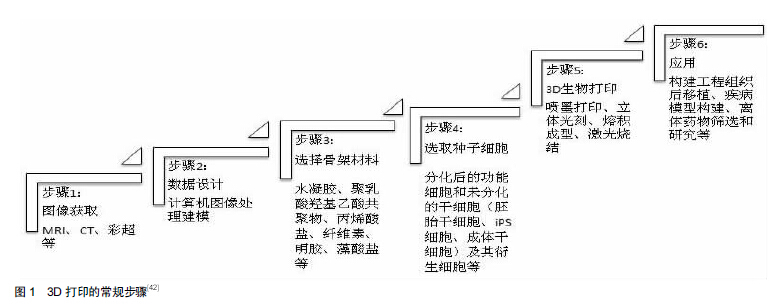
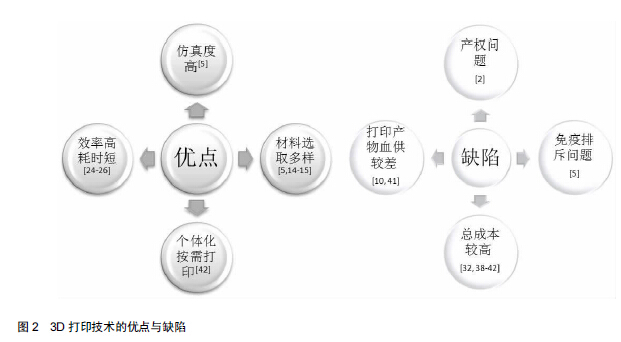
|
[1] 邢远翔.3D打印颠覆医学传统理念[J].中国医院院长,2014, 10(19): 36.
[2] Ventola CL.Medical Applications for 3D Printing: Current and Projected Uses.P T.2014;39(10):704-711.
[3] Mahmood F,Owais K,Montealegre Gallegos M,et al. Echocardiography derived three-dimensional printing of normal and abnormal mitral annuli. Ann Card Anaesth. 2014; 17(4):279-283.
[4] Witschey WR,Pouch AM,McGarvey JR,et al. Three-dimensional ultrasound-derived physical mitral valve modeling.Ann Thorac Surg.2014;98(2):691-694.
[5] Lueders C,Jastram B,Hetzer R,et al.Rapid manufacturing techniques for the tissue engineering of human heart valves.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2014;46(4):593-601.
[6] Costello JP,Olivieri LJ,Krieger A,et al.Utilizing three-dimensional printing technology to assess the feasibility of high-fidelity synthetic ventricular septal defect models for simulation in medical education.World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2014;5(3):421-426.
[7] O’Neill B,Wang DD,Pantelic M,et al.Transcatheter caval valve implantation using multimodality imaging: roles of TEE, CT, and 3D printing.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging. 2015;8(2): 221-225.
[8] Olivieri LJ,Krieger A,Loke YH,et al.Three-dimensional printing of intracardiac defects from three-dimensional echocardiographic images: feasibility and relative accuracy.J Am Soc Echocardiogr.2015;28(4):392-397.
[9] Koroleva A,Gittard S,Schlie S,et al.Fabrication of fibrin scaffolds with controlled microscale architecture by a two-photon polymerization–micromolding technique. Biofabrication.2012;4(1):015001.
[10] Lee VK,Kim DY,Ngo H,et al.Creating perfused functional vascular channels using 3D bio-printing technology. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8092-8102.
[11] Christensen K,Xu C,Chai W,et al.Freeform Inkjet Printing of Cellular Structures with Bifurcations.Biotechnol Bioeng.2014; 112(5):1047-1055.
[12] Poldervaart MT,Gremmels H,van Deventer K,et al.Prolonged presence of VEGF promotes vascularization in 3D bioprinted scaffolds with defined architecture. J Control Release. 2014; 28(184):58-66.
[13] Zhao X,Liu L,Wang J,et al.In vitro vascularization of a combined system based on a 3D printing technique.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2014. doi: 10.1002/term.1863.[Epub ahead of print]
[14] Pati F,Jang J,Ha DH,et al.Printing three-dimensional tissue analogues with decellularized extracellular matrix bioink.Nat Commun.2014;5:3935.
[15] Petrochenko PE,Torgersen J,Gruber P,et al.Laser 3D Printing with sub-microscale resolution of porous elastomeric scaffolds for supporting human bone stem cells.Adv Healthc Mater.2015,4(5):739-747.
[16] Park CJ,Kim HW,Jeong S,et al.Anti-reflux ureteral stent with polymeric flap valve using three-dimensional printing: An in vitro study.J Endourol.2015.[Epub ahead of print]
[17] Mahmood F,Owais K,Taylor C,et al.Three-Dimensional Printing of Mitral Valve Using Echocardiographic Data.JACC Cardiovasc Imaging.2015;8(2):227-229.
[18] Namba K,Higaki A,Kaneko N,et al.Microcatheter shaping for intracranial aneurysm coiling using the 3-dimensional printing rapid prototyping technology: preliminary result in the first 10 consecutive cases.World Neurosurg.2015;84(1):178-186.
[19] Ozbolat IT,Yu Y. Bioprinting toward organ fabrication: challenges and future trends.IEEE Trans Biomed Eng. 2013; 3(60):691-699.
[20] Biglino G,Verschueren P,Zegels R,et al.Rapid prototyping compliant arterial phantoms for in-vitro studies and device testing.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2013;15(2):1532.
[21] Gillis JA,Morris SF.Three-dimensional printing of perforator vascular anatomy. Plast Reconstr Surg.2014;133(1):80-82.
[22] Xu L,Gutbrod SR,Bonifas AP,et al.3D multifunctional integumentary membranes for spatiotemporal cardiac measurements and stimulation across the entire epicardium. Nat Commun.2014;5:3329.
[23] Sulkin MS,Widder E,Shao C,et al.Three-dimensional printing physiology laboratory technology.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2013;305(11): H1569-1573.
[24] Dankowski R,Baszko A,Sutherland M,et al.3D heart model printing for preparation of percutaneous structural interventions. Kardiol Pol.2014;72(6):546-551.
[25] Schmauss D,Gerber N,Sodian R.Three-dimensional printing of models for surgical planning in patients with primary cardiac tumors.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2013; 32(8): 773-785.
[26] Samuel BP,Pinto C,Pietila T,et al.Ultrasound-Derived Three Dimensional Printing in Congenital Heart Disease.J Digit Imaging.2015;28(4):459-461.
[27] Murphy SV,Atala A.3D bioprinting of tissues and organs. Nat Biotechnol.2014;32(8): 773-785.
[28] 杨帆,杨延坤,郑宏.3D 打印技术在先天性心脏病诊疗中的应用[J].中国介入影像与治疗学,2014,11(9):629-631.
[29] Olivieri L,Krieger A,Chen MY,et al.3D heart model guides complex stent angioplasty of pulmonary venous baffle obstruction in a Mustard repair of D-TGA.Int J Cardiol.2014; 172(2):297-298.
[30] 王安琪,冯晓明,杨昭鹏,等. 3D 打印在医疗器械领域的应用现状及展望[J].中国医疗器械信息,2014,20(8):1-7.
[31] Dankowski R,Baszko A,Sutherland M,et al. 3D heart model printing for preparation of percutaneous structural interventions: description of the technology and case report. Kardiol Pol.2014;72(6):546-551.
[32] Erkal JL,Selimovic A,Gross BC,et al.3D printed microfluidic devices with integrated versatile and reusable electrodes.Lab Chip.2014;14(12):2023-2032.
[33] Noecker AM,Chen JF,Zhou Q,et al.Development of patient-specific three-dimensional pediatric cardiac models. ASAIO J.2006;52(3):349-353.
[34] Costello JP,Olivieri LJ,Su L,et al.Incorporating three-dimensional printing into a simulation-based congenital heart disease and critical care training curriculum for resident physicians..Congenit Heart Dis.2015;10(2):185-190.
[35] Poterucha JT,Foley TA,Taggart NW.Percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation in a native outflow tract: 3-dimensional DynaCT rotational angiographic reconstruction and 3-dimensional printed model.JACC Cardiovasc Interv.2014; 7(10):151-152.
[36] Valverde I,Gomez G,Coserria JF,et al.3D printed models for planning endovascular stenting in transverse aortic arch hypoplasia.Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2015;85(6): 1006-1012.
[37] Lee SJ,Heo DN,Park JS,et al.Characterization and preparation of bio-tubular scaffolds for fabricating artificial vascular grafts by combining electrospinning and a 3D printing system.Phys Chem Chem Phys.2015;17(5): 2996-2999.
[38] 杨延坤,郑宏,徐争鸣,等.3D 打印技术辅助下经导管封堵主动脉窦瘤破裂一例[J].中国介入心脏病学杂志,2014,22(2):26.
[39] 刘凯,张学燕.3D打印机与CT 三维重建的结合应用[J].实用医技杂志,2013,20(6):666.
[40] Hoch E,Tovar GEM,Borchers K.Bioprinting of artificial blood vessels: current approaches towards a demanding goal.Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.2014;46(5):767-778.
[41] Lee VK,Kim DY,Ngo H,et al.Creating perfused functional vascular channels using 3D bio-printing technology. Biomaterials. 2014;35(28):8092-8102.
[42] Murphy SV,Atala A.3D bioprinting of tissues and organs.Nat Biotechnol.2014; 32(8):773-785.
|