Y.Advanced functional materials based on polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane (POSS).J Mater Chem. 2012;22(5):1733-1738.[14] Ponticiello MS,Schinagl RM,Cooper GM.Gelatin-based resorbable sponge as a carrier matrix for human mesenchymal stem cells in carlila-ge regeneration therapy.J Mater Sci. 2003;22(6):3829-3831.[15] Venugopal J,Ma LL,Yong T,et al.In vitro study of smooth muscle cells on popycaprolactone and collagen nanofibrous matrices.J Cell Bio Int.2005;29:861-867. [16] Kim YJ,Kwon OH.Crosslinked gelatin nanofibers and their potential for tissue engineering.Key Eng Mate.2007; 342/343: 169-172. [17] Huang ZM,Zhang YZ,Ramakrishna S.Double-layered composite nanofibers and their mechanical performance.J Polym Sci Part B:Polym Phys.2005;43(20):2852.[18] Zhao P,Jiang H,Pan H,et al.Biodegradable fibrous scaffolds composed of gelatin coated poly(epsilon-caprolactone) prepared by coaxial electrospinning.J Biomed Mater Res A.2007;83(2):372-382.[19] Pham QP,Sharma U,Mikos AG.Electrospinning of polymeric nanofibers fro tissue engineering applications: a review. Tissue Eng.2006;12:1197-1211.[20] Lannuttia J,Renekerb D,Mac T,et al.Electrospinning for tissue engineering scaffolds. Mater Sci Eng C.2007;27(3):504-509. |
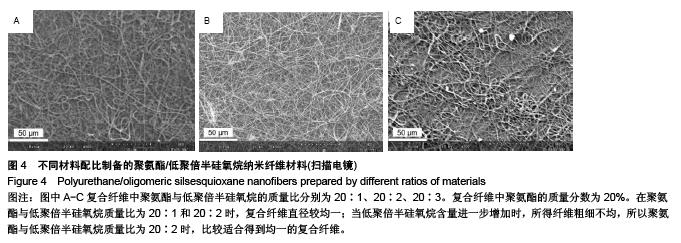
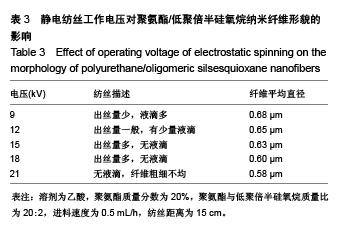
.jpg)
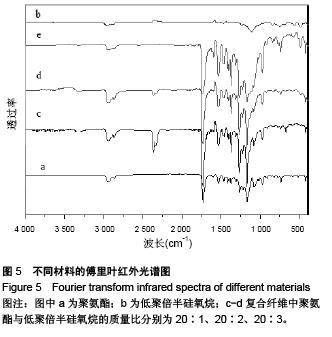
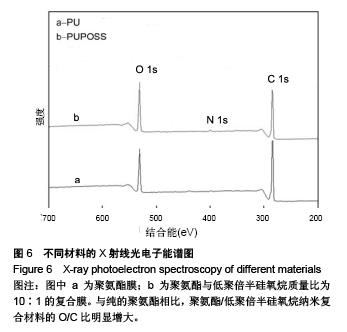
.jpg)